Which protein and amino acids can it catabolize, among gelatin, urea, phenylalanine, sulfur-containing amino acias, and tryptophan? Can it desulfur proteins? Can it produce NH3 from the amino acid phenylalanine?
Which protein and amino acids can it catabolize, among gelatin, urea, phenylalanine, sulfur-containing amino acias, and tryptophan? Can it desulfur proteins? Can it produce NH3 from the amino acid phenylalanine?
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Chapter3: Amino Acids And Peptides
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 54RE: THOUGHT QUESTION Imagine we identify a gene that is directly responsible for the effects of...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:9:54 AM Sun Oct 17
* 73%
Done
Prelab 7 - Tagged (2 of 64)
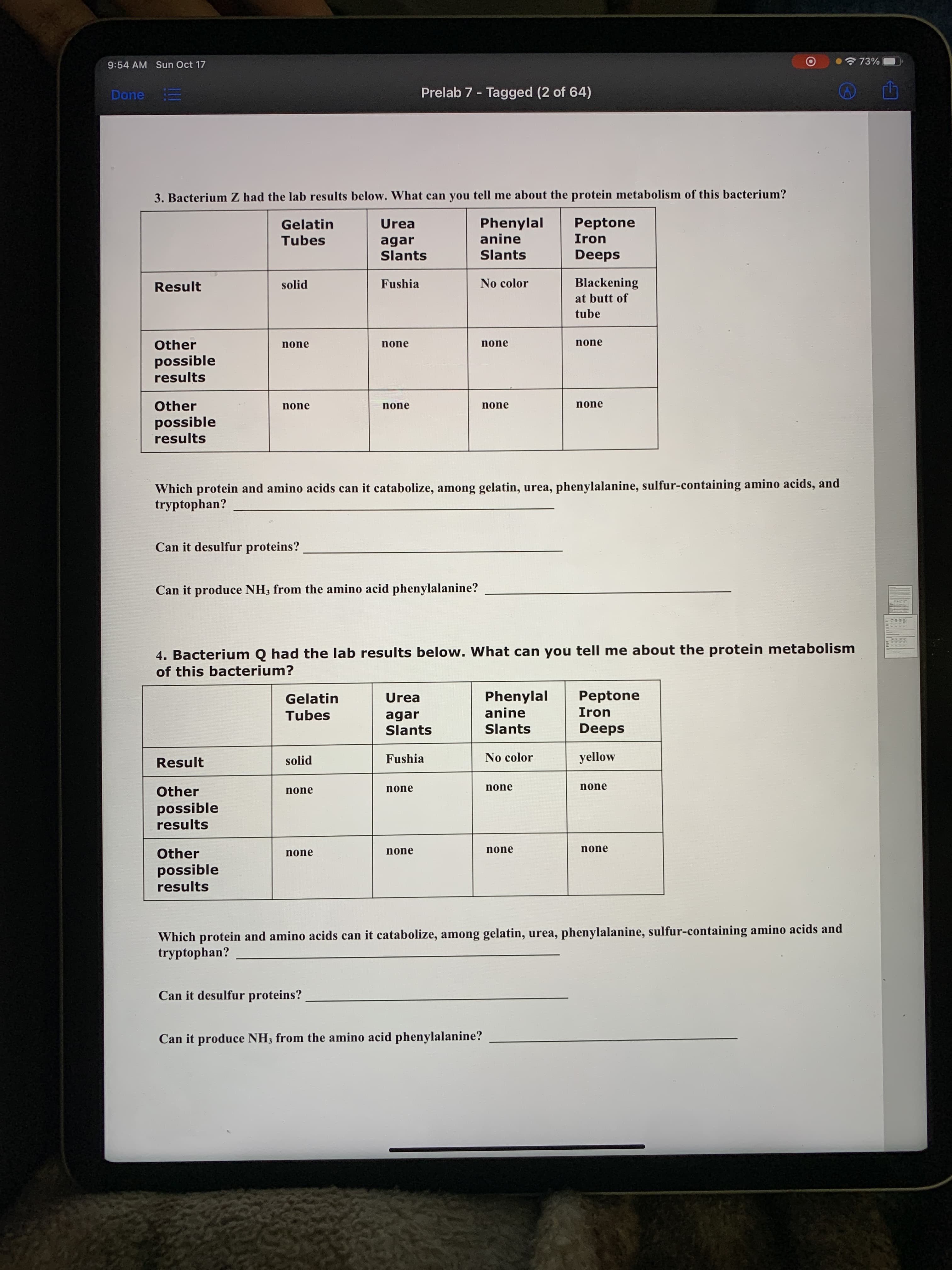
3. Bacterium Z had the lab results below. What can you tell me about the protein metabolism of this bacterium?
Peptone
Phenylal
anine
Gelatin
Urea
Tubes
Iron
agar
Slants
Slants
Deeps
Result
solid
Fushia
No color
Blackening
at butt of
tube
Other
none
none
none
none
possible
results
Other
none
none
none
none
possible
results
Which protein and amino acids can it catabolize, among gelatin, urea, phenylalanine, sulfur-containing amino acids, and
tryptophan?
Can it desulfur proteins?
Can it produce NH3 from the amino acid phenylalanine?
4. Bacterium Q had the lab results below. What can you tell me about the protein metabolism
of this bacterium?
Peptone
Phenylal
anine
Slants
Gelatin
Urea
Tubes
Iron
agar
Slants
Deeps
Result
solid
Fushia
No color
yellow
Other
none
none
none
none
possible
results
Other
none
none
none
none
possible
results
Which protein and amino acids can it catabolize, among gelatin, urea, phenylalanine, sulfur-containing amino acids and
tryptophan?
Can it desulfur proteins?
Can it produce NH3 from the amino acid phenylalanine?
Transcribed Image Text:9:54 AM
Done
Prelab 7 - Tagged (2 of 64)
三:
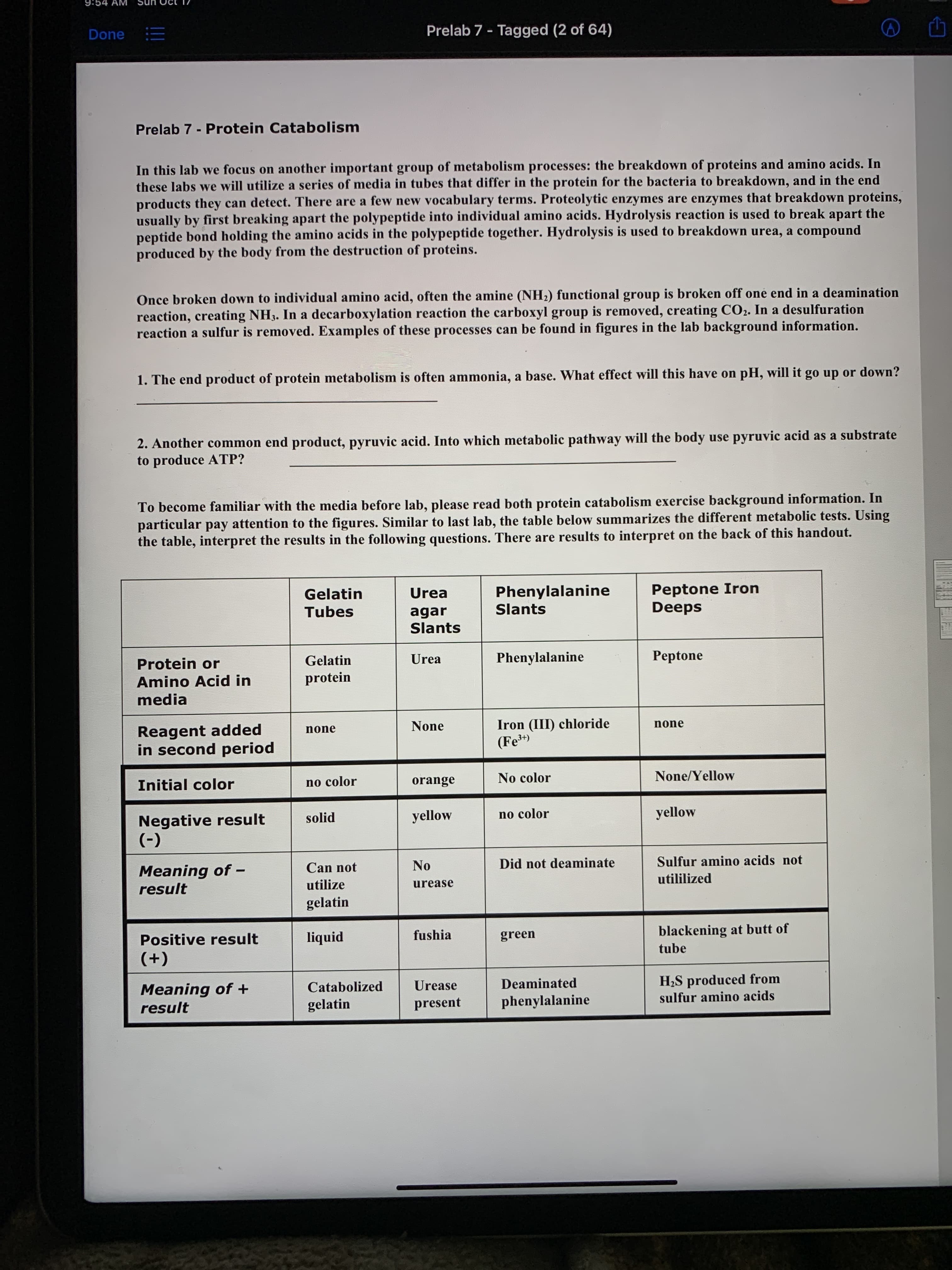
Prelab 7 - Protein Catabolism
In this lab we focus on another important group of metabolism processes: the breakdown of proteins and amino acids. In
these labs we will utilize a series of media in tubes that differ in the protein for the bacteria to breakdown, and in the end
products they can detect. There are a few new vocabulary terms. Proteolytic enzymes are enzymes that breakdown proteins,
usually by first breaking apart the polypeptide into individual amino acids. Hydrolysis reaction is used to break apart the
peptide bond holding the amino acids in the polypeptide together. Hydrolysis is used to breakdown urea, a compound
produced by the body from the destruction of proteins.
Once broken down to individual amino acid, often the amine (NH2) functional group is broken off one end in a deamination
reaction, creating NH3. In a decarboxylation reaction the carboxyl group is removed, creating CO2. In a desulfuration
reaction a sulfur is removed. Examples of these processes can be found in figures in the lab background information.
1. The end product of protein metabolism is often ammonia, a base. What effect will this have on pH, will it go up or down?
2. Another common end product, pyruvic acid. Into which metabolic pathway will the body use pyruvic acid as a substrate
to produce ATP?
To become familiar with the media before lab, please read both protein catabolism exercise background information. In
particular pay attention to the figures. Similar to last lab, the table below summarizes the different metabolic tests. Using
the table, interpret the results in the following questions. There are results to interpret on the back of this handout.
Phenylalanine
Gelatin
Tubes
Peptone Iron
Deeps
Urea
Slants
agar
Slants
Protein or
Amino Acid in
Gelatin
Urea
Phenylalanine
Peptone
protein
media
Reagent added
in second period
None
Iron (III) chloride
(Fe)
none
none
Initial color
no color
orange
No color
None/Yellow
Negative result
solid
yellow
no color
yellow
(-)
Meaning of -
Sulfur amino acids not
utililized
Can not
No
Did not deaminate
result
utilize
urease
gelatin
Positive result
liquid
fushia
green
blackening at butt of
tube
(+)
Meaning of +
result
H2S produced from
sulfur amino acids
Catabolized
Urease
Deaminated
gelatin
present
phenylalanine
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College