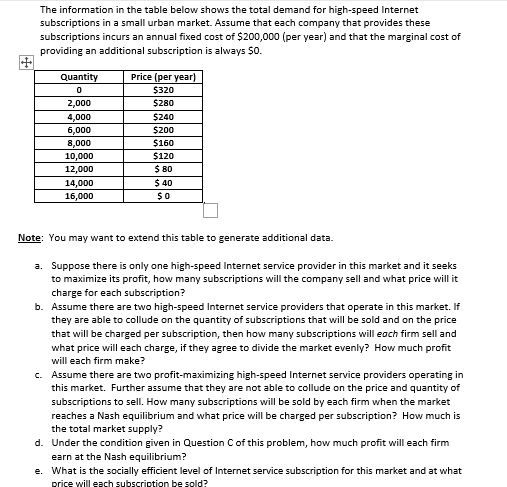
The information in the table below shows the total demand for high-speed Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each company that provides these subscriptions incurs an annual fixed cost of $200,000 (per year) and that the marginal cost of providing an additional subscription is always $0. Quantity 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 12,000 14,000 16,000 Price (per year) $320 $280 $240 $200 $160 $120 $ 80 $ 40 $0 Note: You may want to extend this table to generate additional data. a. Suppose there is only one high-speed Internet service provider in this market and it seeks to maximize its profit, how many subscriptions will the company sell and what price will it charge for each subscription? b. Assume there are two high-speed Internet service providers that operate in this market. If they are able to collude on the quantity of subscriptions that will be sold and on the price that will be charged per subscription, then how many subscriptions will each firm sell and what price will each charge, if they agree to divide the market evenly? How much profit will each firm make? c. Assume there are two profit-maximizing high-speed Internet service providers operating in this market. Further assume that they are not able to collude on the price and quantity of subscriptions to sell. How many subscriptions will be sold by each firm when the market reaches a Nash equilibrium and what price will be charged per subscription? How much is the total market supply?
The information in the table below shows the total demand for high-speed Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each company that provides these subscriptions incurs an annual fixed cost of $200,000 (per year) and that the marginal cost of providing an additional subscription is always $0. Quantity 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 12,000 14,000 16,000 Price (per year) $320 $280 $240 $200 $160 $120 $ 80 $ 40 $0 Note: You may want to extend this table to generate additional data. a. Suppose there is only one high-speed Internet service provider in this market and it seeks to maximize its profit, how many subscriptions will the company sell and what price will it charge for each subscription? b. Assume there are two high-speed Internet service providers that operate in this market. If they are able to collude on the quantity of subscriptions that will be sold and on the price that will be charged per subscription, then how many subscriptions will each firm sell and what price will each charge, if they agree to divide the market evenly? How much profit will each firm make? c. Assume there are two profit-maximizing high-speed Internet service providers operating in this market. Further assume that they are not able to collude on the price and quantity of subscriptions to sell. How many subscriptions will be sold by each firm when the market reaches a Nash equilibrium and what price will be charged per subscription? How much is the total market supply?
Chapter13: Monopoly And Antitrust
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13P
Related questions
Question
please show me complete and neat solution thank you
Transcribed Image Text:+
The information in the table below shows the total demand for high-speed Internet
subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each company that provides these
subscriptions incurs an annual fixed cost $200,000 (per year) and that the marginal cost of
providing an additional subscription is always $0.
Quantity
0
2,000
4,000
6,000
8,000
10,000
12,000
14,000
16,000
Price (per year)
$320
$280
$240
$200
$160
$120
$ 80
$ 40
$0
Note: You may want to extend this table to generate additional data.
a. Suppose there is only one high-speed Internet service provider in this market and it seeks
to maximize its profit, how many subscriptions will the company sell and what price will it
charge for each subscription?
b. Assume there are two high-speed Internet service providers that operate in this market. If
they are able to collude on the quantity of subscriptions that will be sold and on the price
that will be charged per subscription, then how many subscriptions will each firm sell and
what price will each charge, if they agree to divide the market evenly? How much profit
will each firm make?
c. Assume there are two profit-maximizing high-speed Internet service providers operating in
this market. Further assume that they are not able to collude on the price and quantity of
subscriptions to sell. How many subscriptions will be sold by each firm when the market
reaches a Nash equilibrium and what price will be charged per subscription? How much is
the total market supply?
d.
Under the condition given in Question C of this problem, how much profit will each firm
earn at the Nash equilibrium?
e. What is the socially efficient level of Internet service subscription for this market and at what
price will each subscription be sold?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning