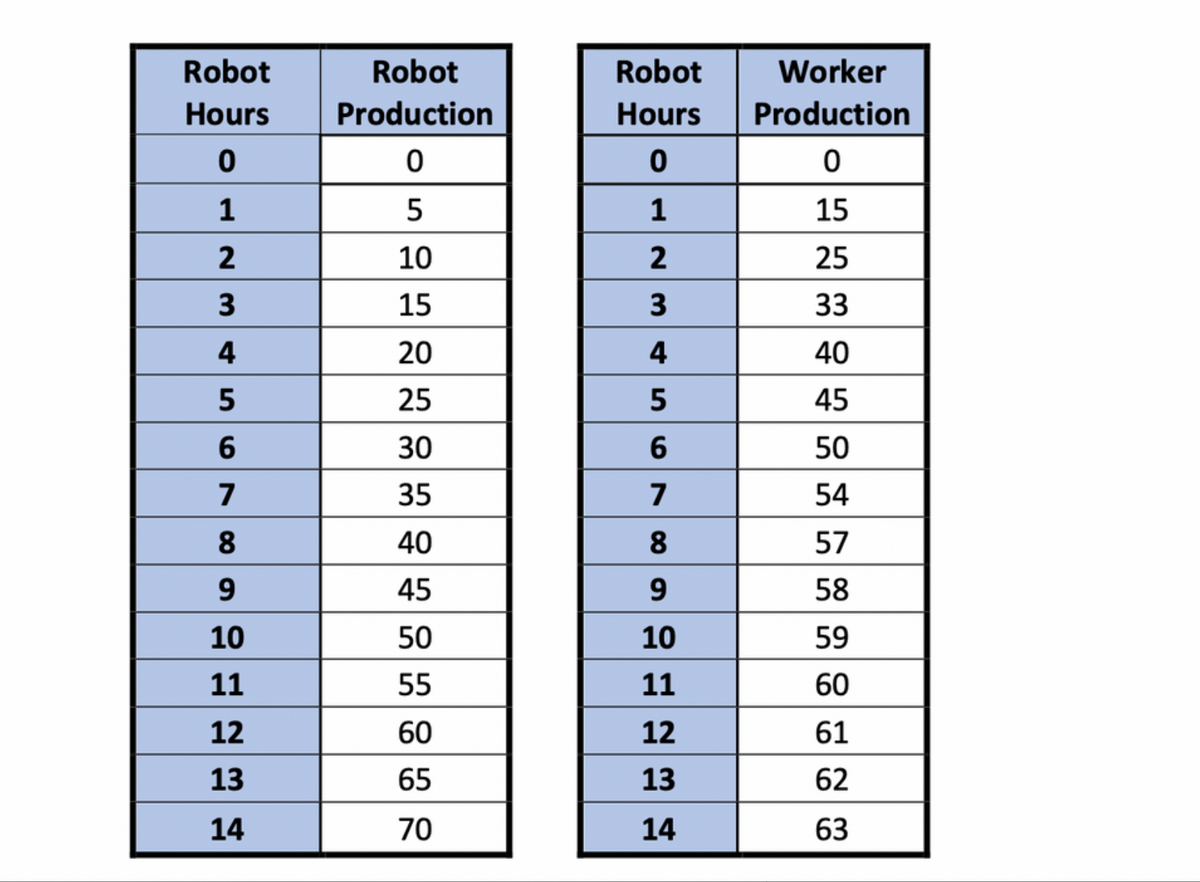
The first is a (human) worker, who must be paid $18 for each hour they spend producing chairs. The second is a robot, that costs $15 of inputs (including electricity and maintenance) for each hour it works. Assume that the sale price of chairs is always sufficiently high that it is profitable to fulfill this 80-chair order. The firm needs to make 80 chairs to fulfill its order. Assume also that the firm is profit maximizing (& therefore cost minimizing). Now suppose that the local economy increases the minimum wage, and the price of an hour of a worker’s time increases from $18 to $27. 1) What does the principle of substitution say should happen to the firm’s use of (i) worker hours and (ii) robot hours? Pls show full calculations
Use the following image to answer:
The first is a (human) worker, who must be paid $18 for each hour they spend producing chairs. The second is a robot, that costs $15 of inputs (including electricity and maintenance) for each hour it works.
Assume that the sale
80-chair order. The firm needs to make 80 chairs to fulfill its order. Assume also that the firm is
profit maximizing (& therefore cost minimizing).
Now suppose that the local economy increases the minimum wage, and the price of an hour of
a worker’s time increases from $18 to $27.
1) What does the principle of substitution say should happen to the firm’s use of (i) worker
hours and (ii) robot hours?
Pls show full calculations
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps









