Treatment A B 162 141 125 143 157 123 165 125 139 145 143 141 149 137 150 178 155 132 Sample 157 143 135 mean Sample 186.8 140.8 106.0 variance (a) Compute the sum of squares between treatments. (b) Compute the mean square between treatments. (c) Compute the sum of squares due to error. (d) Compute the mean square due to error. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) (e) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four decimal places.) Degrees of Freedom Source Sum Mean p-value of Variation of Squares Square Treatments Error Total (f) At the a = 0.05 level of significance, test whether the means for the three treatments are equal. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: HA = HB = HC H: Not all the population means are equal. O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal. H: At least two of the population means are different. O Ho: HA = HB = HC H: HA# HB # HC Ho: Not all the population means are equal. H: HA = HB = Hc O Ho: HA + HB * HC H: HA = HB = Hc %3! Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Treatment A B 162 141 125 143 157 123 165 125 139 145 143 141 149 137 150 178 155 132 Sample 157 143 135 mean Sample 186.8 140.8 106.0 variance (a) Compute the sum of squares between treatments. (b) Compute the mean square between treatments. (c) Compute the sum of squares due to error. (d) Compute the mean square due to error. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) (e) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four decimal places.) Degrees of Freedom Source Sum Mean p-value of Variation of Squares Square Treatments Error Total (f) At the a = 0.05 level of significance, test whether the means for the three treatments are equal. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: HA = HB = HC H: Not all the population means are equal. O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal. H: At least two of the population means are different. O Ho: HA = HB = HC H: HA# HB # HC Ho: Not all the population means are equal. H: HA = HB = Hc O Ho: HA + HB * HC H: HA = HB = Hc %3! Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter5: A Survey Of Other Common Functions
Section5.6: Higher-degree Polynomials And Rational Functions
Problem 5E: Population Genetics In the study of population genetics, an important measure of inbreeding is the...
Related questions
Question
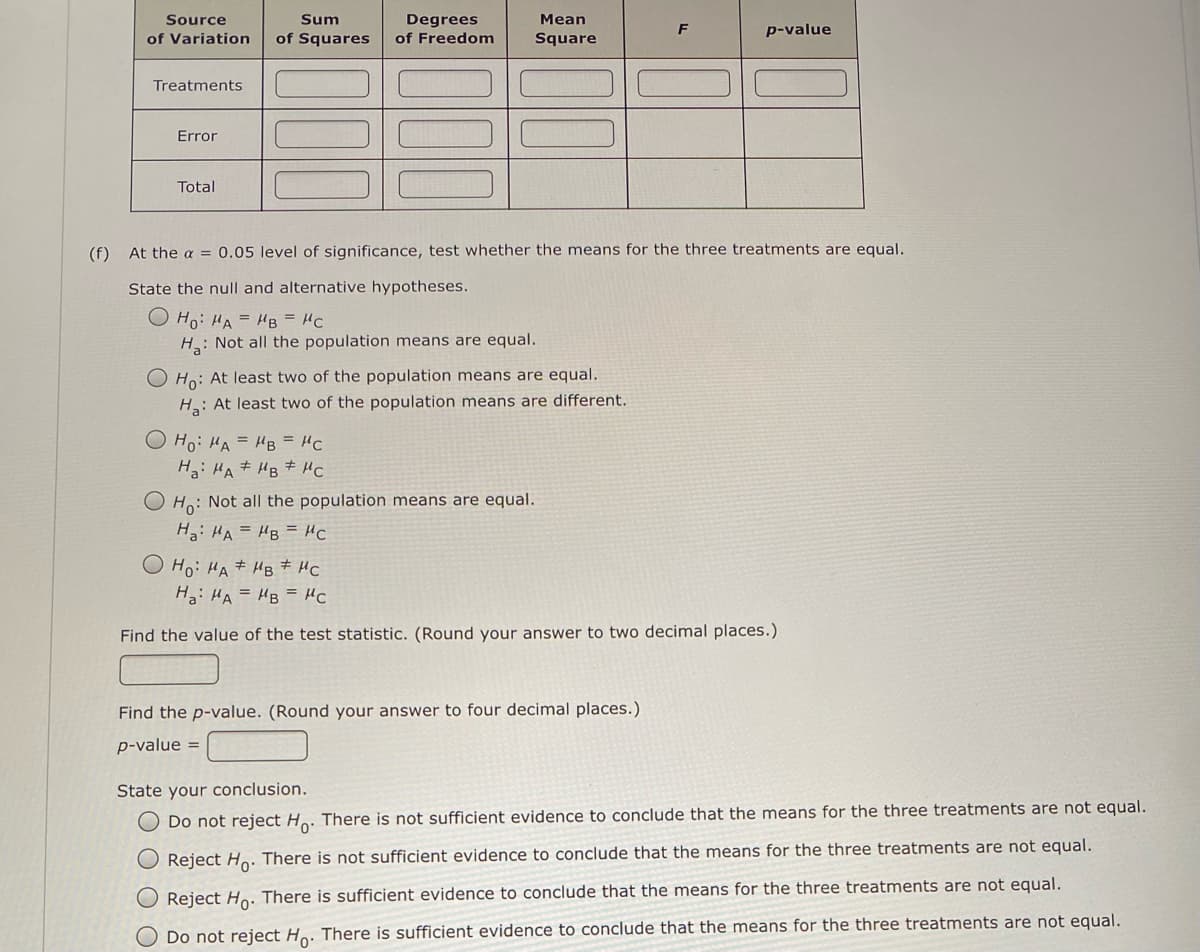
Transcribed Image Text:Source
Sum
Мean
Degrees
of Freedom
F
p-value
of Variation
of Squares
Square
Treatments
Error
Total
(f) At the a = 0.05 level of significance, test whether the means for the three treatments are equal.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
O Ho: HA = HB = HC
H: Not all the population means are equal.
O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal.
H: At least two of the population means are different.
O Ho: HA = HB = HC
H: HA # HB # HC
Ho: Not all the population means are equal.
Ha: HA = HB = HC
Ho: HA# HB # HC
Ha: HA = HB = HC
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
p-value =
State your conclusion.
O Do not reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means for the three treatments are not equal.
O Reject Ho: There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the means for the three treatments are not equal.
Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means for the three treatments are not equal.
Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the means for the three treatments are not equal.

Transcribed Image Text:Treatment
A
162
141
125
143
157
123
165
125
139
145
143
141
149
137
150
178
155
132
Sample
157
143
135
mean
Sample
variance
186.8
140.8
106.0
(a) Compute the sum of squares between treatments.
(b) Compute the mean square between treatments.
(c) Compute the sum of squares due to error.
(d) Compute the mean square due to error. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(e) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four
decimal places.)
Mean
Source
of Variation
Degrees
of Freedom
Sum
F
p-value
of Squares
Square
Treatments
Error
Total
(f) At the a = 0.05 level of significance, test whether the means for the three treatments are equal.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
O Ho: HA = HB = HC
H: Not all the population means are equal.
O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal.
H: At least two of the population means are different.
O Ho: HA = HB = HC
H: HA# HB # Hc
O Ho: Not all the population means are equal.
H: HA = HB = HC
%3D
O Ho: HA + HB * HC
H3: HA = HB = Hc
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the pn-value (Round vour answer to four decimal places
Expert Solution
Step 1
For the given table using Anova single factor
Complete Anova table and Hypotheses test at alpha =0.05 L.O.S
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning