the "free" energy for a fictitious example where the reaction is exothermic (AH=-100 kJ) but has a negative entropy (AS = -20 J/K, 6 kJ at 298K). The amount of free energy in this examples he free energy is the maximum energy available to do work after accounting for the increase in entropy of the system. he free energy is the minimum energy available to do work after accounting for the decrease in entropy of the system. The free energy is the maximum energy available to do work after accounting for the decrease in entropy of the system. The free energy is the minimum energy available to do work after accounting for the increase in entropy of the system. nit Request Answer back
the "free" energy for a fictitious example where the reaction is exothermic (AH=-100 kJ) but has a negative entropy (AS = -20 J/K, 6 kJ at 298K). The amount of free energy in this examples he free energy is the maximum energy available to do work after accounting for the increase in entropy of the system. he free energy is the minimum energy available to do work after accounting for the decrease in entropy of the system. The free energy is the maximum energy available to do work after accounting for the decrease in entropy of the system. The free energy is the minimum energy available to do work after accounting for the increase in entropy of the system. nit Request Answer back
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter16: Thermodynamics: Directionality Of Chemical Reactions
Section16.3: Measuring Dispersal Of Energy: Entropy
Problem 16.3CE
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
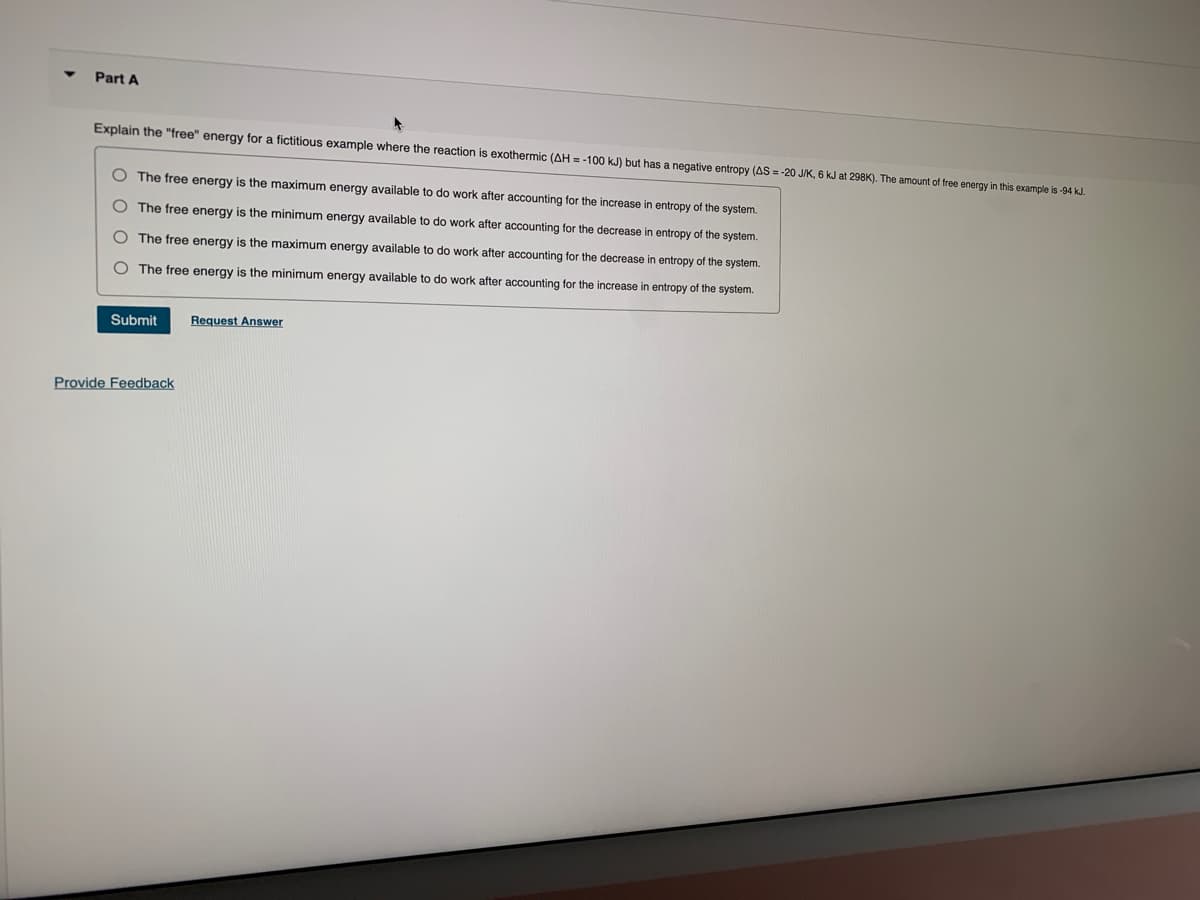
Explain the "free" energy for a fictitious example where the reaction is exothermic (AH = -100 kJ) but has a negative entropy (AS = -20 J/K, 6 kJ at 298K). The amount of free energy in this example is -94 kJ.
O The free energy is the maximum energy available to do work after accounting for the increase in entropy of the system.
The free energy is the minimum energy available to do work after accounting for the decrease in entropy of the system.
The free energy is the maximum energy available to do work after accounting for the decrease in entropy of the system.
The free energy is the minimum energy available to do work after accounting for the increase entropy of the system.
Submit
Provide Feedback
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning