1. Externalities - Definition and examples An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any compensation for that effect. If the impact on the third party is beneficial, it is called a v externality. The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of ex hegative he dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the market equilibrium price and quantity for this good. positive Adjust one or both of the curves to reflect the presence of the externality. If the social cost of producing the good is not equal to the private cost, then you should drag the supply curve to reflect the social costs of producing the good; similarly, if the social value of producing the good is not equal to the private value, then you should drag the demand curve to reflect the social value of consuming the good. (? Supply Demand Demand QUANTITY (Units) With this type of externality, in the absence of government intervention, the market equilibrium quantity produced will be than the socially optimal quantity. greater Which of the following generate the type of externality previously described? Check all that apply. less A leading software company has decided to increase its research budget for inventing new open-source technologies. Your roommate Jake has bought a bird that keeps you up at night with its chirping. Frances has planted hundreds of flowers in her front yard, beautifying the neighborhood both for herself and for her neighbors. The city where you live has turned the publicly owned land next to your house into a park, causing trash dropped by park visitors to pile up in your backyard. PRICE (Dollars per unit)
1. Externalities - Definition and examples An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any compensation for that effect. If the impact on the third party is beneficial, it is called a v externality. The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of ex hegative he dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the market equilibrium price and quantity for this good. positive Adjust one or both of the curves to reflect the presence of the externality. If the social cost of producing the good is not equal to the private cost, then you should drag the supply curve to reflect the social costs of producing the good; similarly, if the social value of producing the good is not equal to the private value, then you should drag the demand curve to reflect the social value of consuming the good. (? Supply Demand Demand QUANTITY (Units) With this type of externality, in the absence of government intervention, the market equilibrium quantity produced will be than the socially optimal quantity. greater Which of the following generate the type of externality previously described? Check all that apply. less A leading software company has decided to increase its research budget for inventing new open-source technologies. Your roommate Jake has bought a bird that keeps you up at night with its chirping. Frances has planted hundreds of flowers in her front yard, beautifying the neighborhood both for herself and for her neighbors. The city where you live has turned the publicly owned land next to your house into a park, causing trash dropped by park visitors to pile up in your backyard. PRICE (Dollars per unit)
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter10: Externalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3PA
Related questions
Question
sub= 24 help
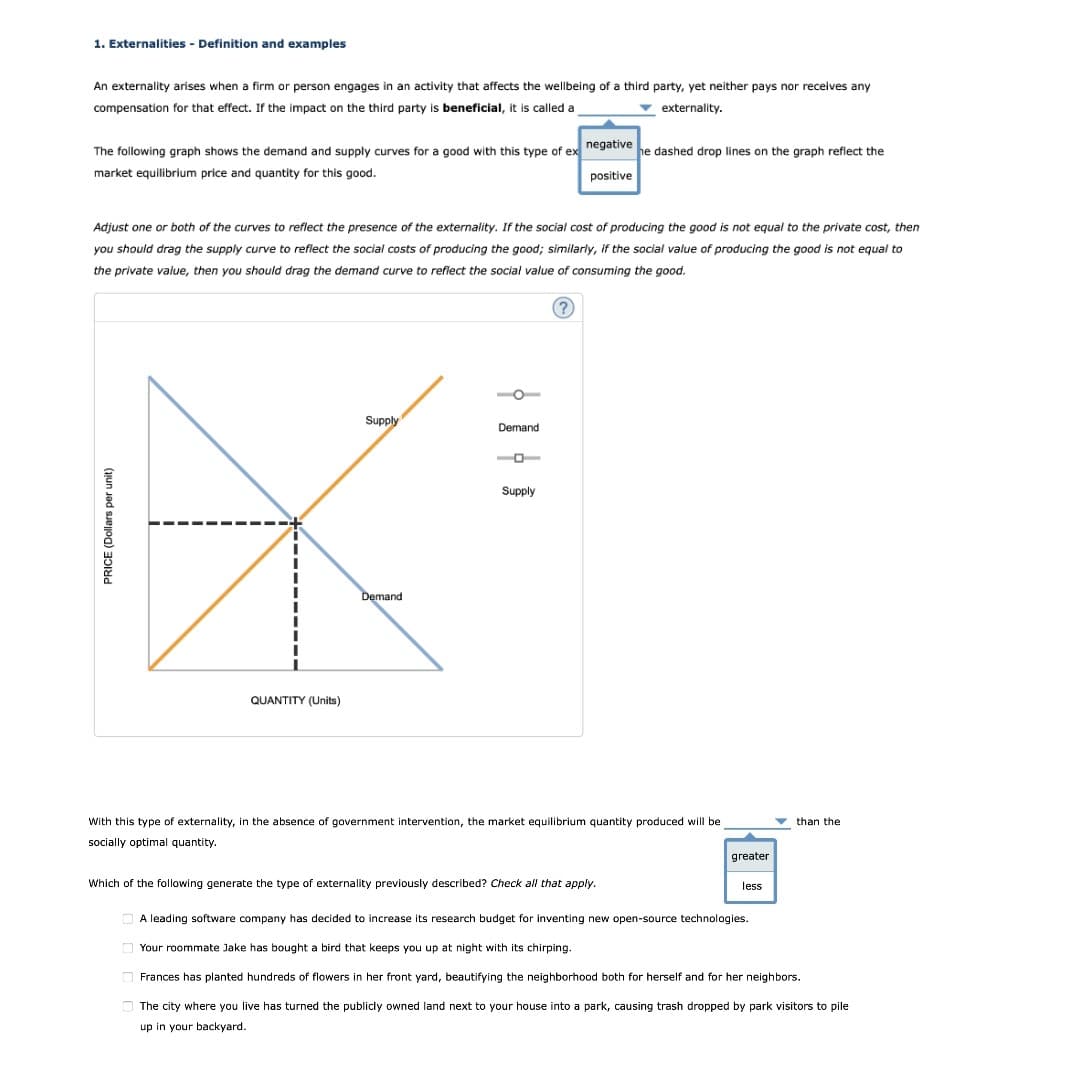
Transcribed Image Text:1. Externalities - Definition and examples
An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any
compensation for that effect. If the impact on the third party is beneficial, it is called a
v externality.
The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of ex negative he dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the
market equilibrium price and quantity for this good.
positive
Adjust one or both of the curves to reflect the presence of the externality. If the social cost of producing the good is not equal to the private cost, then
you should drag the supply curve to reflect the social costs of producing the good; similarly, if the social value of producing the good is not equal to
the private value, then you should drag the demand curve to reflect the social value of consuming the good.
Supply
Demand
Supply
Demand
QUANTITY (Units)
With this type of externality, in the absence of government intervention, the market equilibrium quantity produced will be
v than the
socially optimal quantity.
greater
Which of the following generate the type of externality previously described? Check all that apply.
less
A leading software company has decided to increase its research budget for inventing new open-source technologies.
Your roommate Jake has bought a bird that keeps you up at night with its chirping.
Frances has planted hundreds of flowers in her front yard, beautifying the neighborhood both for herself and for her neighbors.
O The city where you live has turned the publicly owned land next to your house into a park, causing trash dropped by park visitors to pile
up in your backyard.
PRICE (Dollars per unit)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning