1. Problem Description: The total nuclear binding energy is the energy required to split a nucleus of an atom in its component parts: protons and neutrons, or, collectively, the nucleons. It describes how strongly nucleons are bound to each other. When a high amount of energy is needed to separate the nucleons, it means nucleus is very stable and the neutrons and protons are tightly bound to each other. The atomic number or proton number (symbol Z) is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. The sum of the atomic number Z and the number of neutrons N gives the mass number A of an atom. + Binding energy Nucleus (smaller mass) Separated nucleons (greater mass) Figure 1: Binding Energy in the Nucleus The approximate nuclear binding energy Eb in million electron volts, of an atomic nucleus with atomic number Z and mass number A is calculated using the following formula: Eb = a,A – a2A3 (А — 2Z)2 a4 a5 + A A3 AZ where, a, = 15.67, а2 %3D 17.23, аз %3D 0.75, а, = 93.2 ,and
1. Problem Description: The total nuclear binding energy is the energy required to split a nucleus of an atom in its component parts: protons and neutrons, or, collectively, the nucleons. It describes how strongly nucleons are bound to each other. When a high amount of energy is needed to separate the nucleons, it means nucleus is very stable and the neutrons and protons are tightly bound to each other. The atomic number or proton number (symbol Z) is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. The sum of the atomic number Z and the number of neutrons N gives the mass number A of an atom. + Binding energy Nucleus (smaller mass) Separated nucleons (greater mass) Figure 1: Binding Energy in the Nucleus The approximate nuclear binding energy Eb in million electron volts, of an atomic nucleus with atomic number Z and mass number A is calculated using the following formula: Eb = a,A – a2A3 (А — 2Z)2 a4 a5 + A A3 AZ where, a, = 15.67, а2 %3D 17.23, аз %3D 0.75, а, = 93.2 ,and
C++ for Engineers and Scientists
4th Edition
ISBN:9781133187844
Author:Bronson, Gary J.
Publisher:Bronson, Gary J.
Chapter3: Assignment, Formatting, And Interactive Input
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6PP: (Heat transfer) The formula developed in Exercise 5 can be used to determine the cooling time, t,...
Related questions
Question
100%
By python
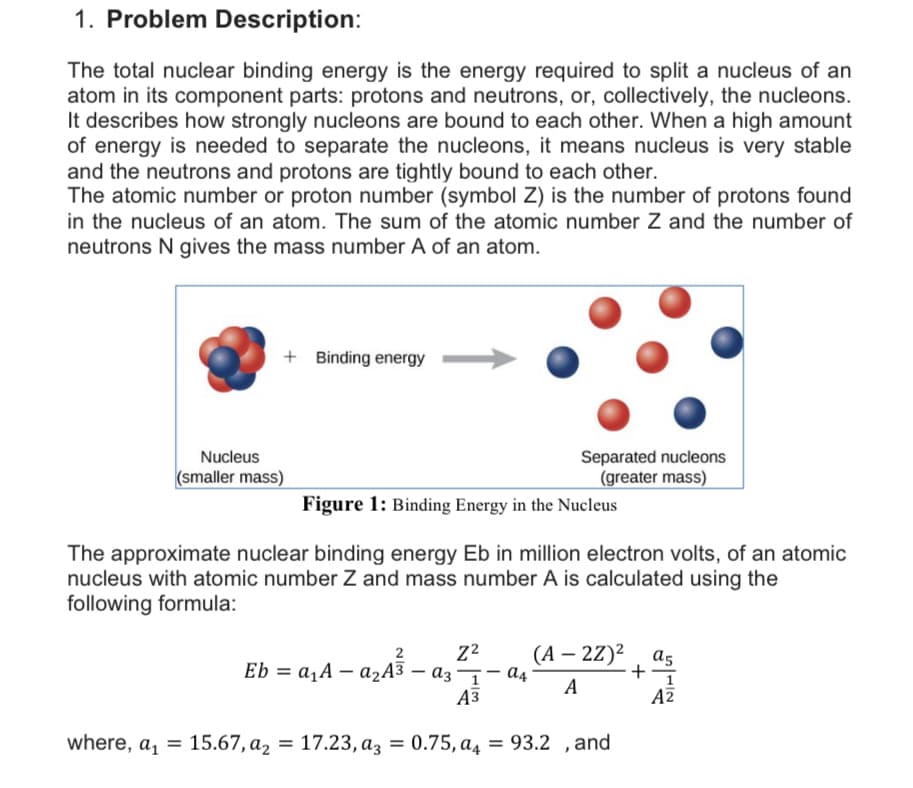
Transcribed Image Text:1. Problem Description:
The total nuclear binding energy is the energy required to split a nucleus of an
atom in its component parts: protons and neutrons, or, collectively, the nucleons.
It describes how strongly nucleons are bound to each other. When a high amount
of energy is needed to separate the nucleons, it means nucleus is very stable
and the neutrons and protons are tightly bound to each other.
The atomic number or proton number (symbol Z) is the number of protons found
in the nucleus of an atom. The sum of the atomic number Z and the number of
neutrons N gives the mass number A of an atom.
+ Binding energy
Nucleus
Separated nucleons
(smaller mass)
(greater mass)
Figure 1: Binding Energy in the Nucleus
The approximate nuclear binding energy Eb in million electron volts, of an atomic
nucleus with atomic number Z and mass number A is calculated using the
following formula:
(А — 2Z)2 , as
+-
2
Eb = a,A – ażA3 – az¬– đ4
А
Аз
AZ
where, a, = 15.67, a, = 17.23, az = 0.75, a4 = 93.2 ,and
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

C++ for Engineers and Scientists
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781133187844
Author:
Bronson, Gary J.
Publisher:
Course Technology Ptr

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337102087
Author:
D. S. Malik
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

C++ for Engineers and Scientists
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781133187844
Author:
Bronson, Gary J.
Publisher:
Course Technology Ptr

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337102087
Author:
D. S. Malik
Publisher:
Cengage Learning