KEY IDEAS The long solenoid S shown (in cross section) in Fig. 30-3 has 220 turns/cm and carries a current i 1.5 A; its diameter D is 3.2 cm. At its center we place a 130-turn closely packed coil C of diameter d 2.1 cm. The current in the solehoid is reduced to zero at a steady rate in 25 ms. What is the magni- tude of the emf that is induced in coil C while the current in the solenoid is changing? 1. Because it is located in the interior of the solenoid, coil C lies within the magnetic field produced by current i in the solenoid; thus, there is a magnetic flux , through coil C. 2. Because current i decreases, flux , also decreases, 3. As Pn decreases, emf & is induced in coil C. 4. The flux through each turn of coil C depends on the area A and orientation of that turn in the solenoid's magnetic field B.Because B is uniform and directed perpendicular to area A, the flux is given by Eq. 30-2 ( BA). 5. The magnitude B of the magnetic field in the interior of a solenoid depends on the solenoid's current i and its number n of turns per unit length, according to Eq. 29-23 (B=Hin). 20000 Axis Figure A coil Cis located inside a solenoid S, which carries current i.
KEY IDEAS The long solenoid S shown (in cross section) in Fig. 30-3 has 220 turns/cm and carries a current i 1.5 A; its diameter D is 3.2 cm. At its center we place a 130-turn closely packed coil C of diameter d 2.1 cm. The current in the solehoid is reduced to zero at a steady rate in 25 ms. What is the magni- tude of the emf that is induced in coil C while the current in the solenoid is changing? 1. Because it is located in the interior of the solenoid, coil C lies within the magnetic field produced by current i in the solenoid; thus, there is a magnetic flux , through coil C. 2. Because current i decreases, flux , also decreases, 3. As Pn decreases, emf & is induced in coil C. 4. The flux through each turn of coil C depends on the area A and orientation of that turn in the solenoid's magnetic field B.Because B is uniform and directed perpendicular to area A, the flux is given by Eq. 30-2 ( BA). 5. The magnitude B of the magnetic field in the interior of a solenoid depends on the solenoid's current i and its number n of turns per unit length, according to Eq. 29-23 (B=Hin). 20000 Axis Figure A coil Cis located inside a solenoid S, which carries current i.
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter23: Faraday’s Law And Inductance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 25P
Related questions
Question
100%
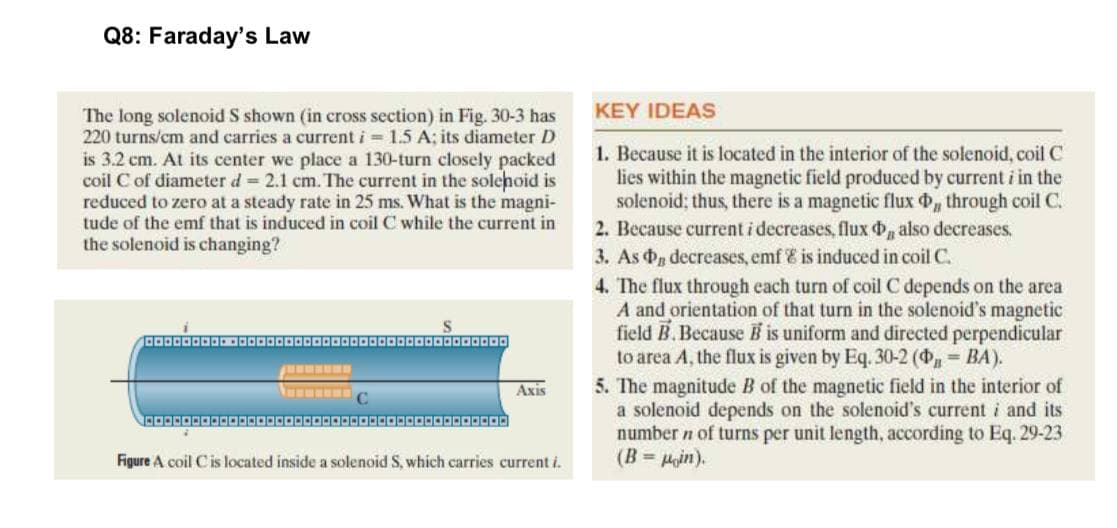
Transcribed Image Text:Q8: Faraday's Law
KEY IDEAS
The long solenoid S shown (in cross section) in Fig. 30-3 has
220 turns/cm and carries a current i = 1.5 A; its diameter D
is 3.2 cm. At its center we place a 130-turn closely packed
coil C of diameter d 2.1 cm. The current in the solehoid is
reduced to zero at a steady rate in 25 ms. What is the magni-
tude of the emf that is induced in coil C while the current in
the solenoid is changing?
1. Because it is located in the interior of the solenoid, coil C
lies within the magnetic field produced by current i in the
solenoid; thus, there is a magnetic flux d, through coil C.
2. Because current i decreases, flux also decreases.
3. As d decreases, emf E is induced in coil C.
4. The flux through each turn of coil C depends on the area
A and orientation of that turn in the solenoid's magnetic
field B.Because B is uniform and directed perpendicular
to area A, the flux is given by Eq. 30-2 (4 = BA).
5. The magnitude B of the magnetic field in the interior of
a solenoid depends on the solenoid's current i and its
number n of turns per unit length, according to Eq. 29-23
(B = Pin).
Axis
Figure A coil Cis located inside a solenoid S, which carries
ent i.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning