The Chamber of Commerce in a Canadian city has conducted an evaluation of 300 restaurants in its metropolitan area. Each restaurant received a rating on a 3-point scale on typical meal price (1 least expensive to 3 most expensive) and quality (1 lowest quality to 3 greatest quality). A crosstabulation of the rating data is shown. Forty-two of the restaurants received a rating of 1 on quality and 1 on meal price, 39 of the restaurants received a rating of 1 on quality and 2 on meal price, and so on. Forty-eight of the restaurants received the highest rating of 3 on both quality and meal price. Quality Quality (x) b. Compute the expected value and variance for quality rating, E(x) = Var(x) = c. Compute the expected value and variance for meal price, y. 1 2 3 Total . (Round your answer to two decimal places) (Round your answer to four decimal places) 1 2 What can you say about the relationship between quality and meal price? 3 1 0.14 0.11 0.01 Meal Price (y) 1 2 3 39 0.26 42 33 3 Total 105 300 a. Develop a bivariate probability distribution for Quality and Meal Price of a randomly selected restaurant in this Canadian city. Let = quality rating and y meal price. Round your answers to two decimal places. 60 78 18 117 Meal Price y 2 0.13 0.20 0.06 3 0.39 54 48 Total 3 84 147 69 0.01 0.18 0.16 0.35 Total 0.28 0.49 0.23 1 E(y): (Round your answer to two decimal places) (Round your answer to four decimal places) Var(y) = d. Your assistant has computed the variance of a +y: Var(x + y) = 1.6784. Compute the covariance of a and y. Round your answer to four decimal places.
The Chamber of Commerce in a Canadian city has conducted an evaluation of 300 restaurants in its metropolitan area. Each restaurant received a rating on a 3-point scale on typical meal price (1 least expensive to 3 most expensive) and quality (1 lowest quality to 3 greatest quality). A crosstabulation of the rating data is shown. Forty-two of the restaurants received a rating of 1 on quality and 1 on meal price, 39 of the restaurants received a rating of 1 on quality and 2 on meal price, and so on. Forty-eight of the restaurants received the highest rating of 3 on both quality and meal price. Quality Quality (x) b. Compute the expected value and variance for quality rating, E(x) = Var(x) = c. Compute the expected value and variance for meal price, y. 1 2 3 Total . (Round your answer to two decimal places) (Round your answer to four decimal places) 1 2 What can you say about the relationship between quality and meal price? 3 1 0.14 0.11 0.01 Meal Price (y) 1 2 3 39 0.26 42 33 3 Total 105 300 a. Develop a bivariate probability distribution for Quality and Meal Price of a randomly selected restaurant in this Canadian city. Let = quality rating and y meal price. Round your answers to two decimal places. 60 78 18 117 Meal Price y 2 0.13 0.20 0.06 3 0.39 54 48 Total 3 84 147 69 0.01 0.18 0.16 0.35 Total 0.28 0.49 0.23 1 E(y): (Round your answer to two decimal places) (Round your answer to four decimal places) Var(y) = d. Your assistant has computed the variance of a +y: Var(x + y) = 1.6784. Compute the covariance of a and y. Round your answer to four decimal places.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.6: Summarizing Categorical Data
Problem 10CYU
Related questions
Question
Please answer B, C, and D.
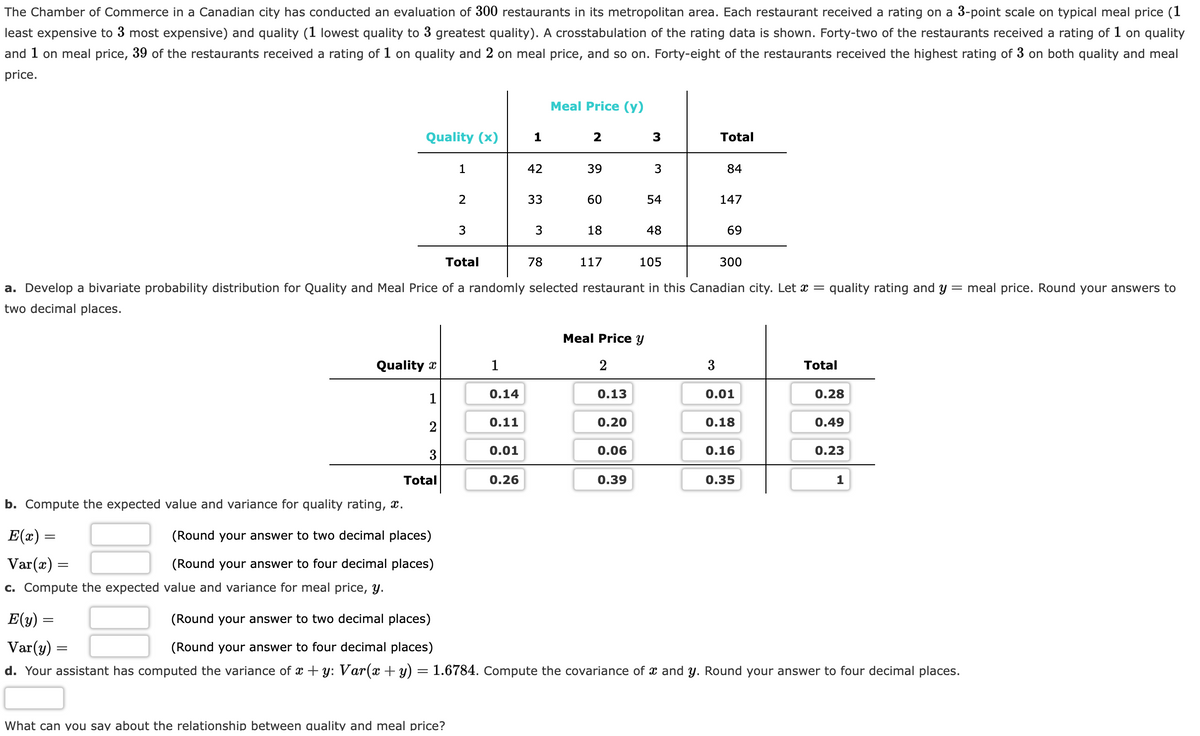
Transcribed Image Text:The Chamber of Commerce in a Canadian city has conducted an evaluation of 300 restaurants in its metropolitan area. Each restaurant received a rating on a 3-point scale on typical meal price (1
least expensive to 3 most expensive) and quality (1 lowest quality to 3 greatest quality). A crosstabulation of the rating data is shown. Forty-two of the restaurants received a rating of 1 on quality
and 1 on meal price, 39 of the restaurants received a rating of 1 on quality and 2 on meal price, and so on. Forty-eight of the restaurants received the highest rating of 3 on both quality and meal
price.
E(y):
Quality (x)
Quality
=
b. Compute the expected value and variance for quality rating, *.
E(x) =
Var(x) =
(Round your answer to two decimal places)
(Round your answer to four decimal places)
c. Compute the expected value and variance for meal price, y.
=
1
2
3
(Round your answer to two decimal places)
(Round your answer to four decimal places)
Var(y)
=
d. Your assistant has computed the variance of x+y: Var(x + y)
Total
1
2
What can you say about the relationship between quality and meal price?
3
1
0.14
0.11
0.01
1
0.26
42
33
3
78
Meal Price (y)
2
Total
105
a. Develop a bivariate probability distribution for Quality and Meal Price of a randomly selected restaurant in this Canadian city. Let x = quality rating and y meal price. Round your answers to
two decimal places.
39
60
18
117
Meal Price y
2
0.13
0.20
0.06
3
0.39
3
54
48
Total
3
84
147
69
300
0.01
0.18
0.16
0.35
Total
0.28
0.49
0.23
1
1.6784. Compute the covariance of x and y. Round your answer to four decimal places.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt