Two different formulas of an oxygenated motor fuel are being tested to study their road octane numbers. The variance of road octar number for formula 1 is o? the mean octane numbers observed are Ij = 89.5 fluid ounces and = 93.1 fluid ounces. Assume normality. = 1.5, and for formula 2 it is o = 1.2. Two random samples of size n¡ = 15and n2 = 20 are tested, a (a) Test the hypotheses Ho : H1 = µ2 versus H1 : Hi < Hz using a = 0.05. Round your answer to three decimal places (e.g. 98.765 Zo = i v Ho- (b) Calculate a 95% two-sided confidence interval on the mean difference road octane number, I¡ – x2. Round your answer to thre decimal places (e.g. 98.765).
Two different formulas of an oxygenated motor fuel are being tested to study their road octane numbers. The variance of road octar number for formula 1 is o? the mean octane numbers observed are Ij = 89.5 fluid ounces and = 93.1 fluid ounces. Assume normality. = 1.5, and for formula 2 it is o = 1.2. Two random samples of size n¡ = 15and n2 = 20 are tested, a (a) Test the hypotheses Ho : H1 = µ2 versus H1 : Hi < Hz using a = 0.05. Round your answer to three decimal places (e.g. 98.765 Zo = i v Ho- (b) Calculate a 95% two-sided confidence interval on the mean difference road octane number, I¡ – x2. Round your answer to thre decimal places (e.g. 98.765).
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
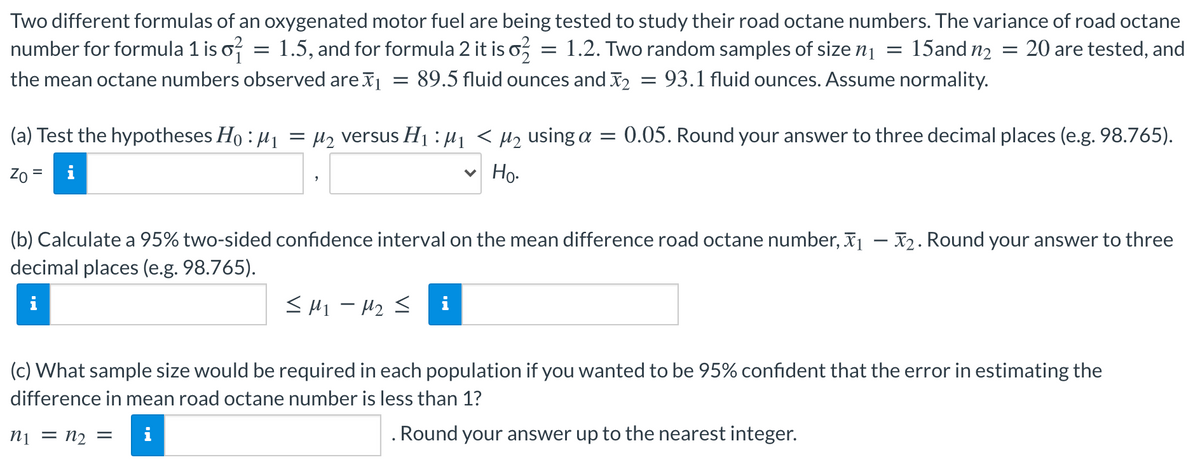
Transcribed Image Text:Two different formulas of an oxygenated motor fuel are being tested to study their road octane numbers. The variance of road octane
number for formula 1 is o? = 1.5, and for formula 2 it is o,
the mean octane numbers observed are = 89.5 fluid ounces and I2 = 93.1 fluid ounces. Assume normality.
= 1.2. Two random samples of size n1 =
15and n2 = 20 are tested, and
(a) Test the hypotheses Ho : H1
H2 versus H1 : µ1 < µ2 using a = 0.05. Round your answer to three decimal places (e.g. 98.765).
%|
Zo
v Ho.
(b) Calculate a 95% two-sided confidence interval on the mean difference road octane number, x1 – X2. Round your answer to three
decimal places (e.g. 98.765).
<H1 - H2 <
(c) What sample size would be required in each population if you wanted to be 95% confident that the error in estimating the
difference in mean road octane number is less than 1?
ni = n2 =
i
. Round your answer up to the nearest integer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman