Use the data in Table 7-2 to predict the energy difference between pent-1-ene and cis-pent-2-ene. Express your answer to two siginificant figures. VO Az ? 6.6 kJ/mol Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
Use the data in Table 7-2 to predict the energy difference between pent-1-ene and cis-pent-2-ene. Express your answer to two siginificant figures. VO Az ? 6.6 kJ/mol Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter18: Aromaticity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3CTQ
Related questions
Question
Predict the energy difference between pent-1-ene and cis-pent-2-ene.
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Use the data in Table 7-2 to predict the energy difference between pent-1-ene and cis-pent-2-ene.
Express your answer to two siginificant figures.
?
6.6
kJ/mol
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining
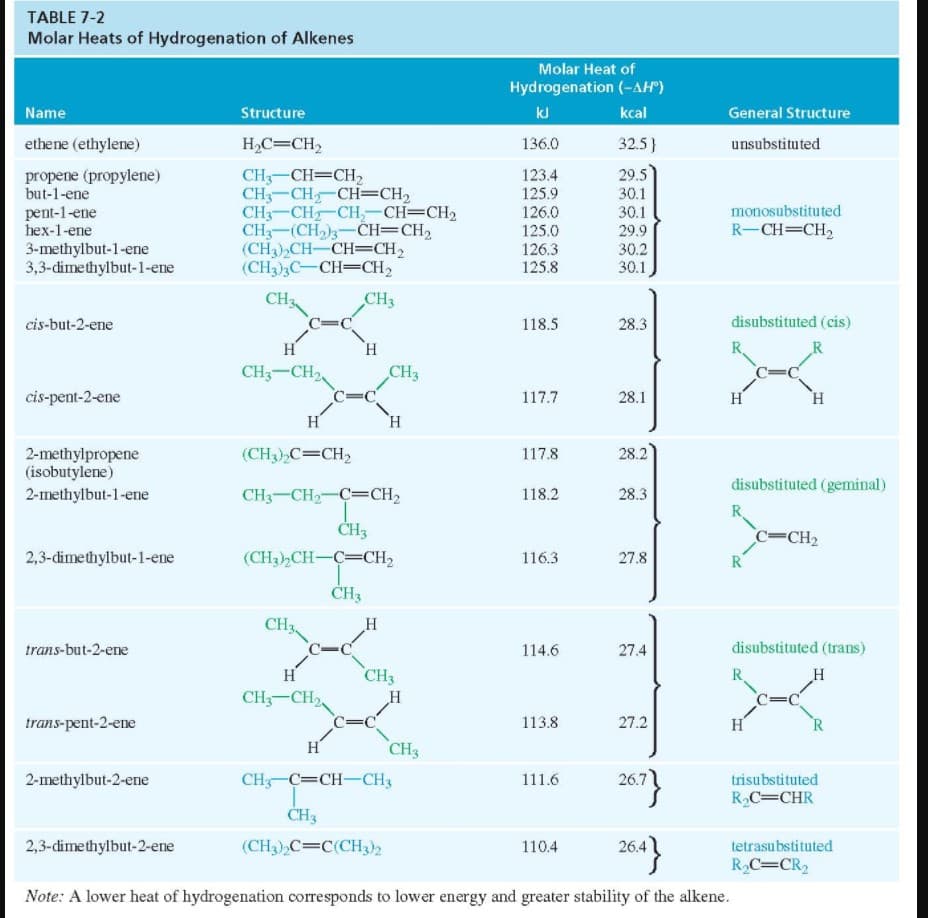
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 7-2
Molar Heats of Hydrogenation of Alkenes
Molar Heat of
Hydrogenation (-AH")
Name
Structure
kJ
kcal
General Structure
ethene (ethylene)
H,C=CH2
136.0
32.5}
unsubstituted
CH3-CH=CH,
CH3-CH CH=CH2
CH3-CH CH,-CH=CH2
CH3-(CH)3-CH=CH2
(CH3),CH-CH=CH2
(CH3),C-CH=CH2
propene (propylene)
123.4
29.5
but-1-ene
125.9
126.0
30.1
monosubstituted
pent-1-ene
hex-1-ene
30.1
125.0
R-CH=CH2
3-methylbut-1-ene
3,3-dimethylbut-1-ene
126.3
125.8
29.9
30.2
30.1
CH3
CH3
cis-but-2-ene
118.5
28.3
disubstituted (cis)
H
H.
R.
R
CH3-CH2
CH3
cis-pent-2-ene
117.7
28.1
H
H.
H
H.
2-methylpropene
(isobutylene)
2-methylbut-1-ene
(CH3),C=CH2
117.8
28.2
disubstituted (geminal)
CH3-CH2-C=CH2
118.2
28.3
R
c=CH2
R
ČH3
2,3-dimethylbut-1-ene
(CH3),CH-C=CH,
116.3
27.8
ČH3
CH3
H.
trans-but-2-ene
114.6
27.4
disubstituted (trans)
H
CH3
R
C=C
H
CH-CH2
H
trans-pent-2-ene
113.8
27.2
H
R
H
CH3
2-methylbut-2-ene
CH C=CH-CH3
111.6
trisubstituted
RC=CHR
ČH3
2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene
(CH3),C=C(CH3)2
110.4
26.4
tetrasubstituted
R,C=CR2
Note: A lower heat of hydrogenation corresponds to lower energy and greater stability of the alkene.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
