The owner of a chain of mini-markets wants to compare the sales performance of two of her stores, Store 1 and Store 2. Sales can vary considerably depending on the day of the week and the season of the year, so she decides to eliminate such effects by making sure to record each store's sales on the same 12 days, chosen at random. She records the sales (in dollars) for each store on these days, as shown in the table below. 89 10 11 12 Day Store 1 Store 2 1 2 Difference (Store 1 - Store 2) Send data to calculator V 3 216 843 794 765 838 729 4 5 87 158 6 627 707 607 923 563 417 628 258 602 477 757 825 -85 166 7 244 557 381 791 522 913 700 -173 -71 123 189 45 156 -125 Based on these data, can the owner conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that the mean daily sales of the two stores differ? Answer this question by performing a hypothesis test regarding (which is u with a letter "d" subscript), the population mean daily sales difference between the two stores. Assume that this population of differences (Store 1 minus Store 2) is normally distributed. Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified (If necessary consult a list of formulas ) Español
The owner of a chain of mini-markets wants to compare the sales performance of two of her stores, Store 1 and Store 2. Sales can vary considerably depending on the day of the week and the season of the year, so she decides to eliminate such effects by making sure to record each store's sales on the same 12 days, chosen at random. She records the sales (in dollars) for each store on these days, as shown in the table below. 89 10 11 12 Day Store 1 Store 2 1 2 Difference (Store 1 - Store 2) Send data to calculator V 3 216 843 794 765 838 729 4 5 87 158 6 627 707 607 923 563 417 628 258 602 477 757 825 -85 166 7 244 557 381 791 522 913 700 -173 -71 123 189 45 156 -125 Based on these data, can the owner conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that the mean daily sales of the two stores differ? Answer this question by performing a hypothesis test regarding (which is u with a letter "d" subscript), the population mean daily sales difference between the two stores. Assume that this population of differences (Store 1 minus Store 2) is normally distributed. Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified (If necessary consult a list of formulas ) Español
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 28EQ
Related questions
Question
A. Find the two critical values at the 0.05 level of significance. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
B. At the 0.05 level, can the owner conclude that the
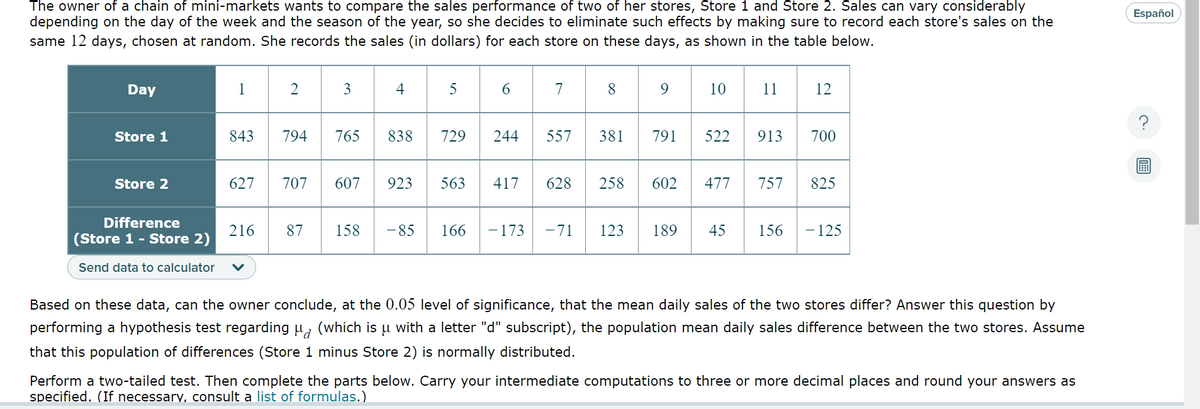
Transcribed Image Text:The owner of a chain of mini-markets wants to compare the sales performance of two of her stores, Store 1 and Store 2. Sales can vary considerably
depending on the day of the week and the season of the year, so she decides to eliminate such effects by making sure to record each store's sales on the
same 12 days, chosen at random. She records the sales (in dollars) for each store on these days, as shown in the table below.
Day
Store 1
Store 2
1
843
Difference
(Store 1 - Store 2)
Send data to calculator v
2
627 707
216
794
87
3
765
607
4
838
923
158 - 85
5
729 244
563
6
166
417
- 173
7
8
9
557 381 791
628 258 602
10
522
477
11
913
12
700
757 825
-71 123 189 45 156 - 125
Based on these data, can the owner conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that the mean daily sales of the two stores differ? Answer this question by
performing a hypothesis test regarding μ (which is u with a letter "d" subscript), the population mean daily sales difference between the two stores. Assume
that this population of differences (Store 1 minus Store 2) is normally distributed.
Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as
specified. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
Español
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage
