If the return to labor decreases, then the income effect: O Offsets the substitution effect if leisure is inferior. Reinforces the substitution effect if leisure is normal. O There is no income effect in this case Offsets the substitution effect if leisure is normal.
If the return to labor decreases, then the income effect: O Offsets the substitution effect if leisure is inferior. Reinforces the substitution effect if leisure is normal. O There is no income effect in this case Offsets the substitution effect if leisure is normal.
Chapter30: The Labor Market
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16E
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:If the return to labor decreases, then the income effect:
Offsets the substitution effect if leisure is inferior.
Reinforces the substitution effect if leisure is normal.
There is no income effect in this case
Offsets the substitution effect if leisure is normal.
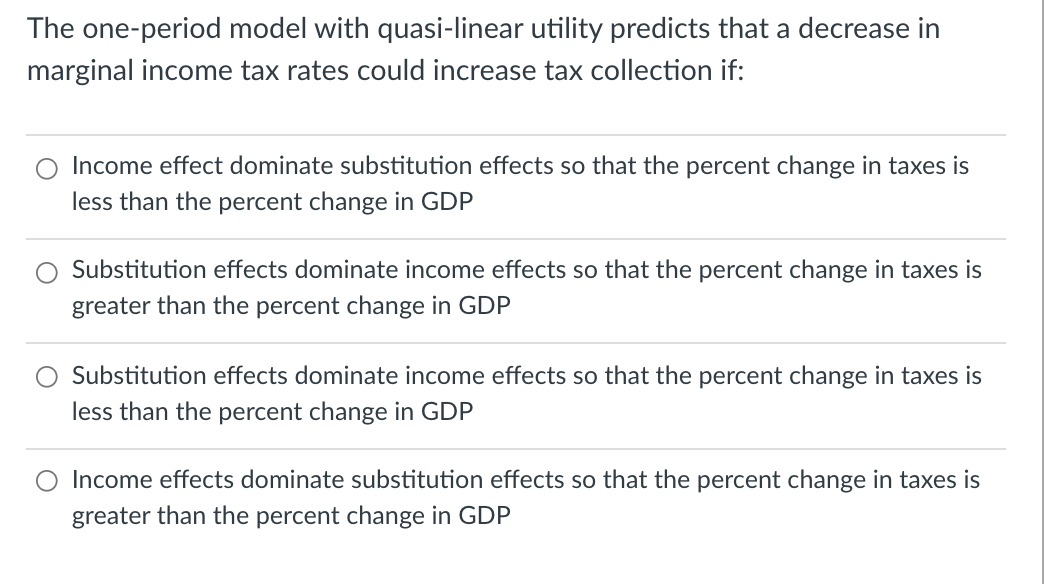
Transcribed Image Text:The one-period model with quasi-linear utility predicts that a decrease in
marginal income tax rates could increase tax collection if:
Income effect dominate substitution effects so that the percent change in taxes is
less than the percent change in GDP
Substitution effects dominate income effects so that the percent change in taxes is
greater than the percent change in GDP
Substitution effects dominate income effects so that the percent change in taxes is
less than the percent change in GDP
O Income effects dominate substitution effects so that the percent change in taxes is
greater than the percent change in GDP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The one-period model with quasi-linear utility predicts that a decrease in marginal income tax rates could increase tax collection if:
Group of answer choices
Substitution effects dominate income effects so that the percent change in taxes is greater than the percent change in
Substitution effects dominate income effects so that the percent change in taxes is less than the percent change in GDP
Income effect dominate substitution effects so that the percent change in taxes is less than the percent change in GDP
Income effects dominate substitution effects so that the percent change in taxes is greater than the percent change in GDP
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you








Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
