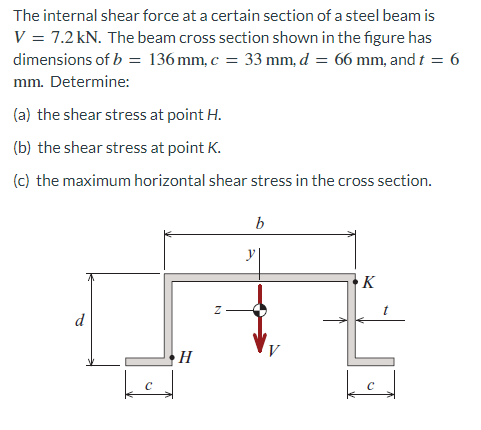
The internal shear force at a certain section of a steel beam is V = 7.2 kN. The beam cross section shown in the figure has dimensions of b = 136 mm, c = 33 mm, d = 66 mm, and t = 6 mm. Determine:
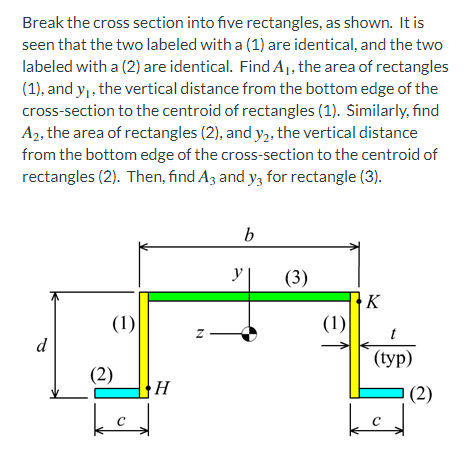
a. find the area and vertical distances from the bottom edge of the cross-section to the centoid of rectangles
b. Find Iz, the area moment of inertia about the z centroidal axis for the cross-section.
c. Find QH, the first moment of area about the z centroidal axis for the entire area below point H. This area has width 2c2c and height tt. Also, find QK, the first moment of area about the z centroidal axis for the entire area above point K with width b and height t.
d. Determine the magnitudes of the shear stress at point H and the shear stress at point K.
e. Find Qmax, the maximum first moment of area about the z centroidal axis for any point in the cross section, and τmax, the maximum horizontal shear stress magnitude in the cross section.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps


