y 74.6 71.1 57.9 49.0 74.6 73.0 68.0 59.8 57.3 48.6 y = USE SALT (a) Obtain the equation of the least squares line. (Round all numerical values to four decimal places.) Interpret the slope. O A one MPa decrease in cube strength is associated with an increase in the predicted axial strength equal to the slope. O A one MPa decrease in axial strength is associated with an increase in the predicted cube strength equal to the slope. O A one MPa increase in axial strength is associated with an increase in the predicted cube strength equal to the slope. A one MPa increase in cube strength is associated with an increase in the predicted axial strength equal to the slope. (b) Calculate the coefficient of determination. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Interpret the coefficient of determination. O The coefficient of determination is the number of the observed samples of axial strength of asphalt that can be explained by variation in cube strength. O The coefficient of determination is the proportion of the observed variation in axial strength of asphalt samples of this type that cannot be attributed to its linear relationship with cube strength. O The coefficient of determination is the number of the observed samples of axial strength of asphalt that cannot be explained by variation in cube strength. The coefficient of determination is the proportion of the observed variation in axial strength of asphalt samples of this type that can be attributed to its linear relationship with cube strength. (c) Calculate an estimate of the error standard deviation in the simple linear regression model. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) MPa
y 74.6 71.1 57.9 49.0 74.6 73.0 68.0 59.8 57.3 48.6 y = USE SALT (a) Obtain the equation of the least squares line. (Round all numerical values to four decimal places.) Interpret the slope. O A one MPa decrease in cube strength is associated with an increase in the predicted axial strength equal to the slope. O A one MPa decrease in axial strength is associated with an increase in the predicted cube strength equal to the slope. O A one MPa increase in axial strength is associated with an increase in the predicted cube strength equal to the slope. A one MPa increase in cube strength is associated with an increase in the predicted axial strength equal to the slope. (b) Calculate the coefficient of determination. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Interpret the coefficient of determination. O The coefficient of determination is the number of the observed samples of axial strength of asphalt that can be explained by variation in cube strength. O The coefficient of determination is the proportion of the observed variation in axial strength of asphalt samples of this type that cannot be attributed to its linear relationship with cube strength. O The coefficient of determination is the number of the observed samples of axial strength of asphalt that cannot be explained by variation in cube strength. The coefficient of determination is the proportion of the observed variation in axial strength of asphalt samples of this type that can be attributed to its linear relationship with cube strength. (c) Calculate an estimate of the error standard deviation in the simple linear regression model. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) MPa
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.1: Measures Of Center
Problem 9PPS
Related questions
Question
Q9 Please answer fill-ins.
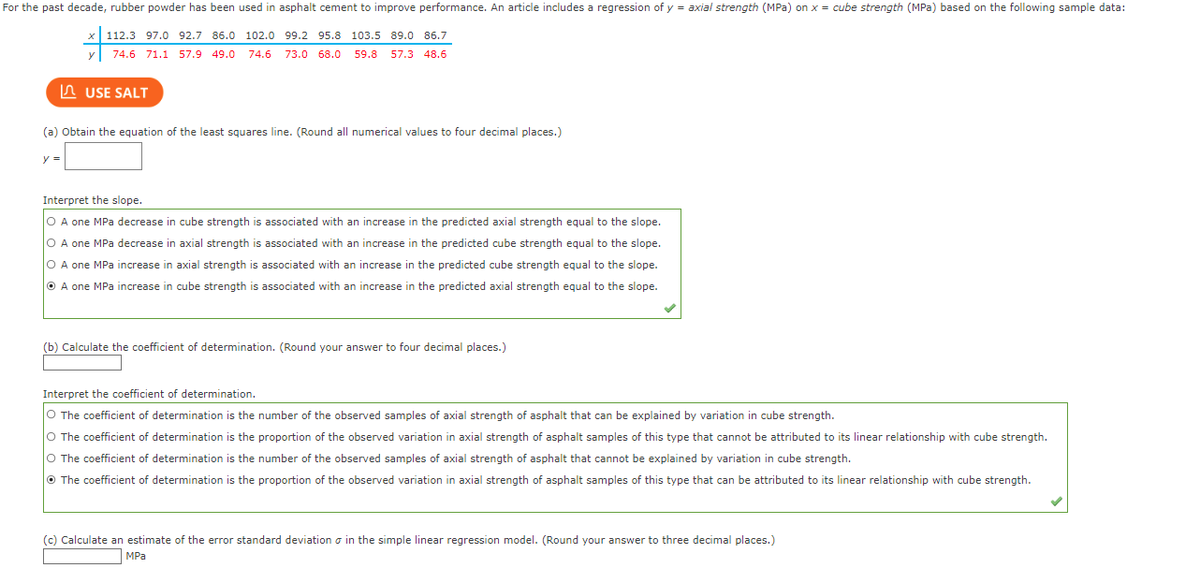
Transcribed Image Text:For the past decade, rubber powder has been used in asphalt cement to improve performance. An article includes a regression of y = axial strength (MPa) on x = cube strength (MPa) based on the following sample data:
112.3 97.0 92.7 86.0 102.0 99.2 95.8 103.5 89.0 86.7
74.6 71.1 57.9 49.0 74.6 73.0 68.0 59.8 57.3 48.6
y =
USE SALT
(a) Obtain the equation of the least squares line. (Round all numerical values to four decimal places.)
Interpret the slope.
O A one MPa decrease in cube strength is associated with an increase in the predicted axial strength equal to the slope.
O A one MPa decrease in axial strength is associated with an increase in the predicted cube strength equal to the slope.
O A one MPa increase in axial strength is associated with an increase in the predicted cube strength equal to the slope.
A one MPa increase in cube strength is associated with an increase in the predicted axial strength equal to the slope.
(b) Calculate the coefficient of determination. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
Interpret the coefficient of determination.
O The coefficient of determination is the number of the observed samples of axial strength of asphalt that can be explained by variation in cube strength.
O The coefficient of determination is the proportion of the observed variation in axial strength of asphalt samples of this type that cannot be attributed to its linear relationship with cube strength.
O The coefficient of determination is the number of the observed samples of axial strength of asphalt that cannot be explained by variation in cube strength.
The coefficient of determination is the proportion of the observed variation in axial strength of asphalt samples of this type that can be attributed to its linear relationship with cube strength.
(c) Calculate an estimate of the error standard deviation in the simple linear regression model. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
MPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill