TITRATION A TITRATION B titrated with CH3CO2H titrated with NaoH Volume of second Volume of second reagent added (mL) pH reagent added (mL) pH 2.87 4.14 4.56 4.92 5.34 5.46 5.61 5.80 0.0 0.0 5.0 5.0 10.0 10.0 15.0 15.0 20.0 20.0 21.0 21.0 22.0 22.0 23.0 23.0 6.12 8.87 11.30 11.56 11.75 I1. 87 11.96 12.22 12.36 12.46 24.0 24.0 25.0 25.0 26.0 26.0 27.0 27.0 28.0 28.0 29.0 29.0 30.0 30.0 35.0 35.0 40.0 40.0 45.0 45.0 50.0 12.52 50.0 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 2. pKą or pK, = 1. Titration A, endpoint pH : 3. Ką or Kp = Titration B, endpoint pH : 4. Why no K asked for Titration A?
TITRATION A TITRATION B titrated with CH3CO2H titrated with NaoH Volume of second Volume of second reagent added (mL) pH reagent added (mL) pH 2.87 4.14 4.56 4.92 5.34 5.46 5.61 5.80 0.0 0.0 5.0 5.0 10.0 10.0 15.0 15.0 20.0 20.0 21.0 21.0 22.0 22.0 23.0 23.0 6.12 8.87 11.30 11.56 11.75 I1. 87 11.96 12.22 12.36 12.46 24.0 24.0 25.0 25.0 26.0 26.0 27.0 27.0 28.0 28.0 29.0 29.0 30.0 30.0 35.0 35.0 40.0 40.0 45.0 45.0 50.0 12.52 50.0 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 2. pKą or pK, = 1. Titration A, endpoint pH : 3. Ką or Kp = Titration B, endpoint pH : 4. Why no K asked for Titration A?
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter18: Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2STP
Related questions
Question
100%
Step by step explanation please
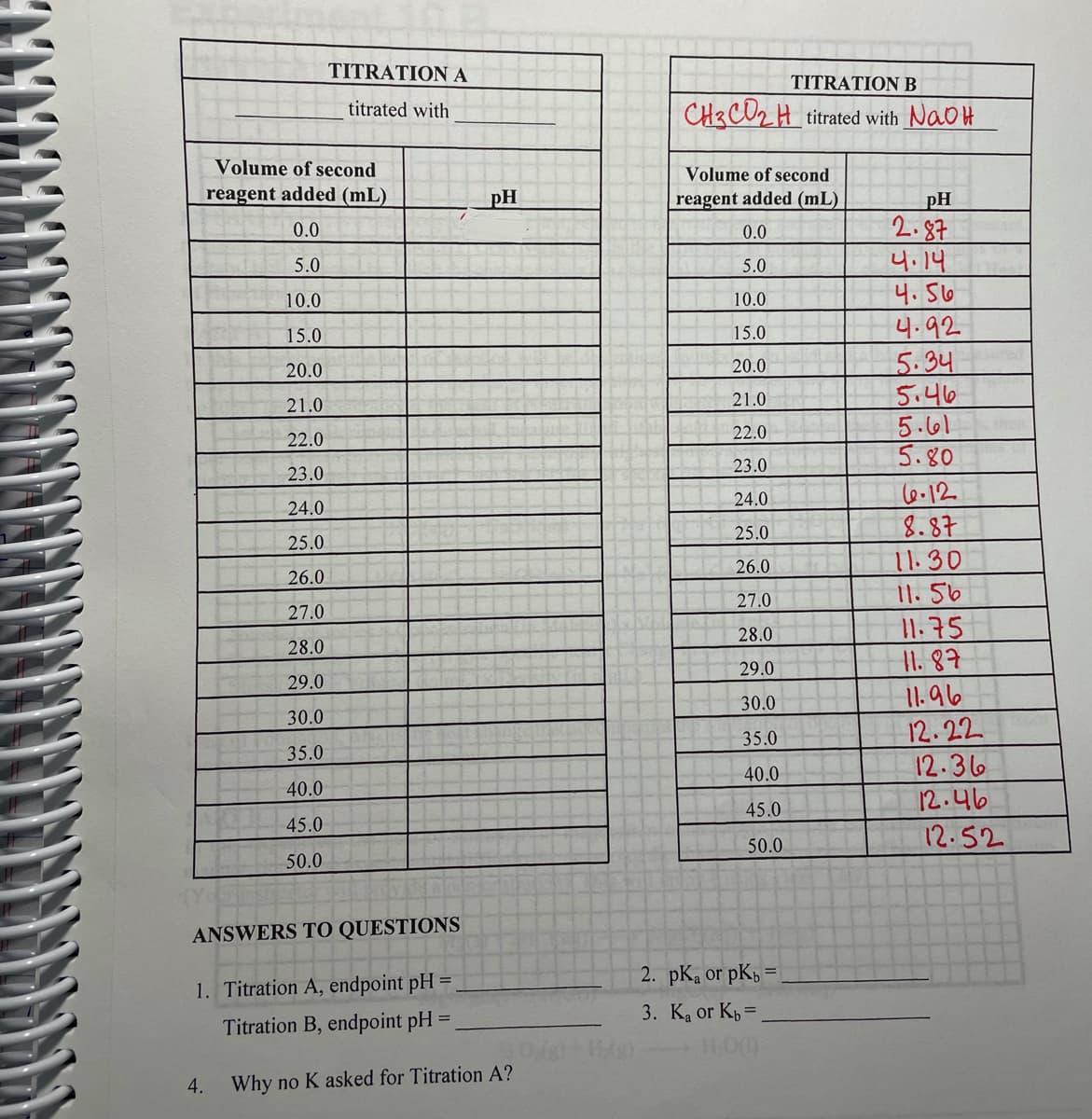
Transcribed Image Text:TITRATIONA
TITRATIONB
titrated with
CH3CD2 H titrated with NaoH
Volume of second
Volume of second
reagent added (mL)
pH
reagent added (mL)
pH
2.87
4.14
4.56
4.92
5.34
5.46
5.61
5.80
0.0
0.0
5.0
5.0
10.0
10.0
15.0
15.0
20.0
20.0
21.0
21.0
22.0
22.0
23.0
23.0
l0.12
8.87
11.30
11. 56
11.75
11. 87
11.96
12.22
12.36
12.46
12.52
24.0
24.0
25.0
25.0
26.0
26.0
27.0
27.0
28.0
28.0
29.0
29.0
30.0
30.0
35.0
35.0
40.0
40.0
45.0
45.0
50.0
50.0
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS
2. pK, or pK =
1. Titration A, endpoint pH =
3. Ka or Kp =
Titration B, endpoint pH =
4. Why no K asked for Titration A?

Transcribed Image Text:EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
WEAR YOUR SAFETY GLASSES WHILE
...
PERFORMING THIS EXPERIMENT
2.
Fill one burette with acid and the other with base. Each student will perform two titrations during this
1.
Clean two burettes; your instructor will describe how.
8.e Inemiheqx
lab.
Drain 25.0 mL of either acid or base (depending on which acid/base you have been assigned) from your
burette into an Erlenmeyer flask. (If “A is to be titrated with B" then A goes in first, and B will be added
to A.)
Read and record the pH in your flask.
Add 5.0 mL of the second reagent (acid or base) to your flask, from the other buret. Read and record the
new pH.
Continue adding this second reagent in 5.0 mL increments until either a total of 20.0 mL has been added
or the pH changes by 3 units from the previous reading. Add ten 1.0 mL portions and then resume 5.0
mL increments until a total of 50.0 mL has been added. After each of these additions the flask should be
swirled to insure mixing and the pH should be measured and recorded in table A.
Rinse your flasks with tap water followed by deionized water. Drain well.
Clean your burettes as described by the instructor.
Refill your burettes with the second acid base set.
10. Repeat steps (3) through (6) for this second titration. Record the pH's in table B.
11. Clean your flasks and burettes.
3.
4.
5.
ig of
6.
7.
issge omo8
8.
9.
HOBM OH
HO,H 1DH
OH+OHX-
ASSIGNMENT
HOHO+ KOH
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

