Which of the following is never negative? * average product marginal product O production elasticity marginal rate of technical substitution The variation in an economic time- series which is caused by major expansions or contractions usually of greater than a year in duration is known as: secular trend O unpredictable random factor cyclical variation seasonal effect
Which of the following is never negative? * average product marginal product O production elasticity marginal rate of technical substitution The variation in an economic time- series which is caused by major expansions or contractions usually of greater than a year in duration is known as: secular trend O unpredictable random factor cyclical variation seasonal effect
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter4: Estimating Demand
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6E
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Ooredoo li
A docs.google.com
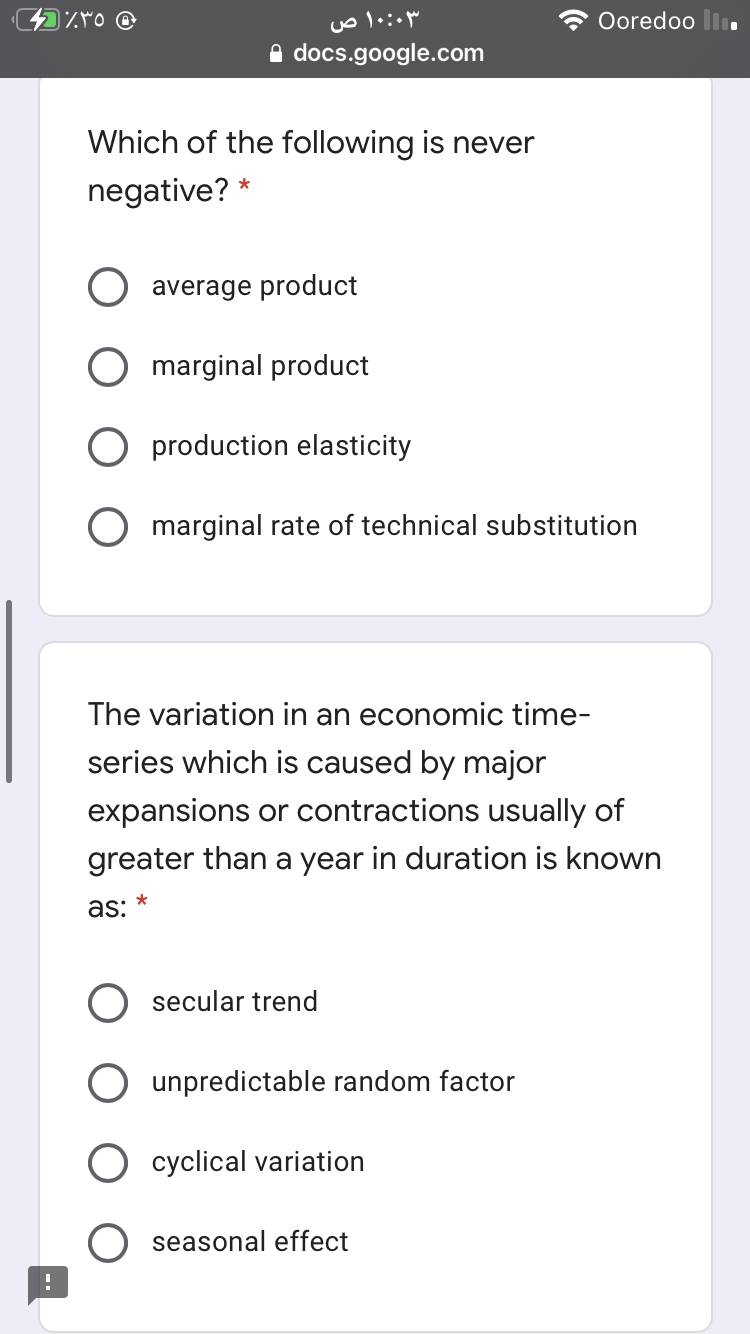
Which of the following is never
negative?
average product
marginal product
production elasticity
O marginal rate of technical substitution
The variation in an economic time-
series which is caused by major
expansions or contractions usually of
greater than a year in duration is known
as:
secular trend
unpredictable random factor
cyclical variation
seasonal effect

Transcribed Image Text:۱۰:۰۳ ص
Ooredoo li
A docs.google.com
Consider the following linear demand
function where QD = quantity
demanded, P = selling price, and Y =
disposable income: QD = -36 - 2.1P +
.24Y. The coefficient of Y (i.e., .24)
indicates that (all other things being
held constant): *
for a one unit increase in disposable
income, quantity demanded would
increase by 2.1 units
for a one percent increase in
disposable income, quantity
demanded would decline by 2.1
percent
for a one percent increase in
disposable income, quantity
demanded would decline by 0.24
percent
for a one percent increase in
disposable income, quantity
demanded would increase by 0.24
percent
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning