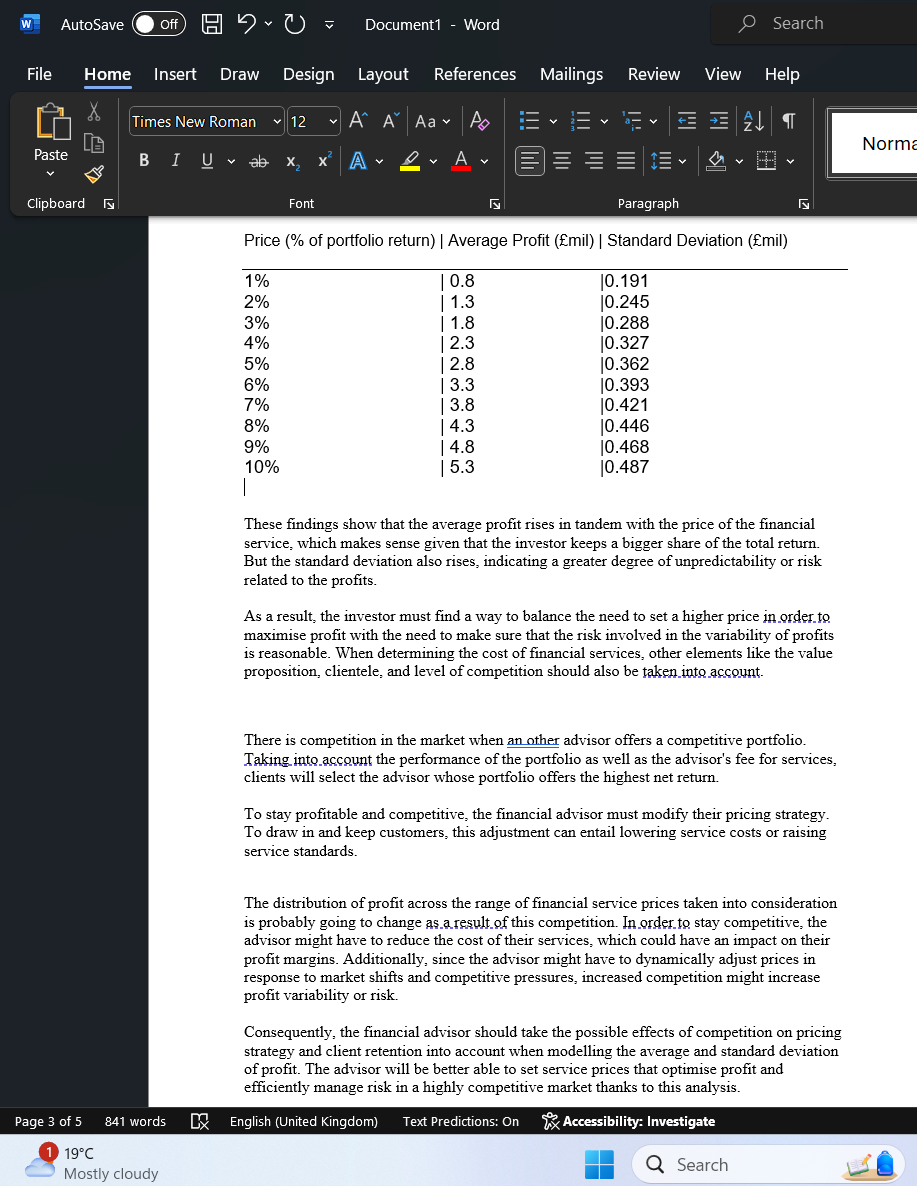
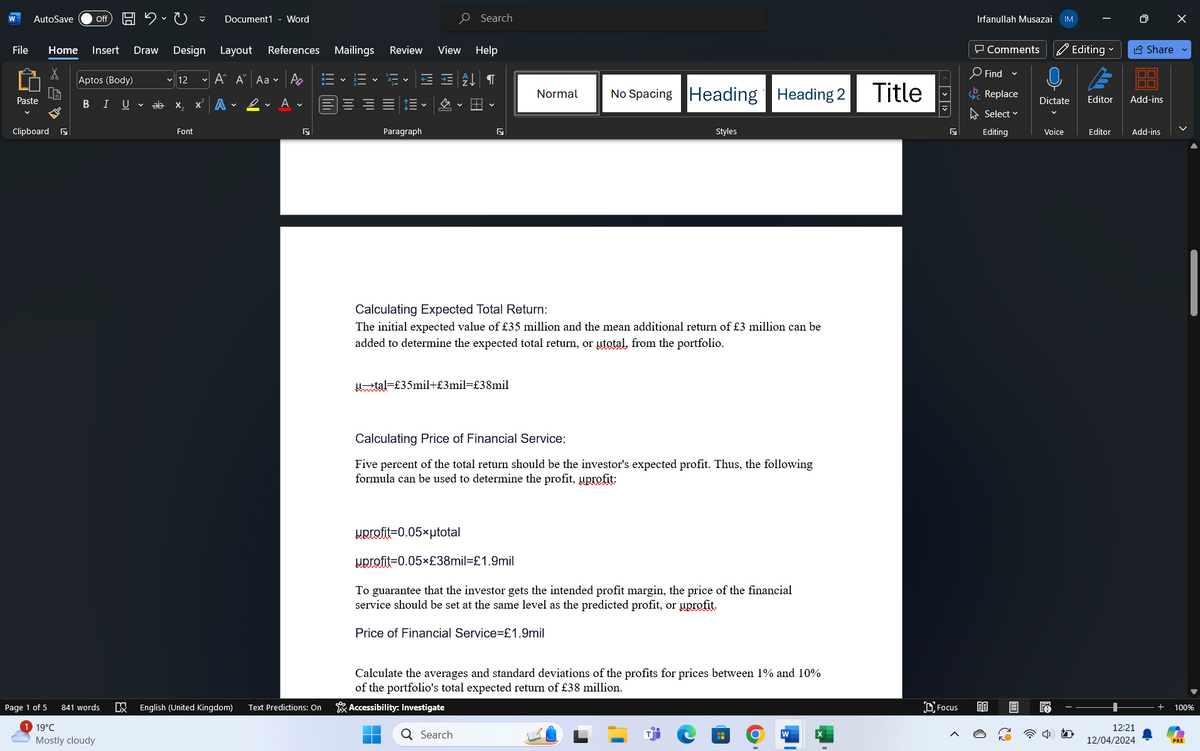
W AutoSave Off C Document1 - Word Search File Home Insert Draw X Lih Paste BIU ab Ро A く A▾ Design Layout References Mailings Review View Help Times New Roman 12 A A Aa Norma 田 Clipboard Page 3 of 5 841 words 1 19°C Mostly cloudy Font Paragraph Price (% of portfolio return) | Average Profit (£mil) | Standard Deviation (£mil) 1% | 0.8 |0.191 2% | 1.3 10.245 3% | 1.8 10.288 4% | 2.3 10.327 5% | 2.8 10.362 6% | 3.3 10.393 7% | 3.8 10.421 8% | 4.3 10.446 9% | 4.8 10.468 10% | 5.3 10.487 | These findings show that the average profit rises in tandem with the price of the financial service, which makes sense given that the investor keeps a bigger share of the total return. But the standard deviation also rises, indicating a greater degree of unpredictability or risk related to the profits. As a result, the investor must find a way to balance the need to set a higher price in order to maximise profit with the need to make sure that the risk involved in the variability of profits is reasonable. When determining the cost of financial services, other elements like the value proposition, clientele, and level of competition should also be taken into account. There is competition in the market when an other advisor offers a competitive portfolio. Taking into account the performance of the portfolio as well as the advisor's fee for services, clients will select the advisor whose portfolio offers the highest net return. To stay profitable and competitive, the financial advisor must modify their pricing strategy. To draw in and keep customers, this adjustment can entail lowering service costs or raising service standards. The distribution of profit across the range of financial service prices taken into consideration is probably going to change as a result of this competition. In order to stay competitive, the advisor might have to reduce the cost of their services, which could have an impact on their profit margins. Additionally, since the advisor might have to dynamically adjust prices in response to market shifts and competitive pressures, increased competition might increase profit variability or risk. Consequently, the financial advisor should take the possible effects of competition on pricing strategy and client retention into account when modelling the average and standard deviation of profit. The advisor will be better able to set service prices that optimise profit and efficiently manage risk in a highly competitive market thanks to this analysis. CX English (United Kingdom) Text Predictions: On Accessibility: Investigate Search W AutoSave Off Document1 - Word Search File Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Help Aptos (Body) ▼ 12 A A Aa P ་་ Normal Paste BI U ab x² A v D✓ A ▾ A v Clipboard لا Page 1 of 5 841 words 19°C Mostly cloudy Font Paragraph Гу No Spacing Heading Heading 2 Title Styles Calculating Expected Total Return: The initial expected value of £35 million and the mean additional return of £3 million can be added to determine the expected total return, or utotal, from the portfolio. tal £35mil+£3mil=£38mil Calculating Price of Financial Service: Five percent of the total return should be the investor's expected profit. Thus, the following formula can be used to determine the profit, uprofit: uprofit=0.05*utotal uprofit=0.05*£38mil=£1.9mil To guarantee that the investor gets the intended profit margin, the price of the financial service should be set at the same level as the predicted profit, or uprofit. Price of Financial Service=£1.9mil English (United Kingdom) Text Predictions: On Calculate the averages and standard deviations of the profits for prices between 1% and 10% of the portfolio's total expected return of £38 million. Accessibility: Investigate Q Search H Ο I* < > >> Irfanullah Musazai IM Comments O Find ▾ Replace Select 1 Editing Share ▾ Dictate Editor Add-ins ✓ Editing Voice Editor Add-ins DFocus BB + 100% 12:21 12/04/2024 PRE
hello so i got a question from my teacher and wanna make sure its correct:
A financial investor builds a portfolio that is worth an expected £35mil. The investor knows that his analysts can build a model to boost the potential return from the portfolio investment. The additional return has a
1)What should the price of his financial service be?
2) Simulate (with a min of 200 repetitions) the average and the standard deviation of the profit the financial advisor realizes when setting the price for his services between 1% and 10% of the total expected return from the portfolio. Then discuss your findings.
3)Now assume the financial advisor knows that another advisor will offer a competitive portfolio. Based on historical data, he knows this competitive portfolio’s total return follows a normal distribution with mean £36mil and standard deviation of £2mil and is priced at 5% of total return. Clients will naturally choose the advisor which offers the portfolio with the highest net How does the distribution of profit over the range of financial prices considered in part B) changes, when the competitor is considered?
My answers are in picture 1 and 2, i am not sure if they are correct:
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps


