1) Calculate the work that the spring does on the block as the spring expands from a length of 2.0 meters to its equilibrium length of 2.5 meters (in the time between diagram A and diagram B above). The sign of the work done by the spring (positive or negative) is important. joules Submit
1) Calculate the work that the spring does on the block as the spring expands from a length of 2.0 meters to its equilibrium length of 2.5 meters (in the time between diagram A and diagram B above). The sign of the work done by the spring (positive or negative) is important. joules Submit
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter13: State Of Matter
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 114A
Related questions
Question
Can you please answer these
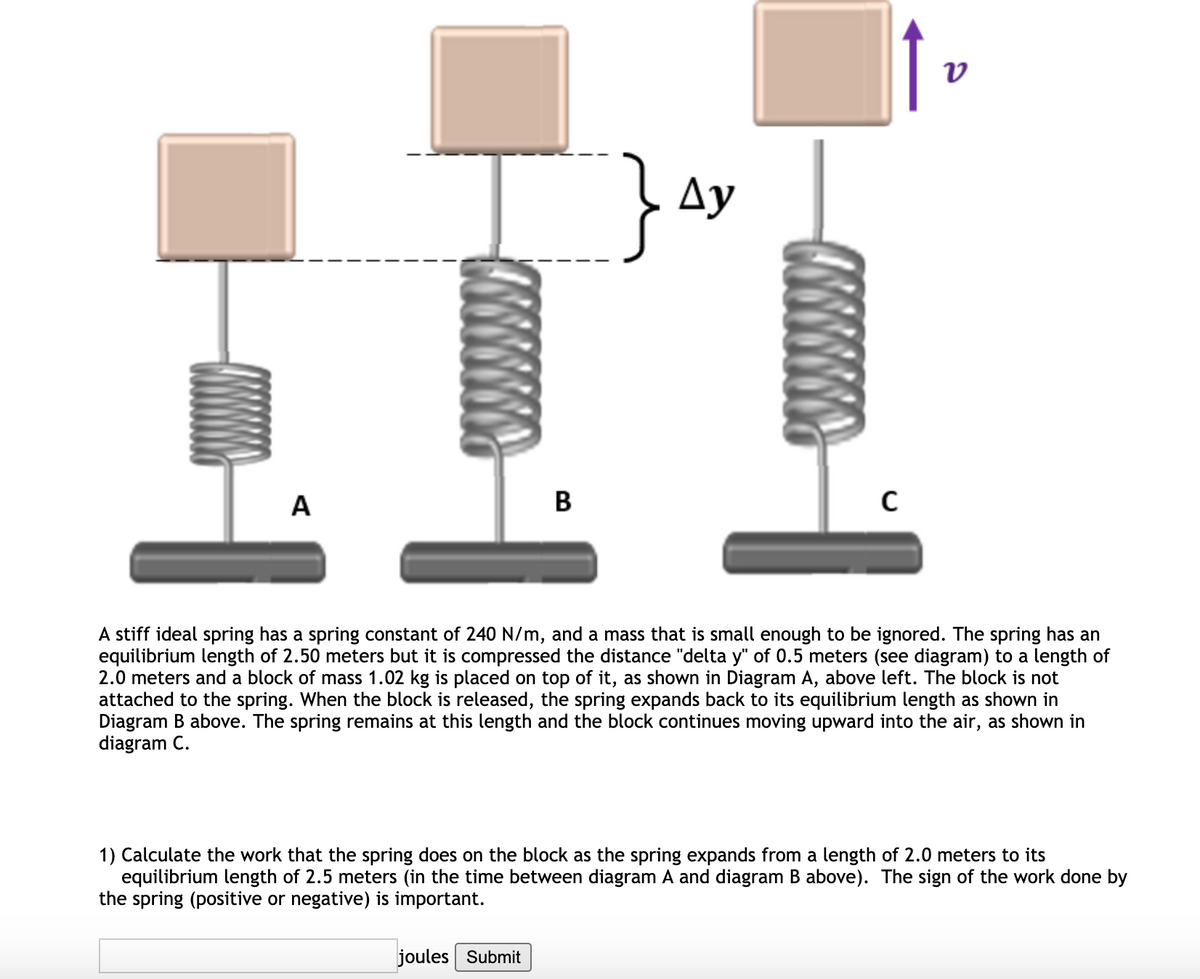
Transcribed Image Text:Ay
A
B
A stiff ideal spring has a spring constant of 240 N/m, and a mass that is small enough to be ignored. The spring has an
equilibrium length of 2.50 meters but it is compressed the distance "delta y" of 0.5 meters (see diagram) to a length of
2.0 meters and a block of mass 1.02 kg is placed on top of it, as shown in Diagram A, above left. The block is not
attached to the spring. When the block is released, the spring expands back to its equilibrium length as shown in
Diagram B above. The spring remains at this length and the block continues moving upward into the air, as shown in
diagram C.
1) Calculate the work that the spring does on the block as the spring expands from a length of 2.0 meters to its
equilibrium length of 2.5 meters (in the time between diagram A and diagram B above). The sign of the work done by
the spring (positive or negative) is important.
joules Submit

Transcribed Image Text:2) Calculate the work that the Earth does on the block (via gravity) as the spring expands from a length of 2.0 meters to
its equilibrium length of 2.5 meters (in the time between diagram A and diagram B above). The sign of the work done
by the Earth (positive or negative) is important.
joules Submit
3) Assuming friction is negligible, calculate the net work done on the block as the spring expands from a length of 2.0
meters to its equilibrium length of 2.5 meters (in the time between diagram A and diagram B above). The sign of the
net work (positive or negative) is important.
joules Submit
4) Assuming friction is negligible, and assuming the block started from rest in Diagram A, above, calculate the speed of
the block as it left the top of the spring, immediately before the image in diagram C, above.
m/s Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning