(1) Complete the above table by filling all blanks. (2) As long as Tony and Jill operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly, what will the weekly market quantity of water supplied by Tony & Jill (Qm), price of water (PM), and their weekly joint profit? QM (Q51) PM = $ (Q52) Profit = $ (Q53)
(1) Complete the above table by filling all blanks. (2) As long as Tony and Jill operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly, what will the weekly market quantity of water supplied by Tony & Jill (Qm), price of water (PM), and their weekly joint profit? QM (Q51) PM = $ (Q52) Profit = $ (Q53)
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter22: Frontiers Of Microeconomics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9PA
Related questions
Question
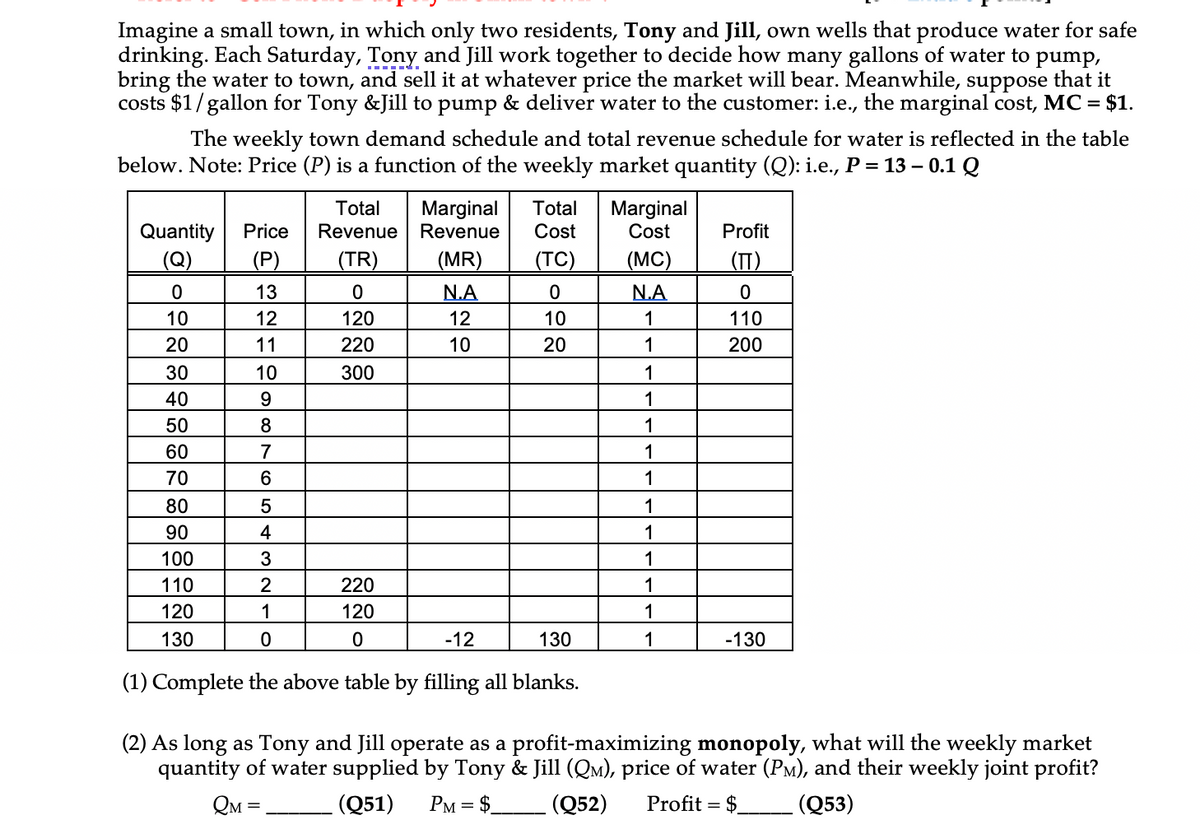
Transcribed Image Text:Imagine a small town, in which only two residents, Tony and Jill, own wells that produce water for safe
drinking. Each Saturday, Tony and Jill work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump,
bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. Meanwhile, suppose that it
costs $1/gallon for Tony &Jill to pump & deliver water to the customer: i.e., the marginal cost, MC =
$1.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table
below. Note: Price (P) is a function of the weekly market quantity (Q): i.e., P = 13 – 0.1 Q
Total
Marginal
Total
Marginal
Cost
Revenue Revenue
Quantity
(Q)
Price
Cost
Profit
(P)
(TR)
(MR)
(TC)
(MC)
(TT)
13
N.A
N.A
10
12
120
12
10
1
110
20
11
220
10
20
1
200
30
10
300
1
40
1
50
8
60
7
70
6
1
80
1
90
4
1
100
3
1
110
220
1
120
1
120
1
130
-12
130
1
-130
(1) Complete the above table by filling all blanks.
(2) As long as Tony and Jill operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly, what will the weekly market
quantity of water supplied by Tony & Jill (QM), price of water (PM), and their weekly joint profit?
QM =
(Q51)
PM = $.
(Q52)
Profit =
(Q53)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning