The molar heat capacity at constant pressure of carbon dioxide is 29.14 J/K.mol. (a) What is the value of its molar heat capacity at constant volume? (b) Calculate the change in enthalpy when 1 mole carbon dioxide is heated from 15°C (the temperature when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs)? J/mol. 4 sig. number normal format. TO FM (c) Calculate molar internal energy when carbon dioxide is heated from 19.16 °C (the temperature when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs). normal format. J/mol 3 sig. number Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all ansavers O J/K.mol. 4 sig. number !!! ge ₂ Save All A 87%F
The molar heat capacity at constant pressure of carbon dioxide is 29.14 J/K.mol. (a) What is the value of its molar heat capacity at constant volume? (b) Calculate the change in enthalpy when 1 mole carbon dioxide is heated from 15°C (the temperature when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs)? J/mol. 4 sig. number normal format. TO FM (c) Calculate molar internal energy when carbon dioxide is heated from 19.16 °C (the temperature when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs). normal format. J/mol 3 sig. number Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all ansavers O J/K.mol. 4 sig. number !!! ge ₂ Save All A 87%F
Chapter2: The Kinetic Theory Of Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 81AP: One process for decaffeinating coffee uses carbon dioxide ( M=44.0 g/mol) at a molar density of...
Related questions
Question
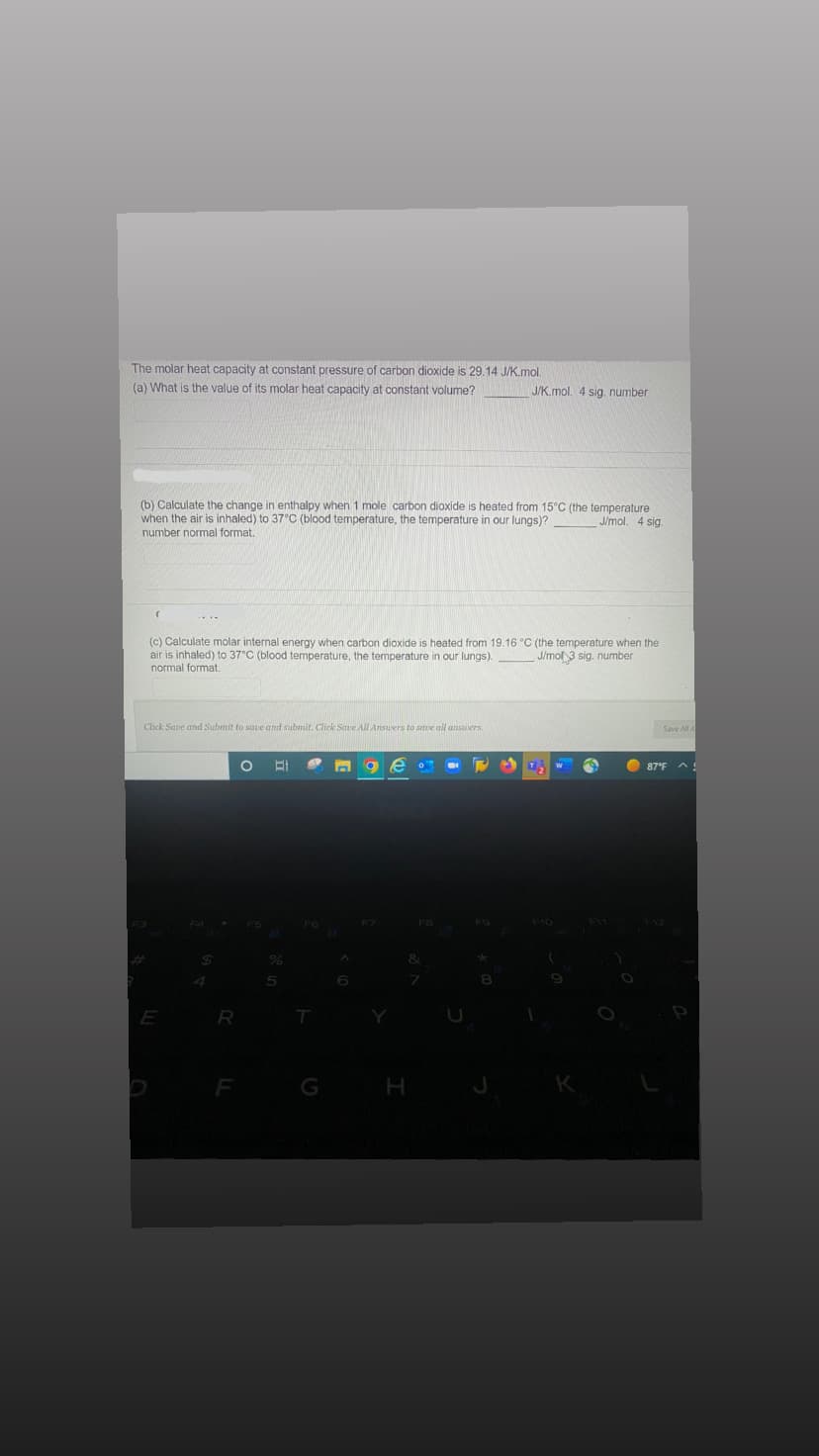
Transcribed Image Text:The molar heat capacity at constant pressure of carbon dioxide is 29.14 J/K.mol.
(a) What is the value of its molar heat capacity at constant volume?
J/mol. 4 sig.
(b) Calculate the change in enthalpy when 1 mole carbon dioxide is heated from 15°C (the temperature
when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs)?
number normal format.
(c) Calculate molar internal energy when carbon dioxide is heated from 19.16 °C (the temperature when the
air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs).
normal format.
J/mol 3 sig. number
Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers.
E
R
O El
5
G
E O
A
J/K.mol. 4 sig. number
H
FO
1₂
Save All A
87°F
^!
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning