The steam reforming of methanol is being used to produce hydrogen for a fuel cell: CH3OH(g) + H20(g) > CO2(g) + 3H2(g) You are using a constant volume isothermal batch reactor. The reactor is charged with 1 mole of CH3OH and 1.5 moles of H20 Reactor conditions: P = 2 atm T= 80°C Assume the Ideal Gas Law applies, where R = 8.314 J/molK %3D AG° (kJ/mol) AH:° (kJ/mol) Component CH:ОН (g) H20 (g) CO2 (g) H2 (g) -162.5 -201.2 -228.4 -241.8 -394.6 -393.5 (a) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH. (b) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH if the temperature is increased to 100°C. Explain the reason for the change. (c) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH if pressure is increased to 4 atm. Explain the reason for the change.
The steam reforming of methanol is being used to produce hydrogen for a fuel cell: CH3OH(g) + H20(g) > CO2(g) + 3H2(g) You are using a constant volume isothermal batch reactor. The reactor is charged with 1 mole of CH3OH and 1.5 moles of H20 Reactor conditions: P = 2 atm T= 80°C Assume the Ideal Gas Law applies, where R = 8.314 J/molK %3D AG° (kJ/mol) AH:° (kJ/mol) Component CH:ОН (g) H20 (g) CO2 (g) H2 (g) -162.5 -201.2 -228.4 -241.8 -394.6 -393.5 (a) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH. (b) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH if the temperature is increased to 100°C. Explain the reason for the change. (c) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH if pressure is increased to 4 atm. Explain the reason for the change.
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Please solve it complete
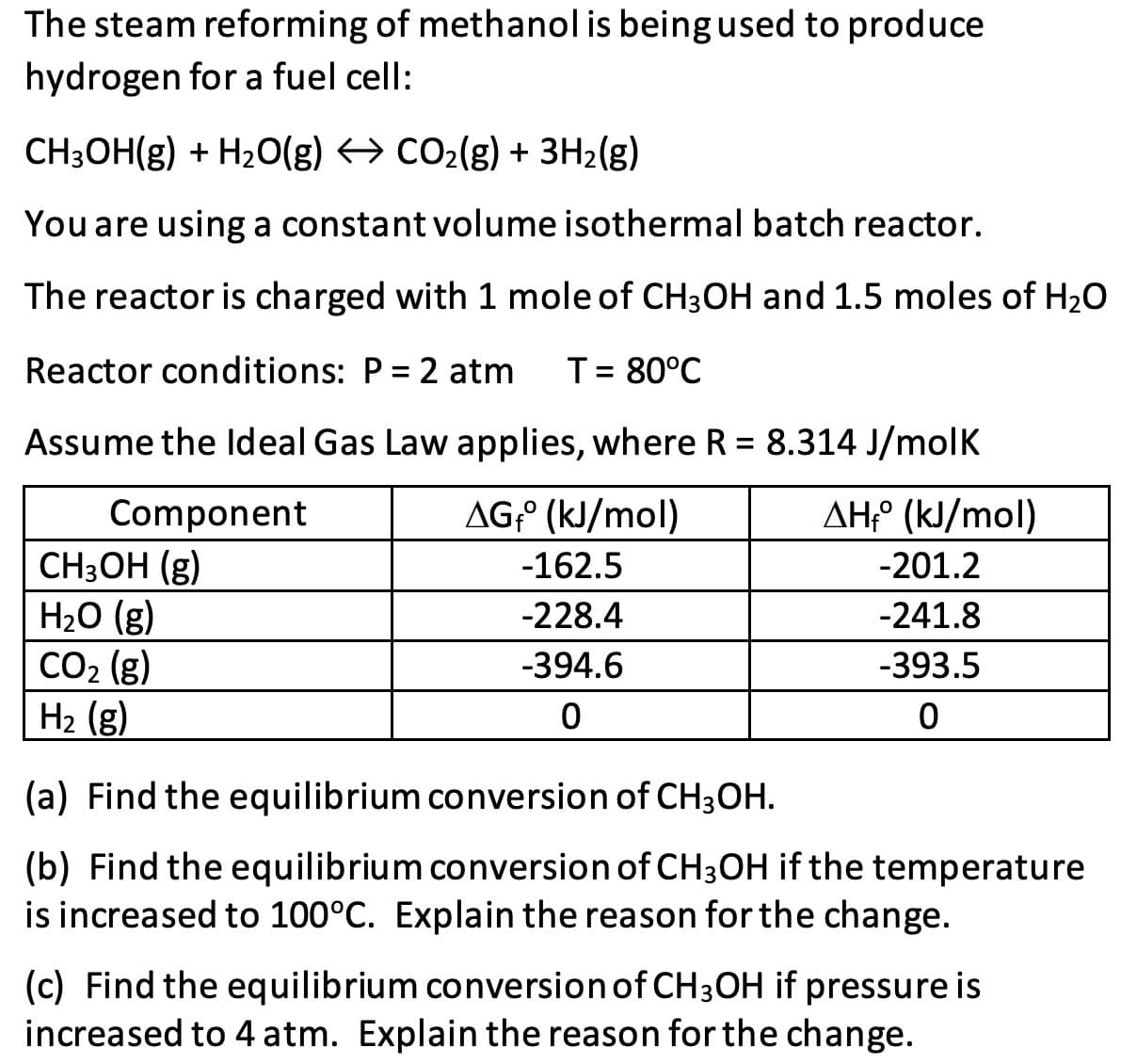
Transcribed Image Text:The steam reforming of methanol is being used to produce
hydrogen for a fuel cell:
CH3OH(g) + H20(g) → CO2(g) + 3H2(g)
You are using a constant volume isothermal batch reactor.
The reactor is charged with 1 mole of CH3OH and 1.5 moles of H20
Reactor conditions: P = 2 atm
T= 80°C
Assume the ldeal Gas Law applies, where R = 8.314 J/molK
%3D
AG;° (kJ/mol)
AH° (kJ/mol)
Component
CH3OH (g)
H2O (g)
CO2 (g)
H2 (g)
-162.5
-201.2
-228.4
-241.8
-394.6
-393.5
(a) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH.
(b) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH if the temperature
is increased to 100°C. Explain the reason for the change.
(c) Find the equilibrium conversion of CH3OH if pressure is
increased to 4 atm. Explain the reason for the change.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The