The major component of household bleach is sodium hypochlorite. In South Africa, bleaching solution is known commonly as "JIK". The solution is made by dissolving the ionic solid in water. Construct a Molecular Orbital diagram using the anion of the solid mentioned above. Label all AO's, MO's and any other relevant features on the diagram. Calculate the bond order for the anion and comment on any possible physical properties that may be evident from your calculation and the MO diagram. Use the Table given below to help you construct your MO diagram. TABLE 5.2 Orbital Potential Energies Orbital Potential Energy (eV) Atomic Number 1s Element 25 2p 35 3p 4p H -13.61 2 Не -24.59 3 Li -5.39 4 Be -9.32 5 B -14.05 -8.30 -19.43 -10.66 7 -25.56 -13.18 8 -32.38 -15.85 F -40.17 -18.65 10 Ne -48.47 -21.59 11 Na -5.14 12 Mg -7.65 13 Al -11.32 -5.98 14 Si -15.89 -7.78 15 P -18.84 -9.65 16 -22.71 -11.62 17 CI -25.23 -13.67 18 Ar -29.24 -15.82 19 K -4.34 20 Ca -6.11 30 Zn -9.39 31 Ga -12.61 -5.93 32 Ge -16.05 -7.54 33 As -18.94 -9.17 34 Se -21.37 - 10.82 35 Br -24.37 -12.49 36 Kr -27.51 -14.22
The major component of household bleach is sodium hypochlorite. In South Africa, bleaching solution is known commonly as "JIK". The solution is made by dissolving the ionic solid in water. Construct a Molecular Orbital diagram using the anion of the solid mentioned above. Label all AO's, MO's and any other relevant features on the diagram. Calculate the bond order for the anion and comment on any possible physical properties that may be evident from your calculation and the MO diagram. Use the Table given below to help you construct your MO diagram. TABLE 5.2 Orbital Potential Energies Orbital Potential Energy (eV) Atomic Number 1s Element 25 2p 35 3p 4p H -13.61 2 Не -24.59 3 Li -5.39 4 Be -9.32 5 B -14.05 -8.30 -19.43 -10.66 7 -25.56 -13.18 8 -32.38 -15.85 F -40.17 -18.65 10 Ne -48.47 -21.59 11 Na -5.14 12 Mg -7.65 13 Al -11.32 -5.98 14 Si -15.89 -7.78 15 P -18.84 -9.65 16 -22.71 -11.62 17 CI -25.23 -13.67 18 Ar -29.24 -15.82 19 K -4.34 20 Ca -6.11 30 Zn -9.39 31 Ga -12.61 -5.93 32 Ge -16.05 -7.54 33 As -18.94 -9.17 34 Se -21.37 - 10.82 35 Br -24.37 -12.49 36 Kr -27.51 -14.22
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter5: Alkenes: Bonding, Nomenclature, And Properties
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.11P: The structure of 1,2-propadiene (allene) is shown to the right. (a) Predict all approximate bond...
Related questions
Question
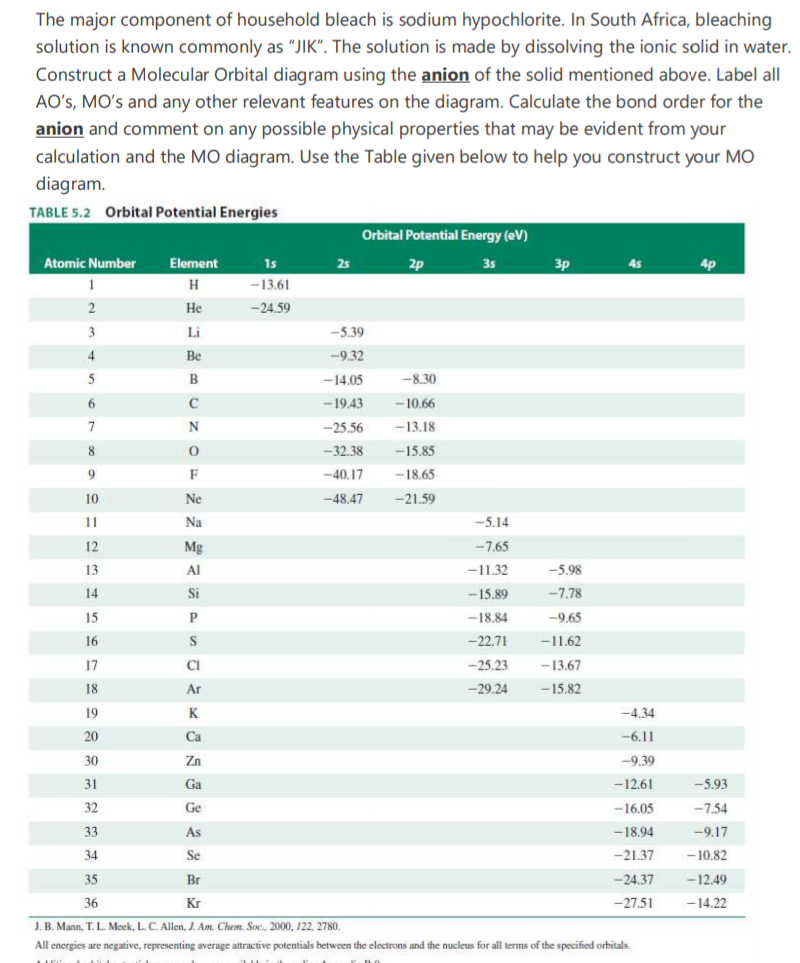
Transcribed Image Text:The major component of household bleach is sodium hypochlorite. In South Africa, bleaching
solution is known commonly as "JIK". The solution is made by dissolving the ionic solid in water.
Construct a Molecular Orbital diagram using the anion of the solid mentioned above. Label all
AO's, MO's and any other relevant features on the diagram. Calculate the bond order for the
anion and comment on any possible physical properties that may be evident from your
calculation and the MO diagram. Use the Table given below to help you construct your MO
diagram.
TABLE 5.2 Orbital Potential Energies
Orbital Potential Energy (eV)
Atomic Number
Element
1s
25
2p
35
3p
45
4p
H.
-13.61
2
He
Не
-24.59
3
Li
-5.39
4
Be
-9.32
5
B
-14.05
-8.30
C
- 19.43
- 10.66
6.
7
-25.56
-13.18
-32.38
-15.85
9
F
-40.17
-18.65
10
Ne
-48.47
-21.59
11
Na
-5.14
12
Mg
-7.65
13
Al
-11.32
-5.98
14
Si
- 15.89
-7.78
15
P
-18.84
-9.65
16
S
-22.71
-11.62
17
CI
-25.23
-13.67
18
Ar
-29.24
-15.82
19
K
-4.34
20
Ca
-6.11
30
Zn
-9.39
31
Ga
-12.61
-5.93
32
Ge
-16.05
-7.54
33
As
-18.94
-9.17
34
Se
-21.37
- 10.82
35
Br
-24.37
-12.49
36
Kr
-27.51
-14.22
J. B. Mann, T. L. Meek, L. C. Allen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 2780.
All energies are negative, representing average attractive potentials between the electrons and the nucleus for all terms of the specified orbitals.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning