1. Consider an example of the Baumol Model concerning the separation of ownership and control in the organisation of the firm. The firm in question is an oligopoly. The manager seeks to maximise total revenue (TR) from sales, under the profit constraint imposed by the external owners, G = 500. The firm faces an inverse demand function of the following form: p = 100-2q, and the total cost function c(q) = 20g. a) What is the optimal choice of output by the manager? Does it satisfy the profit constraint? b) If the profit constraint is changed to G =$800, what happens to the manager's choice? c) Now, the external owners further change the profit constraint to = $1000. If the manager in fact has control over the cost function, what cost level should be achieved for satisfying the new profit constraint? d) What else can the manger do in the face of the new profit constraint?
1. Consider an example of the Baumol Model concerning the separation of ownership and control in the organisation of the firm. The firm in question is an oligopoly. The manager seeks to maximise total revenue (TR) from sales, under the profit constraint imposed by the external owners, G = 500. The firm faces an inverse demand function of the following form: p = 100-2q, and the total cost function c(q) = 20g. a) What is the optimal choice of output by the manager? Does it satisfy the profit constraint? b) If the profit constraint is changed to G =$800, what happens to the manager's choice? c) Now, the external owners further change the profit constraint to = $1000. If the manager in fact has control over the cost function, what cost level should be achieved for satisfying the new profit constraint? d) What else can the manger do in the face of the new profit constraint?
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter12: Price And Output Determination: Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
Solve the following question
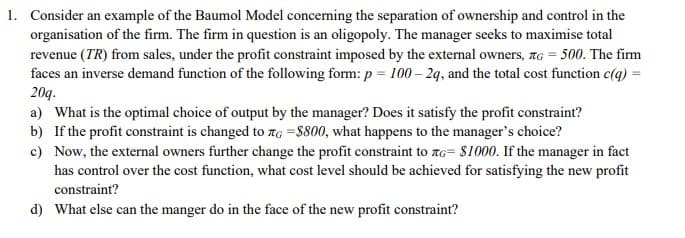
Transcribed Image Text:1. Consider an example of the Baumol Model concerning the separation of ownership and control in the
organisation of the firm. The firm in question is an oligopoly. The manager seeks to maximise total
revenue (TR) from sales, under the profit constraint imposed by the external owners, G = 500. The firm
faces an inverse demand function of the following form: p = 100-2q, and the total cost function c(q) =
20q.
a) What is the optimal choice of output by the manager? Does it satisfy the profit constraint?
b) If the profit constraint is changed to G =$800, what happens to the manager's choice?
c)
Now, the external owners further change the profit constraint to G= $1000. If the manager in fact
has control over the cost function, what cost level should be achieved for satisfying the new profit
constraint?
d) What else can the manger do in the face of the new profit constraint?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning