Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
How would you answer the second question?
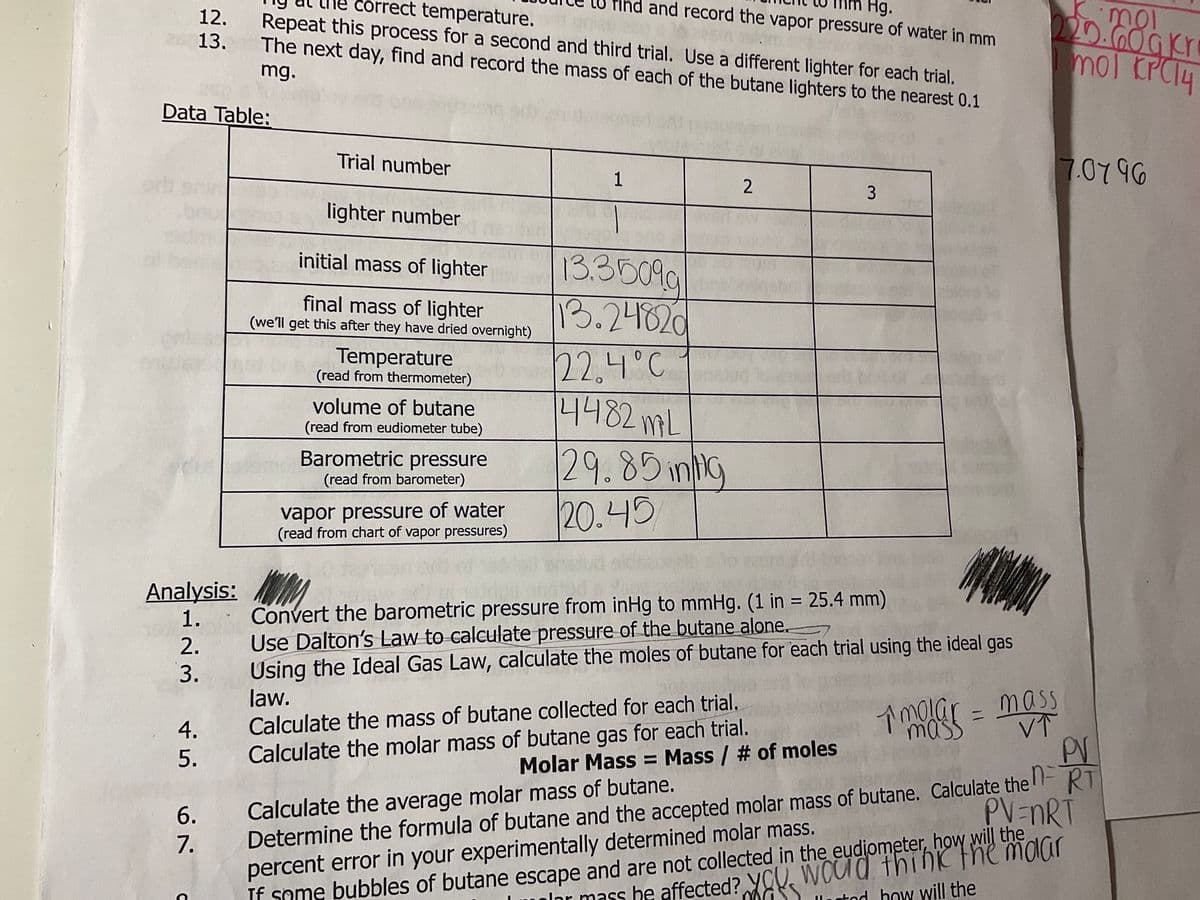
Transcribed Image Text:12.
25 13.
S
Data Table:
Analysis:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
corr rect temperature.
Repeat this process for a second and third trial. Use a different lighter for each trial.
The next day, find and record the mass of each of the butane lighters to the nearest 0.1
mg.
Trial number
lighter number
initial mass of lighter
final mass of lighter
(we'll get this after they have dried overnight)
Temperature
(read from thermometer)
volume of butane
(read from eudiometer tube)
Barometric pressure
(read from barometer)
vapor pressure of water
(read from chart of vapor pressures)
mm Hg.
and record the vapor pressure of water in mm
1
13.35099
13.24820
22.4°C
14482mL
29.85 inlig
20.45
2
3
Convert the barometric pressure from inHg to mmHg. (1 in = 25.4 mm)
Use Dalton's Law to calculate pressure of the butane alone.
Using the Ideal Gas Law, calculate the moles of butane for each trial using the ideal gas
law.
11
220.60gkr
mol KPC14
1 molge = mass
mass
VT
7.07 96
Calculate the mass of butane collected for each trial.
Calculate the molar mass of butane gas for each trial.
PV
Molar Mass = Mass / # of moles
Calculate the average molar mass of butane.
Determine the formula of butane and the accepted molar mass of butane. Calculate the RT
percent error in your experimentally determined molar mass.
PV=nRT
If some bubbles of butane escape and are not collected in the eudjometer, how will the
he
har mass be affected? You would think the molar
lor
stod how will the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY