Write the electron configurations for neutral atoms of gallium (Ga), chlorine (CI), phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca), and sulfur (S). electron configuration for Ga: electron configuration for Cl: electron configuration for P: electron configuration for Ca: electron configuration for S: Arrange the atoms according to both decreasing atomic radius and increasing first ionization energy (IE). Largest radius Smallest first IE
Write the electron configurations for neutral atoms of gallium (Ga), chlorine (CI), phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca), and sulfur (S). electron configuration for Ga: electron configuration for Cl: electron configuration for P: electron configuration for Ca: electron configuration for S: Arrange the atoms according to both decreasing atomic radius and increasing first ionization energy (IE). Largest radius Smallest first IE
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter11: Modern Atomic Theory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 126CP
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Write the electron configurations for neutral atoms of gallium (Ga), chlorine (Cl), phosphorus (P) , calcium (Ca), and sulfur
(S).
electron configuration for Ga:
electron configuration for Cl:
electron configuration for P:
electron configuration for Ca:
electron configuration for S:
Arrange the atoms according to both decreasing atomic radius and increasing first ionization energy (IE).
Largest radius
Smallest first IE
?
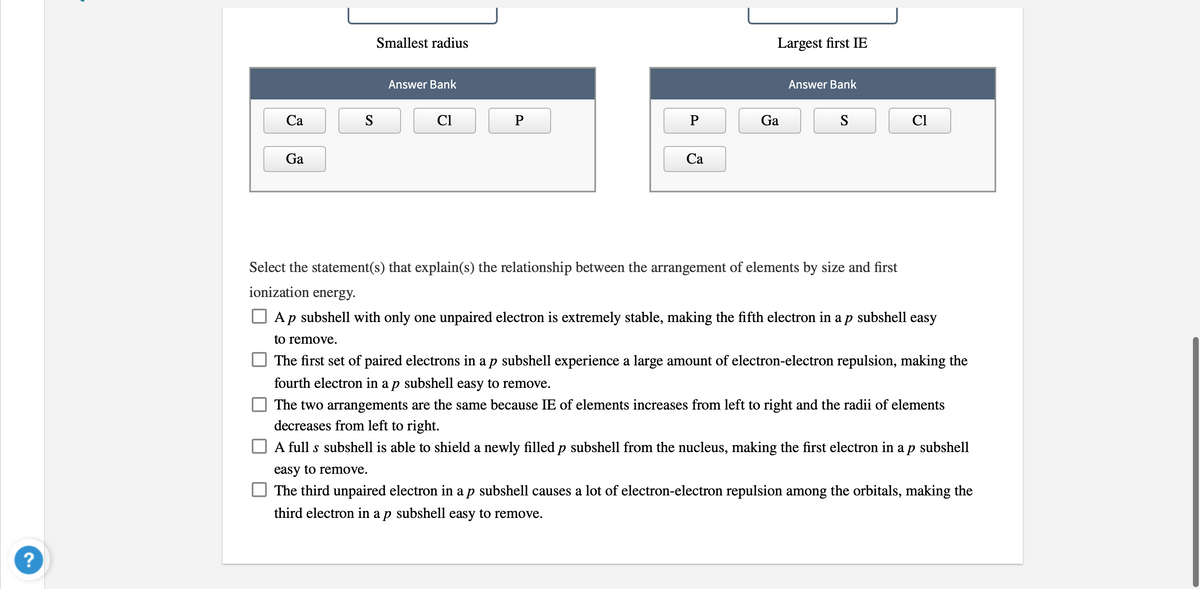
Transcribed Image Text:Smallest radius
Largest first IE
Answer Bank
Answer Bank
Са
S
Cl
P
Ga
S
Cl
Ga
Са
Select the statement(s) that explain(s) the relationship between the arrangement of elements by size and first
ionization energy.
O Ap subshell with only one unpaired electron is extremely stable, making the fifth electron in a p subshell easy
to remove.
The first set of paired electrons in a p subshell experience a large amount of electron-electron repulsion, making the
fourth electron in a p subshell easy to remove.
The two arrangements are the same because IE of elements increases from left to right and the radii of elements
decreases from left to right.
A full s subshell is able to shield a newly filled p subshell from the nucleus, making the first electron in a p subshell
easy to remove.
The third unpaired electron in ap subshell causes a lot of electron-electron repulsion among the orbitals, making the
third electron in a p subshell easy to remove.
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
