Use the information in the following table on labor productivities in Spain and Italy to answer questions a through f. Output per hour worked Wine Suits Spain 4 liters 1 Italy 8 liters 8 a. The absolute advantage in wine is held by Italy and the absolute advantage in suits is held by Italy. b. The relative price of wine in Spain is 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places) and the relative price of wine in Italy is 1 suit c. The opportunity cost of wine in Spain is 0.25 suits(round to two decimal places) and the opportunity cost of wine in Italy is 1 suit. d. The comparative advantage in wine is held by Spain and the comparative advantage in suits is held by Italy. e. The trade price of wine has an upper bound of 1 suit and a lower bound of 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places). f. Assume Spain has 10 hours it can allocate toward the production of wine and suits. Carefully follow the steps below to draw the required objects on the figure to the right. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw Spain's PPC given the data above. Properly label your line. 2.) Using the point drawing tool, assume Spain produces according to its comparative advantage and identify its production point. Label this point A 3.) Using the line drawing tool, given the the trade price of suits is two liters of wine per suit, draw the trade line showing how Spain can gain from trade. Properly label your line. Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects. 慧 12 11- 10 9 8- 7- S 4- 3- 2- 1- 10 Spain 20 Wine 30 TAM
Use the information in the following table on labor productivities in Spain and Italy to answer questions a through f. Output per hour worked Wine Suits Spain 4 liters 1 Italy 8 liters 8 a. The absolute advantage in wine is held by Italy and the absolute advantage in suits is held by Italy. b. The relative price of wine in Spain is 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places) and the relative price of wine in Italy is 1 suit c. The opportunity cost of wine in Spain is 0.25 suits(round to two decimal places) and the opportunity cost of wine in Italy is 1 suit. d. The comparative advantage in wine is held by Spain and the comparative advantage in suits is held by Italy. e. The trade price of wine has an upper bound of 1 suit and a lower bound of 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places). f. Assume Spain has 10 hours it can allocate toward the production of wine and suits. Carefully follow the steps below to draw the required objects on the figure to the right. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw Spain's PPC given the data above. Properly label your line. 2.) Using the point drawing tool, assume Spain produces according to its comparative advantage and identify its production point. Label this point A 3.) Using the line drawing tool, given the the trade price of suits is two liters of wine per suit, draw the trade line showing how Spain can gain from trade. Properly label your line. Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects. 慧 12 11- 10 9 8- 7- S 4- 3- 2- 1- 10 Spain 20 Wine 30 TAM
Chapter18: International Trade And Comparative Advantage
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2TY
Related questions
Question
100%
need help with part f
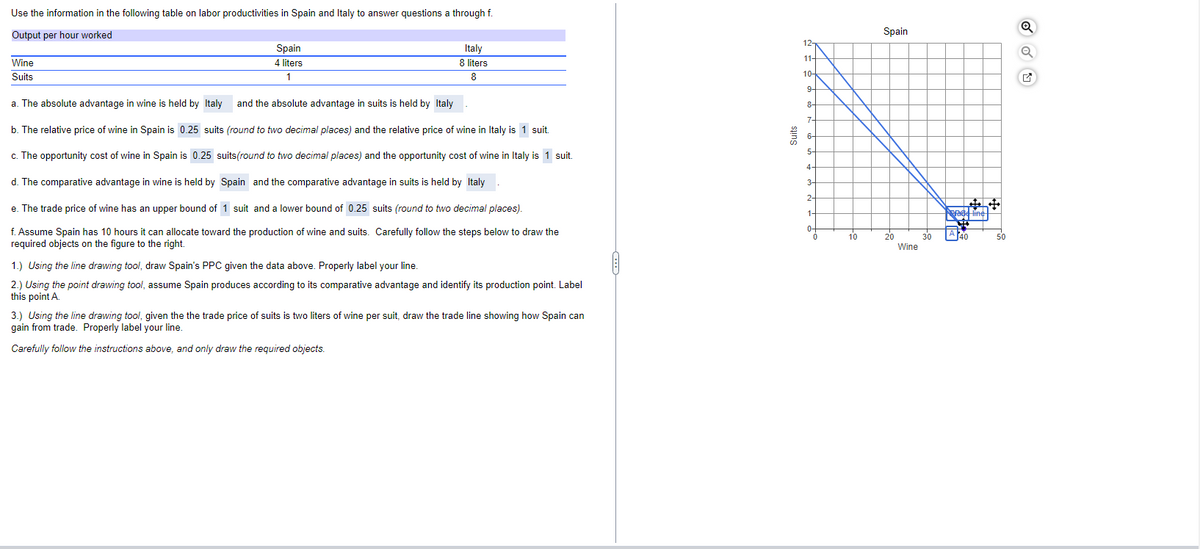
Transcribed Image Text:Use the information in the following table on labor productivities in Spain and Italy to answer questions a through f.
Output per hour worked
Wine
Suits
Spain
4 liters
1
Italy
8 liters
8
a. The absolute advantage in wine is held by Italy and the absolute advantage in suits is held by Italy
b. The relative price of wine in Spain is 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places) and the relative price of wine in Italy is 1 suit.
c. The opportunity cost of wine in Spain is 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places) and the opportunity cost of wine in Italy is 1 suit.
d. The comparative advantage in wine is held by Spain and the comparative advantage in suits is held by Italy
e. The trade price of wine has an upper bound of 1 suit and a lower bound of 0.25 suits (round to two decimal places).
f. Assume Spain has 10 hours it can allocate toward the production of wine and suits. Carefully follow the steps below to draw the
required objects on the figure to the right.
1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw Spain's PPC given the data above. Properly label your line.
2.) Using the point drawing tool, assume Spain produces according to its comparative advantage and identify its production point. Label
this point A.
3.) Using the line drawing tool, given the the trade price of suits is two liters of wine per suit, draw the trade line showing how Spain can
gain from trade. Properly label your line.
Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects.
Suits
12-
11+
10-
9-
8-
7-
6-
5-
4-
3-
2-
1-
0
0
10
Spain
20
Wine
ts
30
A 40
50
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning