1. A. Determine the percentage and number of samples for each stratum using proportional allocation. Assuming the sample size is 50. Program Population (N) Percentage Sample (n) BSBA 45 BSA 27 BSOA 40
1. A. Determine the percentage and number of samples for each stratum using proportional allocation. Assuming the sample size is 50. Program Population (N) Percentage Sample (n) BSBA 45 BSA 27 BSOA 40
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.4: Collecting Data
Problem 6E
Related questions
Question
100%
Helping tags: Statistics, Math
.
.
.
WILL UPVOTE, just pls help me answer question 2 with 2 subparts. Thank you.
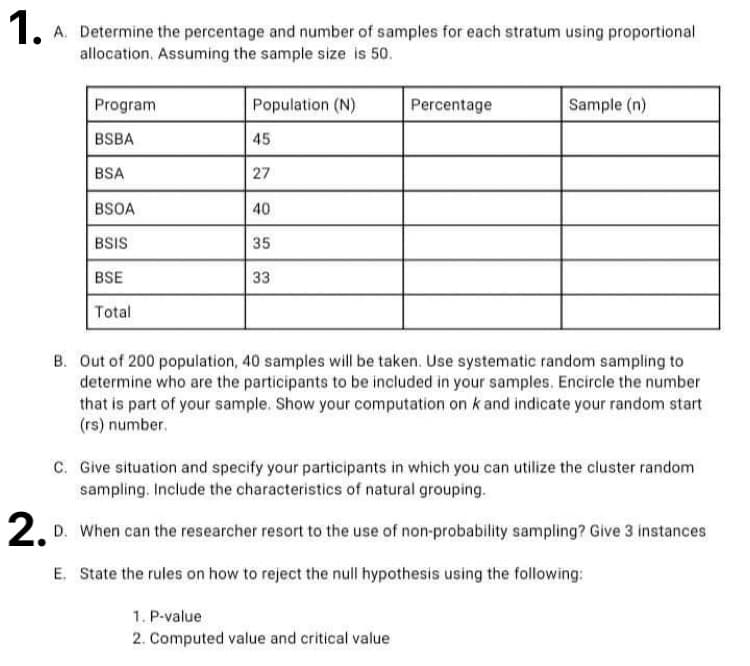
Transcribed Image Text:1. A. Determine the percentage and number of samples for each stratum using proportional
allocation, Assuming the sample size is 50.
Program
Population (N)
Percentage
Sample (n)
BSBA
45
BSA
27
BSOA
40
BSIS
35
BSE
33
Total
B. Out of 200 population, 40 samples will be taken. Use systematic random sampling to
determine who are the participants to be included in your samples. Encircle the number
that is part of your sample. Show your computation on k and indicate your random start
(rs) number.
C. Give situation and specify your participants in which you can utilize the cluster random
sampling. Include the characteristics of natural grouping.
2.
D. When can the researcher resort to the use of non-probability sampling? Give 3 instances
E. State the rules on how to reject the null hypothesis using the following:
1. P-value
2. Computed value and critical value
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
