Yakov owns a plot of land in the desert that isn't worth much. One day, a giant meteorite falls on his property, making a large crater. The event attracts scientists and tourists, and Yakov decides to sell nontransferable admission tickets to the meteor crater to both types of visitors: scientists (Market A) and tourists (Market B). The following graphs show daily demand (D) curves and marginal revenue (MR) curves for the two markets. Yakov's marginal cost of providing admission tickets is zero. Market A Market B 20 20 18 18 18 18 14 14 12 12 10 10 DA MR. MR O 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 3 0 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 QUANTITY (Admission tickets) QUANTITY (Admission tickets) Suppose now that Yakov decides to charge a different price in each market. To maximize revenue, Yakov should charge S per admission in Market B. At these prices, he will sell a total quantity of per admission in Market A and S admission tickets per day. Complete the following table by calculating Yakov's total revenue from selling in a market under the discriminatory price policy. Total Revenue Pricing Policy (Dollars) Discriminatory Yakov charges a higher price in the market with a relatively price elasticity of demand. PRICE (Dollars per ticket) PRICE (Dollars per ticket)
Yakov owns a plot of land in the desert that isn't worth much. One day, a giant meteorite falls on his property, making a large crater. The event attracts scientists and tourists, and Yakov decides to sell nontransferable admission tickets to the meteor crater to both types of visitors: scientists (Market A) and tourists (Market B). The following graphs show daily demand (D) curves and marginal revenue (MR) curves for the two markets. Yakov's marginal cost of providing admission tickets is zero. Market A Market B 20 20 18 18 18 18 14 14 12 12 10 10 DA MR. MR O 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 3 0 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 QUANTITY (Admission tickets) QUANTITY (Admission tickets) Suppose now that Yakov decides to charge a different price in each market. To maximize revenue, Yakov should charge S per admission in Market B. At these prices, he will sell a total quantity of per admission in Market A and S admission tickets per day. Complete the following table by calculating Yakov's total revenue from selling in a market under the discriminatory price policy. Total Revenue Pricing Policy (Dollars) Discriminatory Yakov charges a higher price in the market with a relatively price elasticity of demand. PRICE (Dollars per ticket) PRICE (Dollars per ticket)
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter13: best-practice Tactics: Game Theory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1E
Related questions
Question
please do the questions and the chocies for the last question is (high, low)
thankyou!!
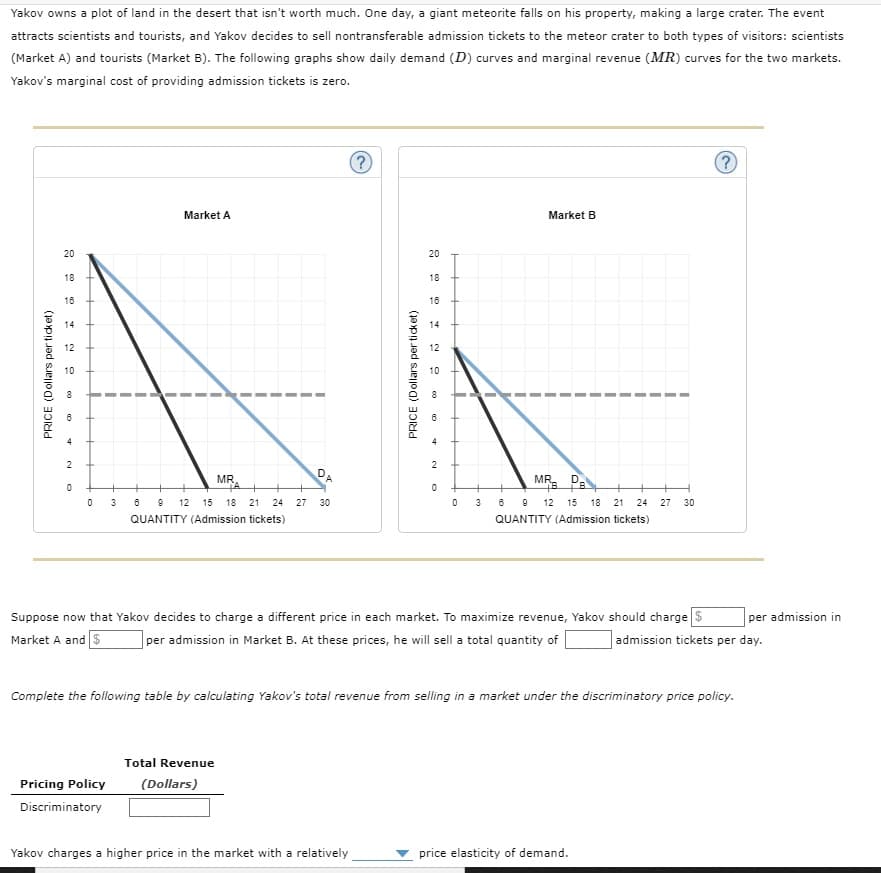
Transcribed Image Text:Yakov owns a plot of land in the desert that isn't worth much. One day, a giant meteorite falls on his property, making a large crater. The event
attracts scientists and tourists, and Yakov decides to sell nontransferable admission tickets to the meteor crater to both types of visitors: scientists
(Market A) and tourists (Market B). The following graphs show daily demand (D) curves and marginal revenue (MR) curves for the two markets.
Yakov's marginal cost of providing admission tickets is zero.
Market A
Market B
20
20
18
18
16
16
14
14
12
12
10
10
4
DA
MR. Pa
3 6 9 12
MR
3
12 15 18
21
24
27
30
15
18
21
24
27
30
QUANTITY (Admission tickets)
QUANTITY (Admission tickets)
Suppose now that Yakov decides to charge a different price in each market. To maximize revenue, Yakov should charge $
per admission in
Market A and$
per admission in Market B. At these prices, he will sell a total quantity of
|admission tickets per day.
Complete the following table by calculating Yakov's total revenue from selling in a market under the discriminatory price policy.
Total Revenue
Pricing Policy
(Dollars)
Discriminatory
Yakov charges a higher price in the market with a relatively
price elasticity of demand.
PRICE (Dollars per ticket)
PRICE (Dollars per ticket)
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
