Using left and right Riemann sums based on the diagrams above, we definitively conclude that + 2x dx < 4 x² + 2x dx < 4 -x2 + 2x dx < 4 Hint: For the last integral, you should consistently choose either to underestimate or overestimate the area. This may require that you use the left Riemann sum for some x-intervals and the right Riemann sum for other x-intervals.
Using left and right Riemann sums based on the diagrams above, we definitively conclude that + 2x dx < 4 x² + 2x dx < 4 -x2 + 2x dx < 4 Hint: For the last integral, you should consistently choose either to underestimate or overestimate the area. This may require that you use the left Riemann sum for some x-intervals and the right Riemann sum for other x-intervals.
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
100%
The rectangles in the graph below illustrate a left and right endpoint Riemann sum
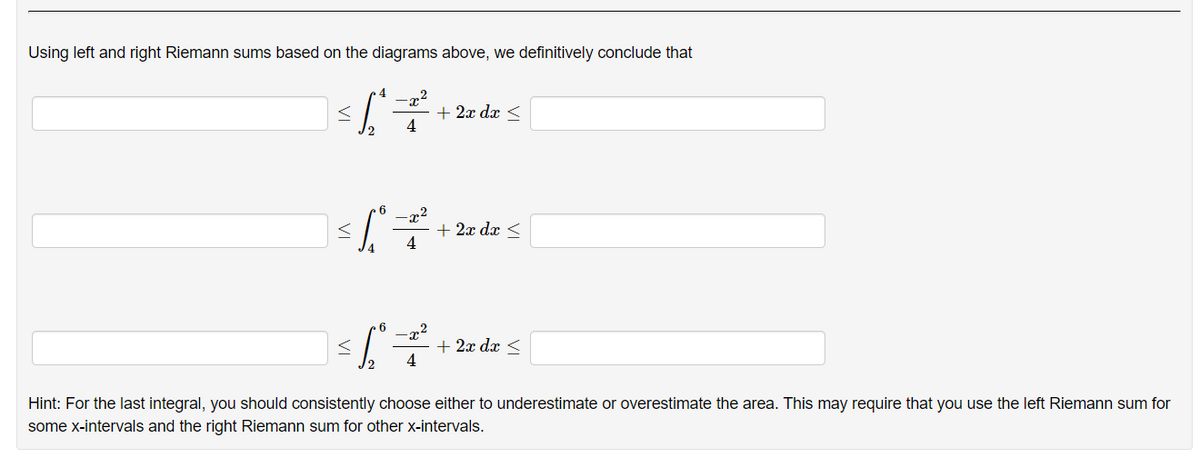
Transcribed Image Text:Using left and right Riemann sums based on the diagrams above, we definitively conclude that
4
-x²
+ 2x dx <
4
6
x²
+ 2x dx <
4
6
+ 2x dx <
4
Hint: For the last integral, you should consistently choose either to underestimate or overestimate the area. This may require that you use the left Riemann sum for
some x-intervals and the right Riemann sum for other x-intervals.
![-x²
+ 2x on the interval 2, 6|.
4
The rectangles in the graph below illustrate a left endpoint Riemann sum for f(x)
The value of this left endpoint Riemann sum is
and it is an underestimate of v the area of the region enclosed
by y = f(x), the x-axis, and the vertical lines x = 2 and x = 6.
F1
Left endpoint Riemann sum for y
+ 2x on [2, 6]
– x²
+ 2x on the interval (2, 6).
4
The rectangles in the graph below illustrate a right endpoint Riemann sum for f(x)
The value of this right endpoint Riemann sum is
and it is an
an underestimate of v the area of the region
enclosed by y = f(x), the x-axis, and the vertical lines x = 2 and x = 6.
X 9
Right endpoint Riemann sum for y =
4
+ 2x on [2,6]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F6c975518-62c0-4b79-b85d-c0bf2063fb13%2F3c7d1e77-ab8b-4881-bb40-d474b045214f%2F006dsii_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:-x²
+ 2x on the interval 2, 6|.
4
The rectangles in the graph below illustrate a left endpoint Riemann sum for f(x)
The value of this left endpoint Riemann sum is
and it is an underestimate of v the area of the region enclosed
by y = f(x), the x-axis, and the vertical lines x = 2 and x = 6.
F1
Left endpoint Riemann sum for y
+ 2x on [2, 6]
– x²
+ 2x on the interval (2, 6).
4
The rectangles in the graph below illustrate a right endpoint Riemann sum for f(x)
The value of this right endpoint Riemann sum is
and it is an
an underestimate of v the area of the region
enclosed by y = f(x), the x-axis, and the vertical lines x = 2 and x = 6.
X 9
Right endpoint Riemann sum for y =
4
+ 2x on [2,6]
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Using left and right Riemann sums based on the diagrams above, we definitively conclude that
6
[..
-x²
+ 2x dx <
8
O≤ f * = 22²2 +
6
6
+ 2x dx
8
-X
0≤ √² = 2² ²³ +
6
4
+ 2x dx <
Hint: For the last integral, you should consistently choose either to underestimate or overestimate the area. This may require that you use the left
Riemann sum for some x-intervals and the right Riemann sum for other x-intervals.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

