The sketch below shows the position of a toy car that moves along a track while a fan is blowing and creating a "headwind". The numbers indicate the time when the car was at a given position (some images overlap). The "tic" marks are 10 centimeters apart. The positive x direction is to the right. 12s 10s 8s 2s -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 (centimeters) In the space below, make a motion diagram of the motion of the cart. Include arrows to represent the (1) velocities and the (2) accelerations. Motion diagrams include: (1) dots to indicate positions (the dots are already drawn), (2) labeled arrows between dots to represent velocities, and (3) labeled arrows above/below the dots to represent accelerations. Put the acceleration arrows slightly above the dots when the cart is moving to the right and slightly below the dots when the cart is moving to the left. 25 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 10 100 110 120 (cm) 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 12s 10s 6s 0• 4s Describe what happens to the following quantities as the cart moves back and forth on the ramp. Describe what happens to the speed during this motion. a. b. Describe the direction of the velocity during this motion. Give direction(s) in terms of left, right or zero. Describe the x-velocity during this motion. What is its sign? Is it increasing, decreasing, constant? Choose +x to be to the right. Note that a quantity is increasing if it either becomes more positive or less negative. C. d. Describe the direction of the acceleration during this motion. Give direction(s) in terms of left, right or zero. e. Describe the x-acceleration during this motion. What is its sign? Is it increasing, decreasing, constant?
The sketch below shows the position of a toy car that moves along a track while a fan is blowing and creating a "headwind". The numbers indicate the time when the car was at a given position (some images overlap). The "tic" marks are 10 centimeters apart. The positive x direction is to the right. 12s 10s 8s 2s -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 (centimeters) In the space below, make a motion diagram of the motion of the cart. Include arrows to represent the (1) velocities and the (2) accelerations. Motion diagrams include: (1) dots to indicate positions (the dots are already drawn), (2) labeled arrows between dots to represent velocities, and (3) labeled arrows above/below the dots to represent accelerations. Put the acceleration arrows slightly above the dots when the cart is moving to the right and slightly below the dots when the cart is moving to the left. 25 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 10 100 110 120 (cm) 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 12s 10s 6s 0• 4s Describe what happens to the following quantities as the cart moves back and forth on the ramp. Describe what happens to the speed during this motion. a. b. Describe the direction of the velocity during this motion. Give direction(s) in terms of left, right or zero. Describe the x-velocity during this motion. What is its sign? Is it increasing, decreasing, constant? Choose +x to be to the right. Note that a quantity is increasing if it either becomes more positive or less negative. C. d. Describe the direction of the acceleration during this motion. Give direction(s) in terms of left, right or zero. e. Describe the x-acceleration during this motion. What is its sign? Is it increasing, decreasing, constant?
University Physics Volume 3
17th Edition
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Chapter5: Relativity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 38P: Describe the shape of the world line on a space-time diagram of (a) an object that remains at rest...
Related questions
Question
Only C,D, and E
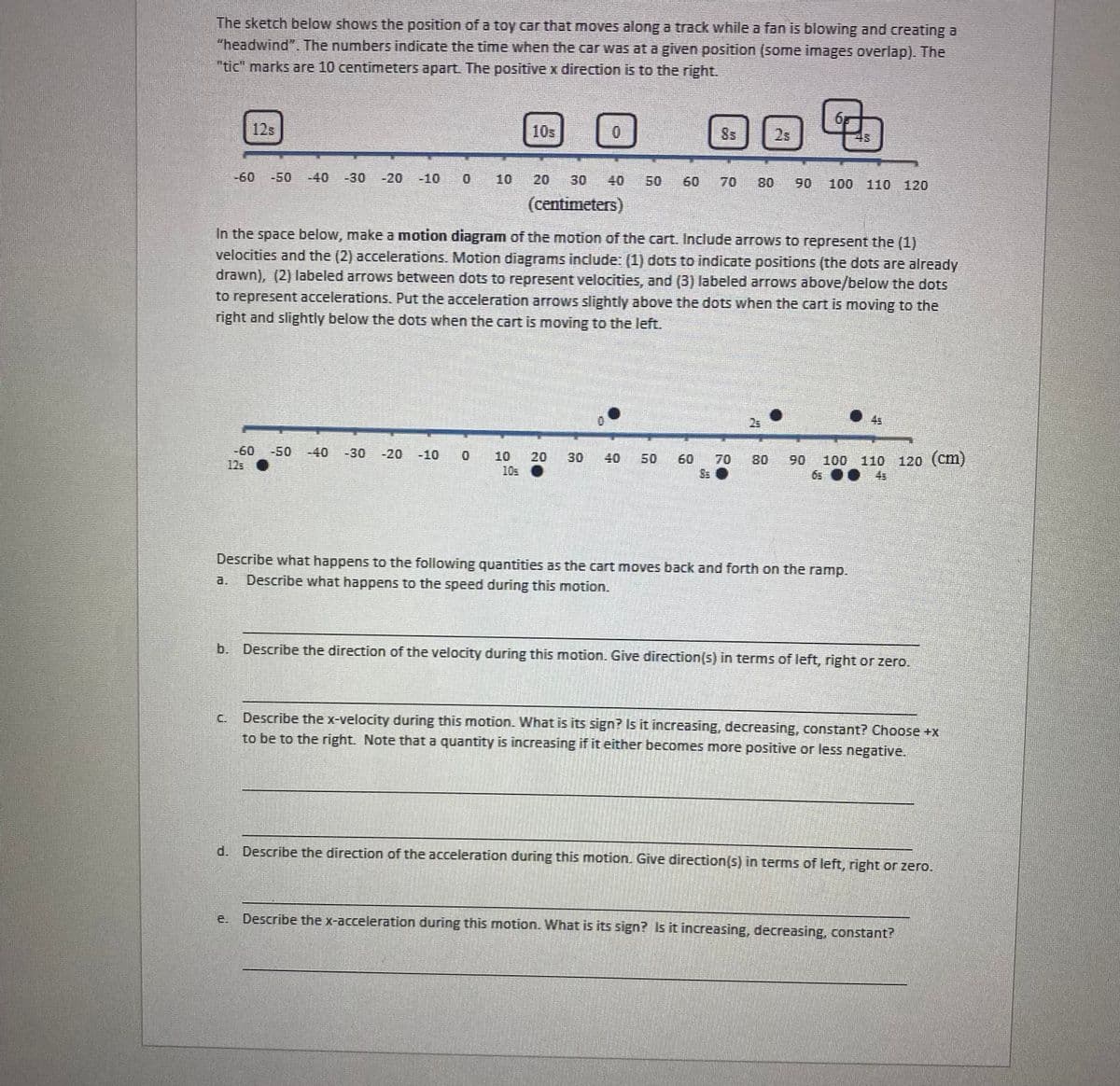
Transcribed Image Text:The sketch below shows the position of a toy car that moves along a track while a fan is blowing and creating a
"headwind". The numbers indicate the time when the car was at a given position (some images overlap). The
"tic" marks are 10 centimeters apart. The positive x direction is to the right.
12s
103
8s
2s
43
-60 -50
-40
-30 -20 -10 0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100 110 120
(centimeters)
In the space below, make a motion diagram of the motion of the cart. Include arrows to represent the (1)
velocities and the (2) accelerations. Motion diagrams include: (1) dots to indicate positions (the dots are already
drawn), (2) labeled arrows between dots to represent velocities, and (3) labeled arrows above/below the dots
to represent accelerations. Put the acceleration arrows slightly above the dots when the cart is moving to the
right and slightly below the dots when the cart is moving to the left.
25
4s
-60 -50 -40
125
-30 -20 -10 0
10
20
10s
90 100 110 120 (cm)
6s .. 4s
30
40
50
60
70
80
Describe what happens to the following quantities as the cart moves back and forth on the ramp.
Describe what happens to the speed during this motion.
a.
b. Describe the direction of the velocity during this motion. Give direction(s) in terms of left, right or zero.
Describe the x-velocity during this motion. What is its sign? Is it increasing, decreasing, constant? Choose +x
to be to the right. Note that a quantity is increasing if it either becomes more positive or less negative.
C.
d. Describe the direction of the acceleration during this motion. Give direction(s) in terms of left, right or zero.
e.
Describe the x-acceleration during this motion. What is its sign? Is it increasing, decreasing, constant?
In
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill