Unlike most packaged food products, alcohol beverage container labels are not required to show calorie or nutrient content. An article reported on a pilot study in which each of 56 individuals in a sample was asked to estimate the calorie content of a 12 oz can of beer known to contain 153 calories. The resulting sample mean estimated calorie level was 192 and the sample standard deviation was 87. Does this data suggest that the true average estimated calorie content in the population sampled exceeds the actual content? Test the appropriate hypotheses at significance level 0.001. State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses. ⒸH₂-153 M₂ 153 ⒸM₂-153 M₂ 153 ⒸM₂-153 M₁153 Mo: H-153 MM> 153 Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) P-value= State the conclusion in the problem context. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content.
Unlike most packaged food products, alcohol beverage container labels are not required to show calorie or nutrient content. An article reported on a pilot study in which each of 56 individuals in a sample was asked to estimate the calorie content of a 12 oz can of beer known to contain 153 calories. The resulting sample mean estimated calorie level was 192 and the sample standard deviation was 87. Does this data suggest that the true average estimated calorie content in the population sampled exceeds the actual content? Test the appropriate hypotheses at significance level 0.001. State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses. ⒸH₂-153 M₂ 153 ⒸM₂-153 M₂ 153 ⒸM₂-153 M₁153 Mo: H-153 MM> 153 Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) P-value= State the conclusion in the problem context. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.3: Measures Of Spread
Problem 1GP
Related questions
Question
Q4
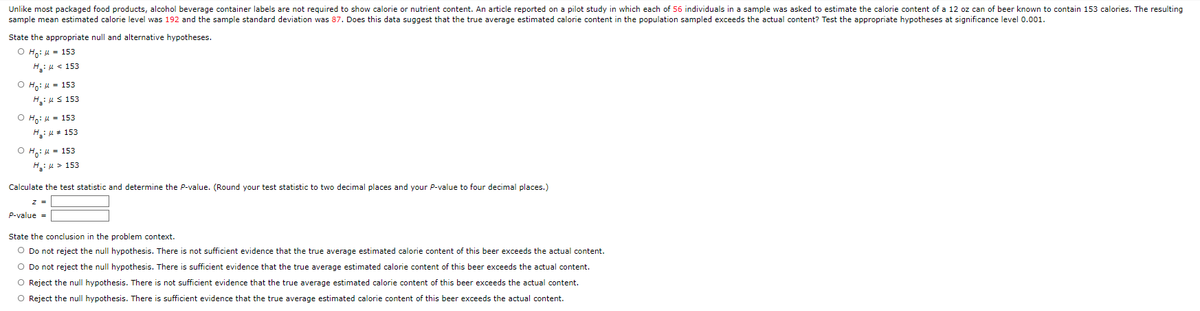
Transcribed Image Text:Unlike most packaged food products, alcohol beverage container labels are not required to show calorie or nutrient content. An article reported on a pilot study in which each of 56 individuals in a sample was asked to estimate the calorie content of a 12 oz can of beer known to contain 153 calories. The resulting
sample mean estimated calorie level was 192 and the sample standard deviation was 87. Does this data suggest that the true average estimated calorie content in the population sampled exceeds the actual content? Test the appropriate hypotheses at significance level 0.001.
State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses.
O Ho: 153
H₂: μ< 153
O Ho: μ = 153
H₂: ≤ 153
O Ho: μ = 153
H₂: μ = 153
OH: μ = 153
H₂:μ> 153
Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.)
P-value =
State the conclusion in the problem context.
O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content.
O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content.
O Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content.
O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence that the true average estimated calorie content of this beer exceeds the actual content.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill