ute solution of hydrochloric acid with a mass of 606.87 g and containing 0.31625 mol of HCl was exactly neutralized in a imeter by the sodium hydroxide in 615.48 g of a comparably dilute solution. The temperature increased 16.101 to 19.526°C. The specific heat of the HCl solution was 4.031 J-g*4°C*4; that of the NaOH solution was 4.046 J-g1°C!. neat capacity of the calorimeter was 77.99 J°C!. Incorrect. er the balanced equation for the reaction. Include states in your answer. NaOH(s) + HCl(g) »NAC1(s) + H,O(1) Textbook and Media X Incorrect. e the data above to calculate the heat evolved. What is the heat of neutralization per mole of HCI? Assume that the original utions made independent contributions to the total heat capacity of the system following their mixing. -53.463 kJ/mol Hint Assistance Used The total heat capacity of the system is the sum of the three heat capacities: heat capacityHci + heat capacityNaOH + heat capacitycalorimeter-
ute solution of hydrochloric acid with a mass of 606.87 g and containing 0.31625 mol of HCl was exactly neutralized in a imeter by the sodium hydroxide in 615.48 g of a comparably dilute solution. The temperature increased 16.101 to 19.526°C. The specific heat of the HCl solution was 4.031 J-g*4°C*4; that of the NaOH solution was 4.046 J-g1°C!. neat capacity of the calorimeter was 77.99 J°C!. Incorrect. er the balanced equation for the reaction. Include states in your answer. NaOH(s) + HCl(g) »NAC1(s) + H,O(1) Textbook and Media X Incorrect. e the data above to calculate the heat evolved. What is the heat of neutralization per mole of HCI? Assume that the original utions made independent contributions to the total heat capacity of the system following their mixing. -53.463 kJ/mol Hint Assistance Used The total heat capacity of the system is the sum of the three heat capacities: heat capacityHci + heat capacityNaOH + heat capacitycalorimeter-
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter6: Thermochemisty
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.109QP: A 21.3-mL sample of 0.977 M NaOH is mixed with 29.5 mL of 0.918 M HCl in a coffee-cup calorimeter...
Related questions
Question
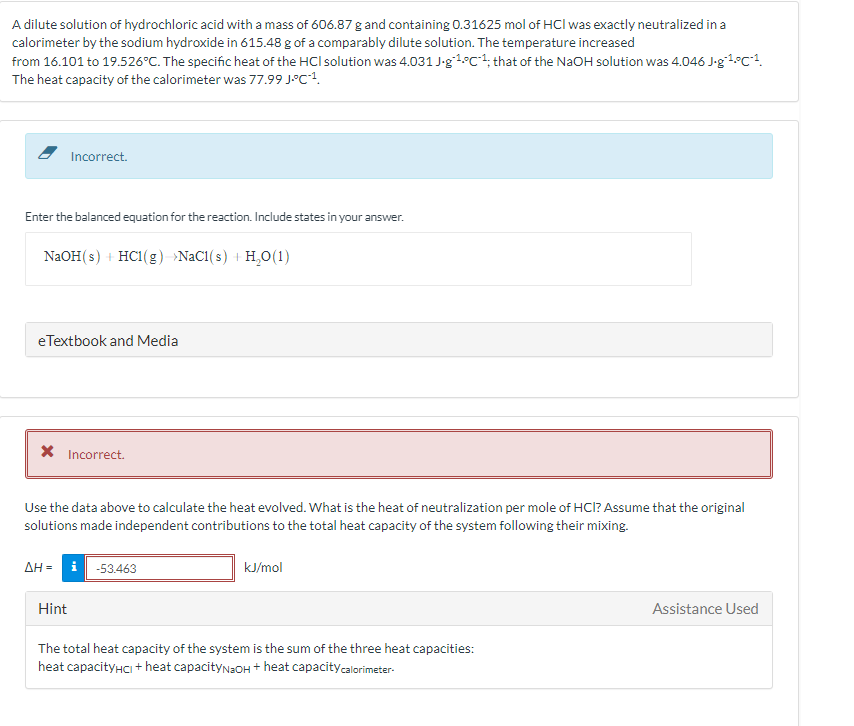
Transcribed Image Text:A dilute solution of hydrochloric acid with a mass of 606.87 g and containing 0.31625 mol of HCl was exactly neutralized in a
calorimeter by the sodium hydroxide in 615.48 g of a comparably dilute solution. The temperature increased
from 16.101 to 19.526°C. The specific heat of the HCl solution was 4.031 J-g1°c+, that of the NaOH solution was 4.046 J-g°4°C*!.
The heat capacity of the calorimeter was 77.99 J°C1.
Incorrect.
Enter the balanced equation for the reaction. Include states in your answer.
NaOH(s) + HC1(g) »NaC1(s) + H,O(1)
eTextbook and Media
X Incorrect.
Use the data above to calculate the heat evolved. What is the heat of neutralization per mole of HCl? Assume that the original
solutions made independent contributions to the total heat capacity of the system following their mixing.
AH = i -53.463
kJ/mol
Hint
Assistance Used
The total heat capacity of the system is the sum of the three heat capacities:
heat capacityHCI + heat capacityNaOH + heat capacitycalorimeter-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning