Use the tabulated electrode potentials to calculate K for the oxidation of zinc by H+ (at 25 ∘C): Zn(s)+2H+(aq)→Zn2+(aq)+H2(g) Express your answer using two significant figures.
Use the tabulated electrode potentials to calculate K for the oxidation of zinc by H+ (at 25 ∘C): Zn(s)+2H+(aq)→Zn2+(aq)+H2(g) Express your answer using two significant figures.
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter18: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18.101QE: At 298 K, the solubility product constant for PbC2O4 is 8.5 1010, and the standard reduction...
Related questions
Question
Use the tabulated electrode potentials to calculate K for the oxidation of zinc by H+ (at 25 ∘C):
Zn(s)+2H+(aq)→Zn2+(aq)+H2(g)
Express your answer using two significant figures.
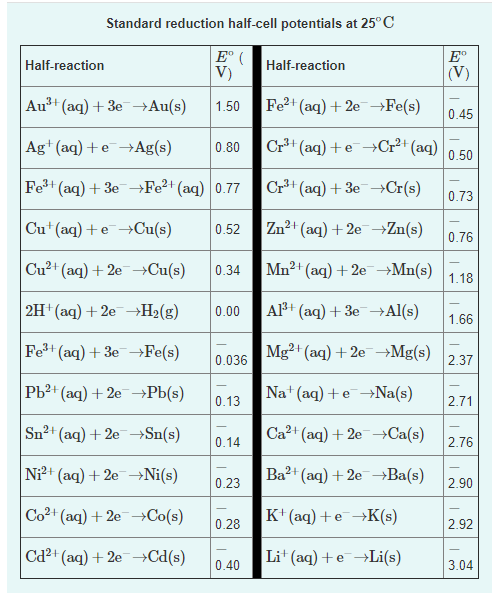
Transcribed Image Text:Standard reduction half-cell potentials at 25° C
E° (
V)
E°
Half-reaction
Half-reaction
|(V)
Au+ (aq) + 3e→Au(s)
1.50
Fe2+ (aq) + 2e-→Fe(s)
0.45
Ag+ (aq) + e→Ag(s)
0.80
Cr (aq) + e —уCr? (aq)
0.50
Fe+ (aq) + 3e →Fe2+ (aq) 0.77
Cr+ (aq) + 3e→Cr(s)
0.73
Cu" (аq) + е —Cu(s)
0.52
Zn2+ (aq) +2e-→Zn(s)
0.76
Cu?+ (aq) + 2e-→Cu(s)
Mn2+ (aq) + 2e →Mn(s)
0.34
1.18
2H*(aq) + 20→H2(g)
0.00
Al+ (aq) + 3e -→Al(s)
1.66
Fe+ (aq) + 3e-→Fe(s)
Mg2+ (aq) + 2e–→Mg(s)
2.37
0.036
Pb2+ (aq) + 2e →Pb(s)
Na+ (aq) + e¯→Na(s)
0.13
2.71
Sn2+ (aq) + 2e→Sn(s)
Ca2+ (aq) + 2e→Ca(s)
0.14
2.76
Ni?+ (aq) + 2e–→Ni(s)
Ва2 (аq) + 2е Ba(s)
0.23
2.90
Co2+ (aq) + 2e¯→Co(s)
K* (aq) + e→K(s)
0.28
2.92
Cd2+ (aq) + 2e→Cd(s)
Lit (aq) + E→L¡(s)
0.40
3.04
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,