The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool Market for Goods 250 225 I Quantity Demanded 25 200 (Units) 175 Demand Price (Dollars per unit) 125.00 150 125 100 75 Demand 50 25 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Units) On the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 40, and 50 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results: 3130 2817 Total Revenue 2504 2 2191 1878 1585 1252 930 626 313 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Number of units) Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 10 versus 9 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 10th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 10th unit produced is 5 Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 20 versus 19 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 20th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 20th unit produced is S TO TAL REVENUE (Dollas)
The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool Market for Goods 250 225 I Quantity Demanded 25 200 (Units) 175 Demand Price (Dollars per unit) 125.00 150 125 100 75 Demand 50 25 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Units) On the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 40, and 50 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results: 3130 2817 Total Revenue 2504 2 2191 1878 1585 1252 930 626 313 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Number of units) Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 10 versus 9 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 10th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 10th unit produced is 5 Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 20 versus 19 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 20th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 20th unit produced is S TO TAL REVENUE (Dollas)
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter7: Consumers, Producers, And The Efficiency Of Markets
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11PA
Related questions
Question
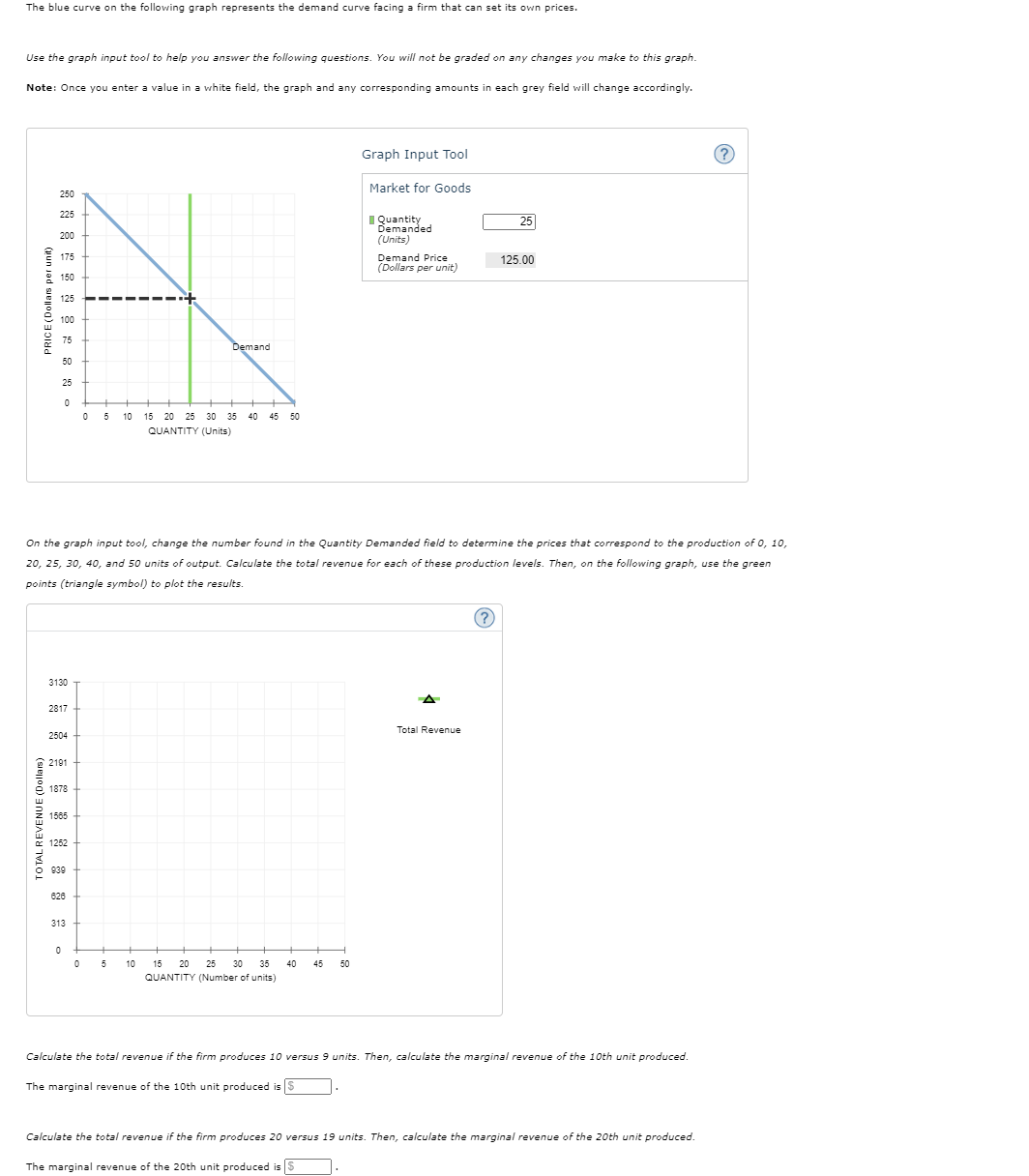
Transcribed Image Text:The blue curve on the follovwing graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices.
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
Graph Input Tool
Market for Goods
250
225
I Quantity
Demanded
25
200
(Units)
175
Demand Price
(Dollars per unit)
125.00
150
125
100
75
Demand
50
25
30
QUANTITY (Units)
5
10 15 20 25
35 40
45 50
On the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 10,
20, 25, 30, 40, and 50 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green
points (triangle symbol) to plot the results
3130
2817
Total Revenue
2504
2191
1878 +
1565
1252
939
626
313
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
QUANTITY (Number of units)
Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 10 versus 9 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 10th unit produced.
The marginal revenue of the 10th unit produced is S
Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 20 versus 19 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 20th unit produced.
The marginal revenue of the 20th unit produced is S
TOTAL REVENUE (Dollars)
PRICE (Dollars per unit)
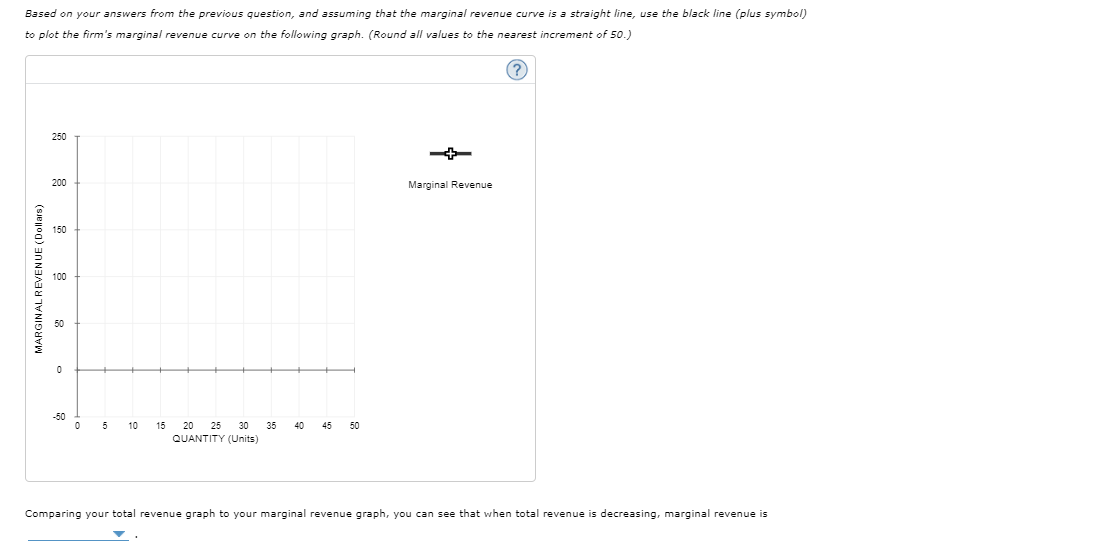
Transcribed Image Text:Based on your answers from the previous question, and assuming that the marginal revenue curve is a straight line, use the black line (plus symbol)
to plot the firm's marginal revenue curve on the following graph. (Round all values to the nearest increment of 50.)
(?
250
200
Marginal Revenue
150
100
50
-50
5
10
15
20 25 30
35
40
45 50
QUANTITY (Units)
Comparing your total revenue graph to your marginal revenue graph, you can see that when total revenue is decreasing, marginal revenue is
MARGINAL REVENUE (Dollars)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


