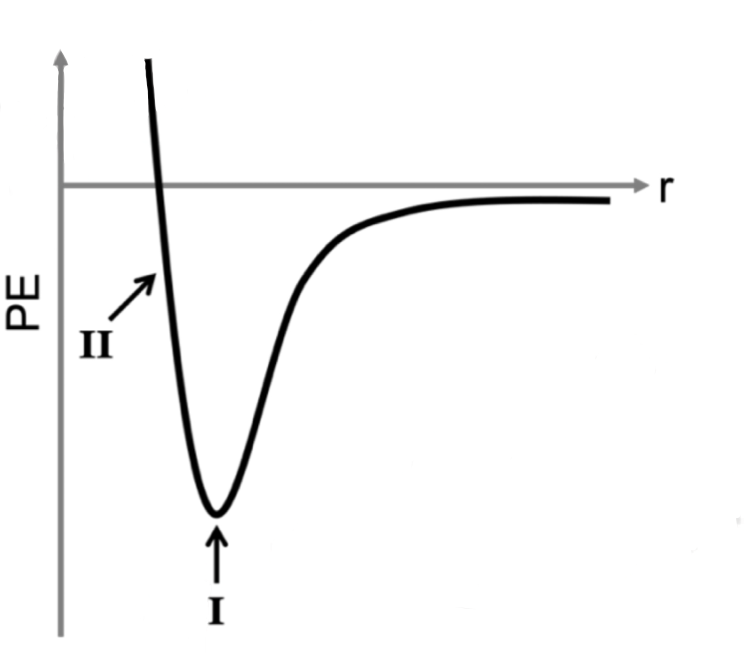
The graph to the right represents the potential energy vs. interatomic distance between two xenon atoms interacting via London dispersion forces. What happens to the kinetic energy (KE) of the atoms if the distance between them changes from point I to point II, and what causes this energy change? Change in KE Cause of Change A) Decreases KE decreases because attractive forces dominate at this distance range, which cause the atoms to lose speed and therefore also lose KE. B) Decreases KE decreases because repulsive forces dominate at this distance range, which cause the atoms to lose speed and therefore also lose KE. D) Increases KE increases because attractive forces dominate at this distance range, which cause the atoms to gain speed and therefore also gain KE. D) Increases KE increases because repulsive forces dominate at this distance range, which cause the atoms to gain speed and therefore also gain KE. E) No Change Because energy must be conserved, the kinetic energy of the system remains constant until an unbalanced force acts on it.
Types of Chemical Bonds
The attractive force which has the ability of holding various constituent elements like atoms, ions, molecules, etc. together in different chemical species is termed as a chemical bond. Chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds between its constituents. Stronger the chemical bond, more will be the stability in the chemical compounds. Hence, it can be said that bonding defines the stability of chemical compounds.
Polarizability In Organic Chemistry
Polarizability refers to the ability of an atom/molecule to distort the electron cloud of neighboring species towards itself and the process of distortion of electron cloud is known as polarization.
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
A coordinate covalent bond is also known as a dative bond, which is a type of covalent bond. It is formed between two atoms, where the two electrons required to form the bond come from the same atom resulting in a semi-polar bond. The study of coordinate covalent bond or dative bond is important to know about the special type of bonding that leads to different properties. Since covalent compounds are non-polar whereas coordinate bonds results always in polar compounds due to charge separation.
The graph to the right represents the potential energy vs. interatomic distance between two xenon atoms interacting via London dispersion forces. What happens to the kinetic energy (KE) of the atoms if the distance between them changes from point I to point II, and what causes this energy change?
Change in KE Cause of Change
A) Decreases KE decreases because attractive forces dominate at this distance range,
which cause the atoms to lose speed and therefore also lose KE.
B) Decreases KE decreases because repulsive forces dominate at this distance range,
which cause the atoms to lose speed and therefore also lose KE.
D) Increases KE increases because attractive forces dominate at this distance range,
which cause the atoms to gain speed and therefore also gain KE.
D) Increases KE increases because repulsive forces dominate at this distance range,
which cause the atoms to gain speed and therefore also gain KE.
E) No Change Because energy must be conserved, the kinetic energy of the system
remains constant until an unbalanced force acts on it.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









