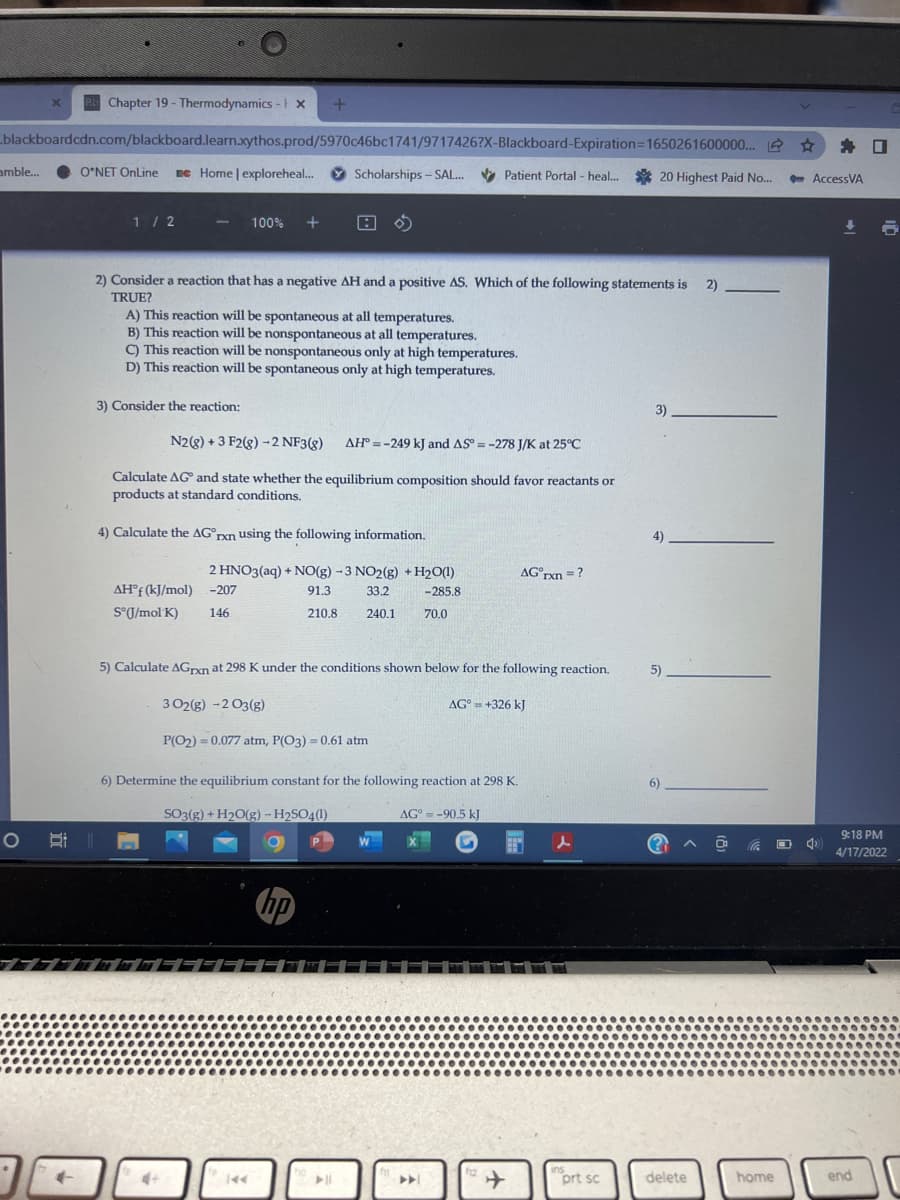
tion that has a negative AH and a positive AS. Which of the following statements is 2) - ion will be spontaneous at all temperatures. Fon will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures. ion will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures. ion will be spontaneous only at high temperatures. action: 3) D+3 F2(g) - 2 NF3(8) AH° =-249 kJ and AS = -278 J/K at 25°C %3D %3D und state whether the equilibrium composition should favor reactants or ndard conditions. G°pxn using the following information. 4). 2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) -3 NO2(g) + H2O(1) AG°rxn =? %3D -207 91.3 33.2 -285.8 146 210.8 240.1 70.0
tion that has a negative AH and a positive AS. Which of the following statements is 2) - ion will be spontaneous at all temperatures. Fon will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures. ion will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures. ion will be spontaneous only at high temperatures. action: 3) D+3 F2(g) - 2 NF3(8) AH° =-249 kJ and AS = -278 J/K at 25°C %3D %3D und state whether the equilibrium composition should favor reactants or ndard conditions. G°pxn using the following information. 4). 2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) -3 NO2(g) + H2O(1) AG°rxn =? %3D -207 91.3 33.2 -285.8 146 210.8 240.1 70.0
Chemistry for Engineering Students
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781285199023
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.29PAE
Related questions
Question
#2 please
Transcribed Image Text:eChapter 19 - Thermodynamics -tx
blackboardcdn.com/blackboard.learn.xythos.prod/5970c46bc1741/9717426?X-Blackboard-Expiration3D1650261600000.. 2
身口
amble...
O*NET OnLine
Be Home | exploreheal.
O Scholarships - SAL.
* Patient Portal - heal.
20 Highest Paid No..
- AccessVA
1/ 2
100%
2) Consider a reaction that has a negative AH and a positive AS. Which of the following statements is
2).
TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
D) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
3) Consider the reaction:
3).
N2(8) + 3 F2(g) -2 NF3(g)
AH° = -249 kJ and AS = -278 J/K at 25°C
Calculate AG and state whether the equilibrium composition should favor reactants or
products at standard conditions,
4) Calculate the AG°rxn using the following information.
4)
2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) -3 NO2(g) + H2O(1)
AG°rxn =?
AH°f (kJ/mol) -207
91.3
33.2
-285.8
S°J/mol K)
146
210.8
240.1
70.0
5) Calculate AGrxn at 298 K under the conditions shown below for the following reaction.
5)
3 02(g) -2 O3(g)
AG° = +326 kJ
%3D
P(O2) = 0.077 atm, P(O3) = 0.61 atm
6) Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 298 K.
6)
SO3(g) + H2O(g) – H2SO4(1)
AG° = -90.5 kJ
9:18 PM
(? ^
4/17/2022
hp
ins
prt sc
12
4+
delete
home
end
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
