TABLE 10.3 Van der Waals Constants for Gas Molecules Substance a (L²-atm/mol?) b (L/mol) Не 0.0341 0.02370 Ne 0.211 0.0171 Ar 1.34 0.0322 Kr 2.32 0.0398 Xe 4.19 0.0510 На 0.244 0.0266 N2 1.39 0.0391 O2 1.36 0.0318 F2 1.06 0.0290 Cl, 6.49 0.0562 Н-о 5.46 0.0305 NH3 4.17 0.0371 CH4 2.25 0.0428 CO2 3.59 0.0427 CCI4 20.4 0.1383 45 -- Ideal gas Gas A Gas B Gas C 40 35 30 25 20 15 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 Temperature (K) Pressure (atm)
TABLE 10.3 Van der Waals Constants for Gas Molecules Substance a (L²-atm/mol?) b (L/mol) Не 0.0341 0.02370 Ne 0.211 0.0171 Ar 1.34 0.0322 Kr 2.32 0.0398 Xe 4.19 0.0510 На 0.244 0.0266 N2 1.39 0.0391 O2 1.36 0.0318 F2 1.06 0.0290 Cl, 6.49 0.0562 Н-о 5.46 0.0305 NH3 4.17 0.0371 CH4 2.25 0.0428 CO2 3.59 0.0427 CCI4 20.4 0.1383 45 -- Ideal gas Gas A Gas B Gas C 40 35 30 25 20 15 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 Temperature (K) Pressure (atm)
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter8: Properties Of Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 70QRT
Related questions
Question
The graph below shows the change in pressure as the temperature
increases for a 1-mol sample of a gas confined to a
1-L container. The four plots correspond to an ideal gas and
three real gases: CO2, N2, and Cl2. (a) At room temperature,
all three real gases have a pressure less than the ideal gas.
Which van der Waals constant, a or b, accounts for the influence
intermolecular forces have in lowering the pressure of a
real gas? (b) Use the van der Waals constants in Table 10.3 to
match the labels in the plot (A, B, and C) with the respective
gases (CO2, N2, and Cl2).
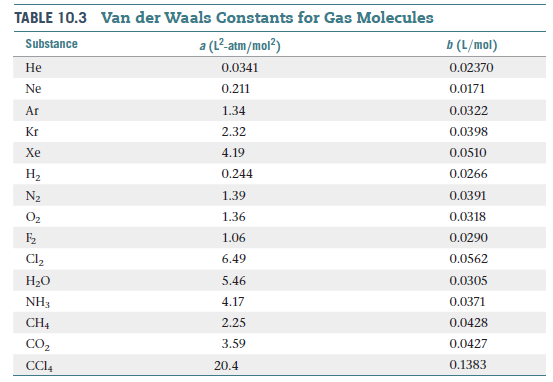
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 10.3 Van der Waals Constants for Gas Molecules
Substance
a (L²-atm/mol?)
b (L/mol)
Не
0.0341
0.02370
Ne
0.211
0.0171
Ar
1.34
0.0322
Kr
2.32
0.0398
Xe
4.19
0.0510
На
0.244
0.0266
N2
1.39
0.0391
O2
1.36
0.0318
F2
1.06
0.0290
Cl,
6.49
0.0562
Н-о
5.46
0.0305
NH3
4.17
0.0371
CH4
2.25
0.0428
CO2
3.59
0.0427
CCI4
20.4
0.1383
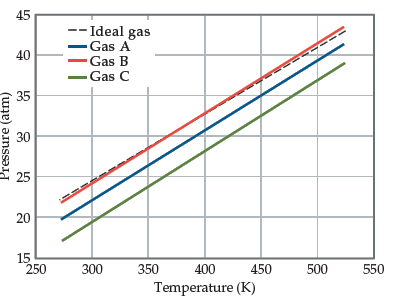
Transcribed Image Text:45
-- Ideal gas
Gas A
Gas B
Gas C
40
35
30
25
20
15
250
300
350
400
450
500
550
Temperature (K)
Pressure (atm)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning