The aqueous humor circulates within the eye, flowing in at a constant rate Qin = 2 µl/min, and draining from the eye at Qout- At steady state, Qout = Qin: The eye also acts like an elastic vessel, in that its volume increases if the intraocular pressure p increases. This is expressed by V = Cp (6.21) where V is the volume of the eye (normally about 4 cm³) and C is the com- pliance of the eye (approximately 3 µul/mmHg). Finally, the outflow rate Qout equals p/R, where R is the (effectively constant) resistance to outflow (about 4 mmHg min/ul). (a) Balancing mass, show that: dp P – Pss (6.22) dt RC where pss is the steady-state pressure in the eye, equal to RQin- (b) If you poke your eye and increase the pressure by an amount Sp = 10 mmHg, how long does it take the pressure to return to within 5% of its steady-state value?
The aqueous humor circulates within the eye, flowing in at a constant rate Qin = 2 µl/min, and draining from the eye at Qout- At steady state, Qout = Qin: The eye also acts like an elastic vessel, in that its volume increases if the intraocular pressure p increases. This is expressed by V = Cp (6.21) where V is the volume of the eye (normally about 4 cm³) and C is the com- pliance of the eye (approximately 3 µul/mmHg). Finally, the outflow rate Qout equals p/R, where R is the (effectively constant) resistance to outflow (about 4 mmHg min/ul). (a) Balancing mass, show that: dp P – Pss (6.22) dt RC where pss is the steady-state pressure in the eye, equal to RQin- (b) If you poke your eye and increase the pressure by an amount Sp = 10 mmHg, how long does it take the pressure to return to within 5% of its steady-state value?
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
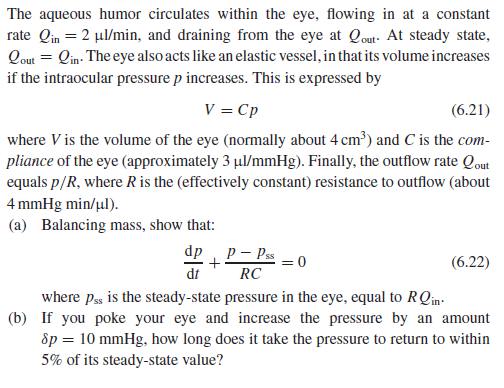
Transcribed Image Text:The aqueous humor circulates within the eye, flowing in at a constant
rate Qin = 2 µl/min, and draining from the eye at Qout- At steady state,
Qout = Qin: The eye also acts like an elastic vessel, in that its volume increases
if the intraocular pressure p increases. This is expressed by
V = Cp
(6.21)
where V is the volume of the eye (normally about 4 cm³) and C is the com-
pliance of the eye (approximately 3 µul/mmHg). Finally, the outflow rate Qout
equals p/R, where R is the (effectively constant) resistance to outflow (about
4 mmHg min/ul).
(a) Balancing mass, show that:
dp
P – Pss
(6.22)
dt
RC
where pss is the steady-state pressure in the eye, equal to RQin-
(b) If you poke your eye and increase the pressure by an amount
Sp = 10 mmHg, how long does it take the pressure to return to within
5% of its steady-state value?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY