The plant in the picture has mass of 22 kg, and is hanging at a distance of 1.9 meters from the wall. The horizontal rod has mass of 9.5 kg. Assume that its weight is evenly distributed, therefore it can be treated as a single force at the center of mass. The rod is 2.6 meters long, and there is a cable at a 23° angle supporting it at the end.
The plant in the picture has mass of 22 kg, and is hanging at a distance of 1.9 meters from the wall. The horizontal rod has mass of 9.5 kg. Assume that its weight is evenly distributed, therefore it can be treated as a single force at the center of mass. The rod is 2.6 meters long, and there is a cable at a 23° angle supporting it at the end.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter14: Static Equilibrium, Elasticity, And Fracture
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 31PQ: A wooden door 2.1 m high and 0.90 m wide is hung by two hinges 1.8 m apart. The lower hinge is 15 cm...
Related questions
Question
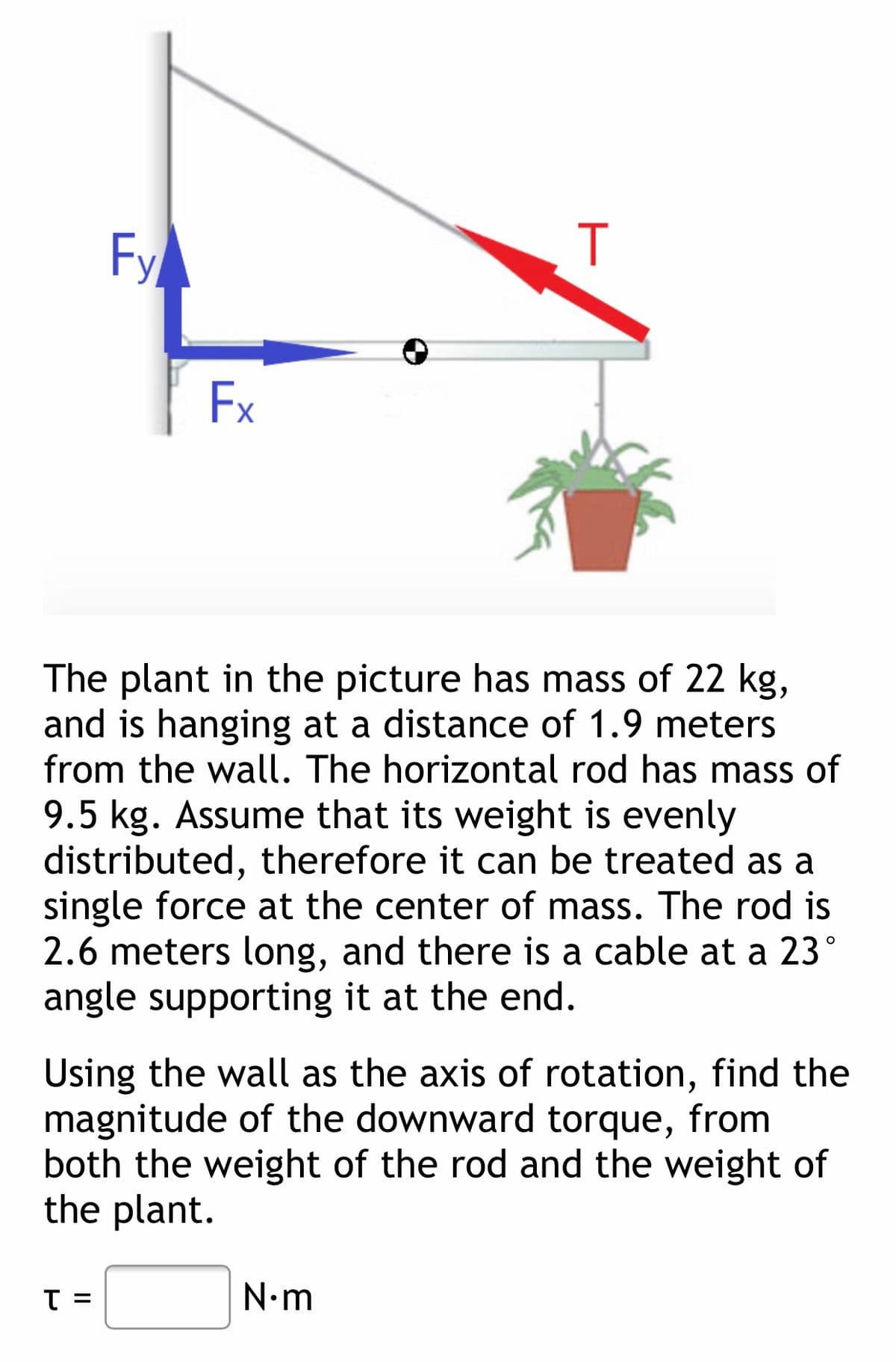
Transcribed Image Text:Fy
Ex
The plant in the picture has mass of 22 kg,
and is hanging at a distance of 1.9 meters
from the wall. The horizontal rod has mass of
9.5 kg. Assume that its weight is evenly
distributed, therefore it can be treated as a
single force at the center of mass. The rod is
2.6 meters long, and there is a cable at a 23°
angle supporting it at the end.
Using the wall as the axis of rotation, find the
magnitude of the downward torque, from
both the weight of the rod and the weight of
the plant.
T =
N•m

Transcribed Image Text:The downward torque is balanced by the
upward torque from the force of tension. Find
the magnitude of the force of tension.
T =
F is the contact force between the rod and
the wall. Using the other horizontal force in
the problem, find the horizontal component
of F (the normal force) that must be present
for the rod to be at equilibrium.
F.
There is a vertical force from a component of
the tension, but this is not enough to balance
the donward forces. Find the vertical force
that must be present for the wall to keep the
rod up.
F,
N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning