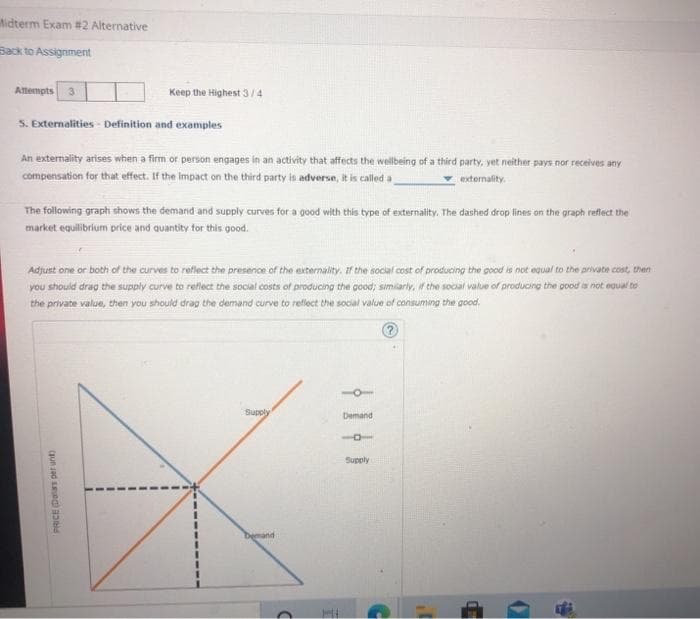
S. Externalities - Definition and examples An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any compensation for that effect. If the Impact on the third party is adverse, it is called a externality. The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of externality. The dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the market equilibrium price and quantity for this good. Adjust one or both of the curves to reflect the presence of the externality. If the social cost of producing the good is not equal to the private cost, then you should drag the supply curve to reflect the social costs of producing the good; simiarly, f the social value of producing the good is not equal to the private value, then you should drag the demand curve to reflect the social value of connuming the good.
S. Externalities - Definition and examples An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any compensation for that effect. If the Impact on the third party is adverse, it is called a externality. The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of externality. The dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the market equilibrium price and quantity for this good. Adjust one or both of the curves to reflect the presence of the externality. If the social cost of producing the good is not equal to the private cost, then you should drag the supply curve to reflect the social costs of producing the good; simiarly, f the social value of producing the good is not equal to the private value, then you should drag the demand curve to reflect the social value of connuming the good.
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter22: Frontiers Of Microeconomics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6PA
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:tidterm Exam #2 Alternative
Back to Assignment
Attempts
3.
Keep the Highest 3/4
S. Externalities - Definition and examples
An externality arises when a firm or person engages in an activity that affects the wellbeing of a third party, yet neither pays nor receives any
compensation for that effect. If the Impact on the third party is adverse, it is called a
extemality.
The following graph shows the demand and supply curves for a good with this type of externality. The dashed drop lines on the graph reflect the
market equilibrium price and quantity for this good.
Adjust one or both of the curves to reflect the presence of the externality. af the social cost of producing the good is not egual to the private cost, then
you should drag the supply curve to reflecet the social costs of producing the good; simiarly, f the social value of producing the pood is not equal to
the private value, then you should drag the demand curve to reflect the social value of consuming the good.
Supply
Demand
Supply
bemand
PRICE Dalas per unt)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506756
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning