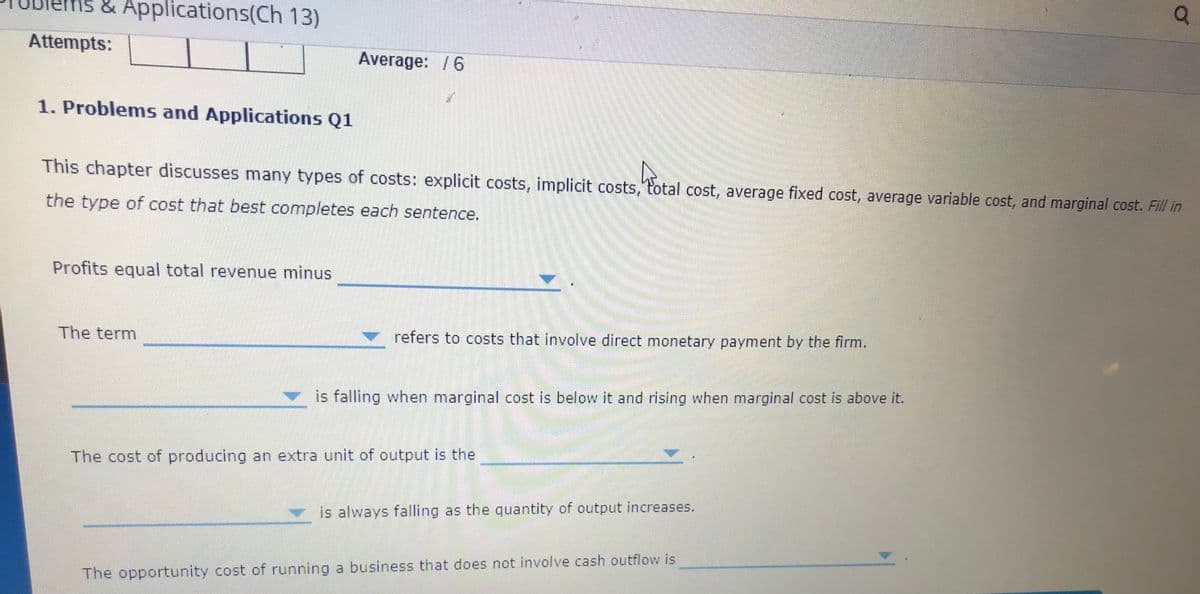
This chapter discusses many types of costs: explicit costs, implicit costs, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, and marginal cost. Fill in the type of cost that best completes each sentence. Profits equal total revenue minus The term refers to costs that involve direct monetary payment by the firm. is falling when marginal cost is below it and rising when marginal cost is above it. The cost of producing an extra unit of output is the is always falling as the quantity of output increases. The opportunity cost of running a business that does not involve cash outflow is
This chapter discusses many types of costs: explicit costs, implicit costs, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, and marginal cost. Fill in the type of cost that best completes each sentence. Profits equal total revenue minus The term refers to costs that involve direct monetary payment by the firm. is falling when marginal cost is below it and rising when marginal cost is above it. The cost of producing an extra unit of output is the is always falling as the quantity of output increases. The opportunity cost of running a business that does not involve cash outflow is
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Course List)
16th Edition
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Chapter8: Costs And The Supply Of Goods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19CQ
Related questions
Question
image 1 :
This chapter discusses many types of costs: explicit costs, implicit costs, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost , and marginal cost.
Fill in the type of cost that best completes each sentence.
Profits equal total revenue minus
(average fixed cost , average variable cost , explicit cost , implicit cost , marginal cost , total cost)
The term (average fixed cost , average variable cost , explicit cost , implicit cost , marginal cost , total cost) refers to costs that involve direct monetary payment by the firm.
(average fixed cost , average variable cost , explicit cost , implicit cost , marginal cost , total cost) is falling when marginal cost is below it and rising when marginal cost is above it.
The cost of producing an extra unit of output is the (average fixed cost , average variable cost , explicit cost , implicit cost , marginal cost , total cost) .
(average fixed cost , average variable cost , explicit cost , implicit cost , marginal cost , total cost) is always falling as the quantity of output increases.
The opportunity cost of running a business that does not involve cash outflow is (average fixed cost , average variable cost , explicit cost , implicit cost , marginal cost , total cost) .
image 2 :
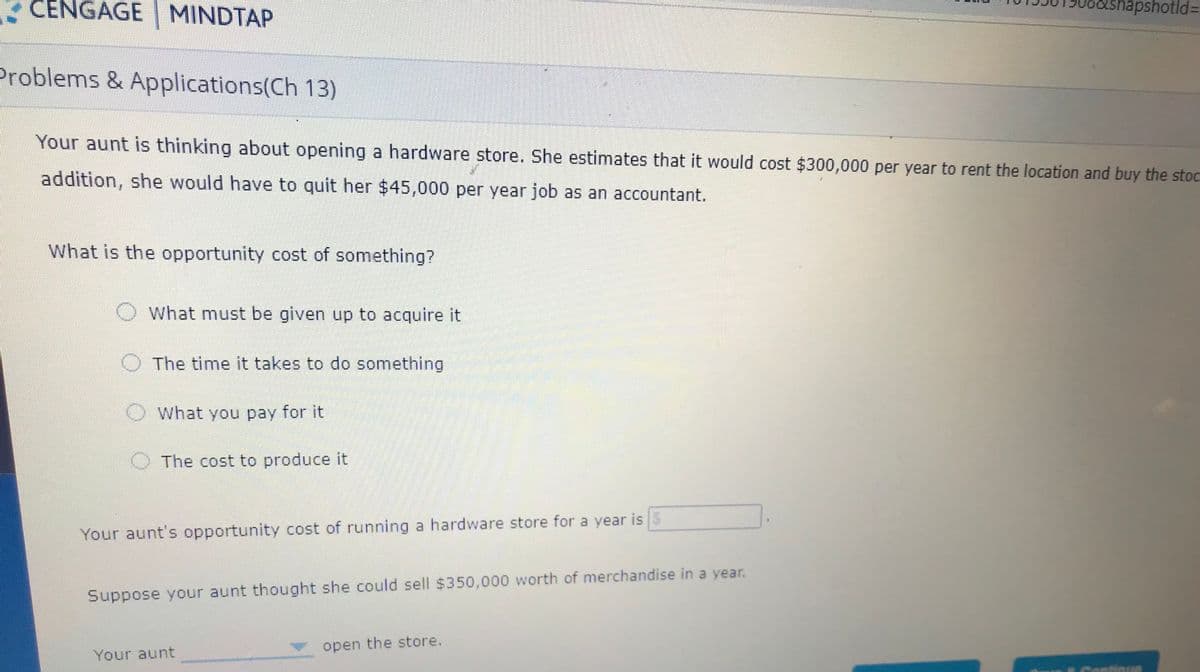
Your aunt is thinking about opening a hardware store. She estimates that it would cost $300,000 per year to rent the location and buy the stock. In addition, she would have to quit her $45,000 per year job as an accountant.
What is the opportunity cost of something?
What must be given up to acquire it
The time it takes to do something
What you pay for it
The cost to produce it
Your aunt's opportunity cost of running a hardware store for a year is $ ?
Suppose your aunt thought she could sell $350,000 worth of merchandise in a year.
Your aunt (should , or should not) ? open the store
Transcribed Image Text:ms & Applications(Ch 13)
Attempts:
Average: /6
1. Problems and Applications Q1
This chapter discusses many types of costs: explicit costs, implicit costs, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, and marginal cost. Fill in
the type of cost that best completes each sentence.
Profits equal total revenue minus
The term
refers to costs that involve direct monetary payment by the firm.
is falling when marginal cost is below it and rising when marginal cost is above it.
The cost of producing an extra unit of output is the
v is always falling as the quantity of output increases.
The opportunity cost of running a business that does not involve cash outflow is
Transcribed Image Text:CENGAGE MINDTAP
isnapshotld%3D
Problems & Applications(Ch 13)
Your aunt is thinking about opening a hardware store. She estimates that it would cost $300,000 per year to rent the location and buy the stoc
addition, she would have to quit her $45,000 per year job as an accountant.
What is the opportunity cost of something?
OWhat must be given up to acquire it
The time it takes to do something
What you pay for it
O The cost to produce it
Your aunt's opportunity cost of running a hardware store for a year is
Suppose your aunt thought she could sell $350,000 worth of merchandise in a year.
open the store.
Your aunt
antinue
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
