Write an equilibrium constant expression for each of the following reactions. If gases are involved, write the expression in terms of partial pressures. Enclose pressures in parentheses and do NOT write the chemical formula as a subscript. For example, enter (PNH₂)2 as (P NH3)2. If either the numerator or denominator is 1, please ente (a) (b) (c) (d) COCI₂ (9) → CO(g) + Cl₂(9) Kp 2 MnO₂ (s) Kp = PbCl₂(s) → Pb²+ (aq) + 2 Cl(aq) C6H14(1) Kp 2 MnO(s) + O₂(g) = C6H14 (9)
Write an equilibrium constant expression for each of the following reactions. If gases are involved, write the expression in terms of partial pressures. Enclose pressures in parentheses and do NOT write the chemical formula as a subscript. For example, enter (PNH₂)2 as (P NH3)2. If either the numerator or denominator is 1, please ente (a) (b) (c) (d) COCI₂ (9) → CO(g) + Cl₂(9) Kp 2 MnO₂ (s) Kp = PbCl₂(s) → Pb²+ (aq) + 2 Cl(aq) C6H14(1) Kp 2 MnO(s) + O₂(g) = C6H14 (9)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter15: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PS: Write equilibrium constant expressions for the following reactions. For gases, use either pressures...
Related questions
Question
Help

Transcribed Image Text:Write an equilibrium constant expression for each of the following reactions. If gases are involved, write the expression in terms of partial pressures.
Enclose pressures in parentheses and do NOT write the chemical formula as a subscript. For example, enter (PNH3)2 as (P NH3)2. If either the numerator or denominator is 1, please enter 1.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
COCI₂(g) ← CO(g) + Cl₂(9)
Kp
2 MnO₂ (s)
Kp =
2 MnO(s) + O₂(g)
PbCl₂(s) ← Pb²+ (aq) + 2 CI (aq)
C6H14(1) ← C6H14 (9)
Kp =
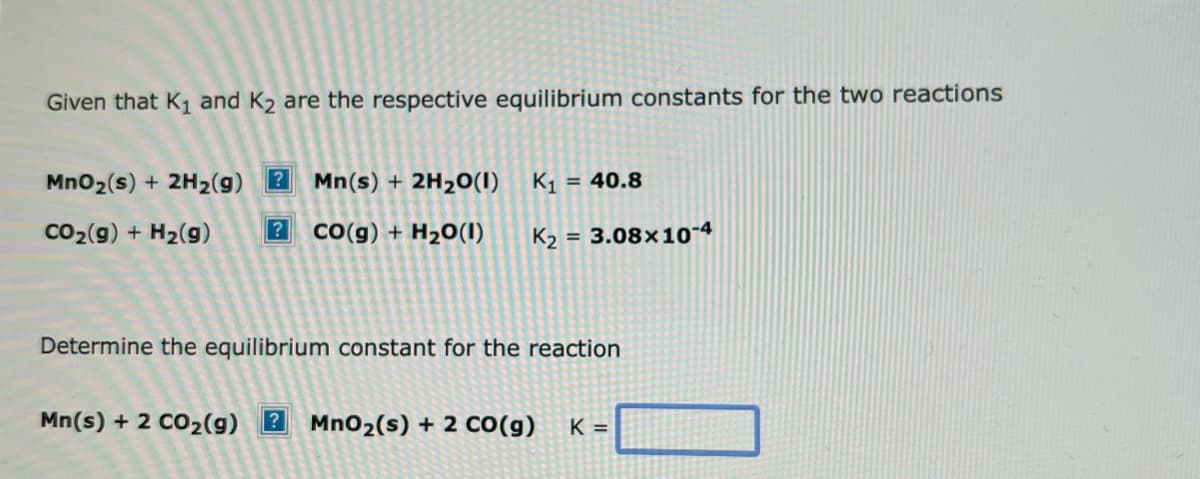
Transcribed Image Text:Given that K₁ and K₂ are the respective equilibrium constants for the two reactions
MnO₂ (s) + 2H₂(g) ? Mn(s) + 2H₂O(1)
CO₂(g) + H₂(9) ? CO(g) + H₂O(1)
K₁= = 40.8
K₂=
= 3.08x10-4
Determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction
Mn(s) + 2 CO₂(g) 2 MnO₂ (s) + 2 CO(g) K =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
