Two blocks initially at rest, each having a mass of 20 kg, are connected by a string as shown in the figure. The coefficient of sliding friction between the block and the inclined plane is 0.28. The plane is inclined at 350 with the horizontal. The blocks are accelerating at a magnitude of 0.8 m/s2. Assuming the pulleys to be light and frictionless. If the work due to force of friction at B is -105.84 J, find: a. The displacement moved by the block. ( Ans. -3.0 m) b. The work done by the Normal force at B. (Ans. 0 J). c. The work done by the Gravitation force at B. (Ans. 0 J)
Two blocks initially at rest, each having a mass of 20 kg, are connected by a string as shown in the figure. The coefficient of sliding friction between the block and the inclined plane is 0.28. The plane is inclined at 350 with the horizontal. The blocks are accelerating at a magnitude of 0.8 m/s2. Assuming the pulleys to be light and frictionless. If the work due to force of friction at B is -105.84 J, find: a. The displacement moved by the block. ( Ans. -3.0 m) b. The work done by the Normal force at B. (Ans. 0 J). c. The work done by the Gravitation force at B. (Ans. 0 J)
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter7: Dry Friction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.78P: The figure shows a steel bar being processed by a rolling mill. Given that P=80kN and r =0.016,...
Related questions
Question
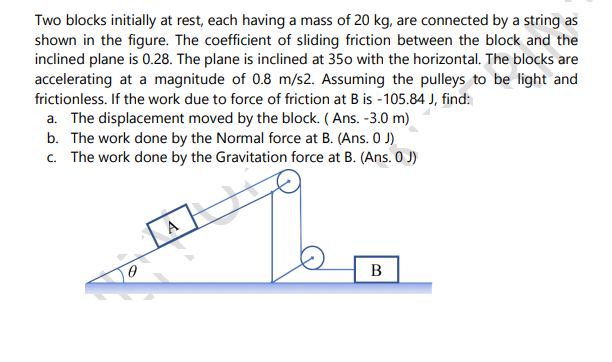
Transcribed Image Text:Two blocks initially at rest, each having a mass of 20 kg, are connected by a string as
shown in the figure. The coefficient of sliding friction between the block and the
inclined plane is 0.28. The plane is inclined at 350 with the horizontal. The blocks are
accelerating at a magnitude of 0.8 m/s2. Assuming the pulleys to be light and
frictionless. If the work due to force of friction at B is -105.84 J, find:
a. The displacement moved by the block. ( Ans. -3.0 m)
b. The work done by the Normal force at B. (Ans. 0 J).
c. The work done by the Gravitation force at B. (Ans. 0 J)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L