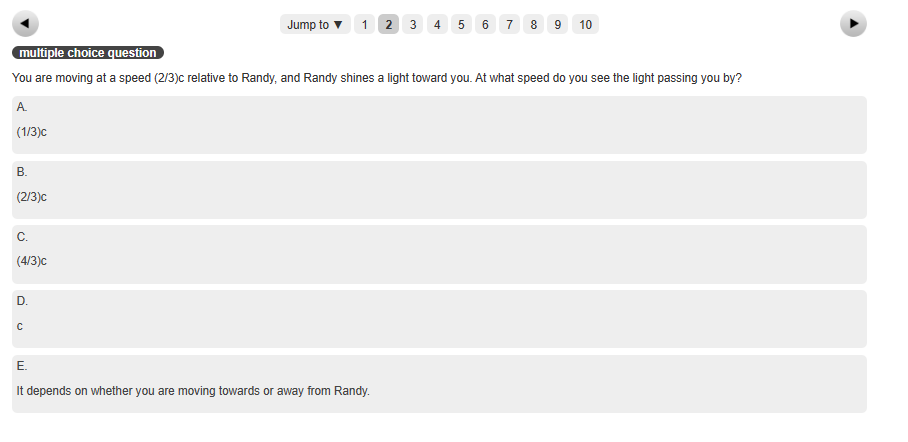
You are moving at a speed (2/3)c relative to Randy, and Randy shines a light toward you. At what speed do you see the light passing you by? A (1/3)c B. (2/3)c C. (4/3)c D. C E. It depends on whether you are moving towards or away from Randy.
You are moving at a speed (2/3)c relative to Randy, and Randy shines a light toward you. At what speed do you see the light passing you by? A (1/3)c B. (2/3)c C. (4/3)c D. C E. It depends on whether you are moving towards or away from Randy.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter39: Relativity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 39.37P
Related questions
Question
2 parts
Transcribed Image Text:B.
(2/3)c
multiple choice question
You are moving at a speed (2/3)c relative to Randy, and Randy shines a light toward you. At what speed do you see the light passing you by?
A
(1/3)c
C.
(4/3)c
D.
Jump to 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
с
8 9 10
E.
It depends on whether you are moving towards or away from Randy.
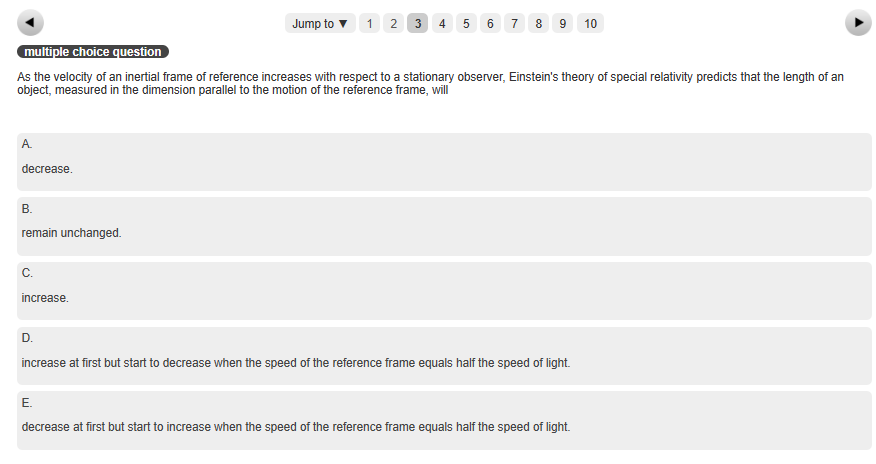
Transcribed Image Text:multiple choice question
As the velocity of an inertial frame of reference increases with respect to a stationary observer, Einstein's theory of special relativity predicts that the length of an
object, measured in the dimension parallel to the motion of the reference frame, will
A
decrease.
B.
remain unchanged.
Jump to 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
increase.
D.
increase at first but start to decrease when the speed of the reference frame equals half the speed of light.
E.
decrease at first but start to increase when the speed of the reference frame equals half the speed of light.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning