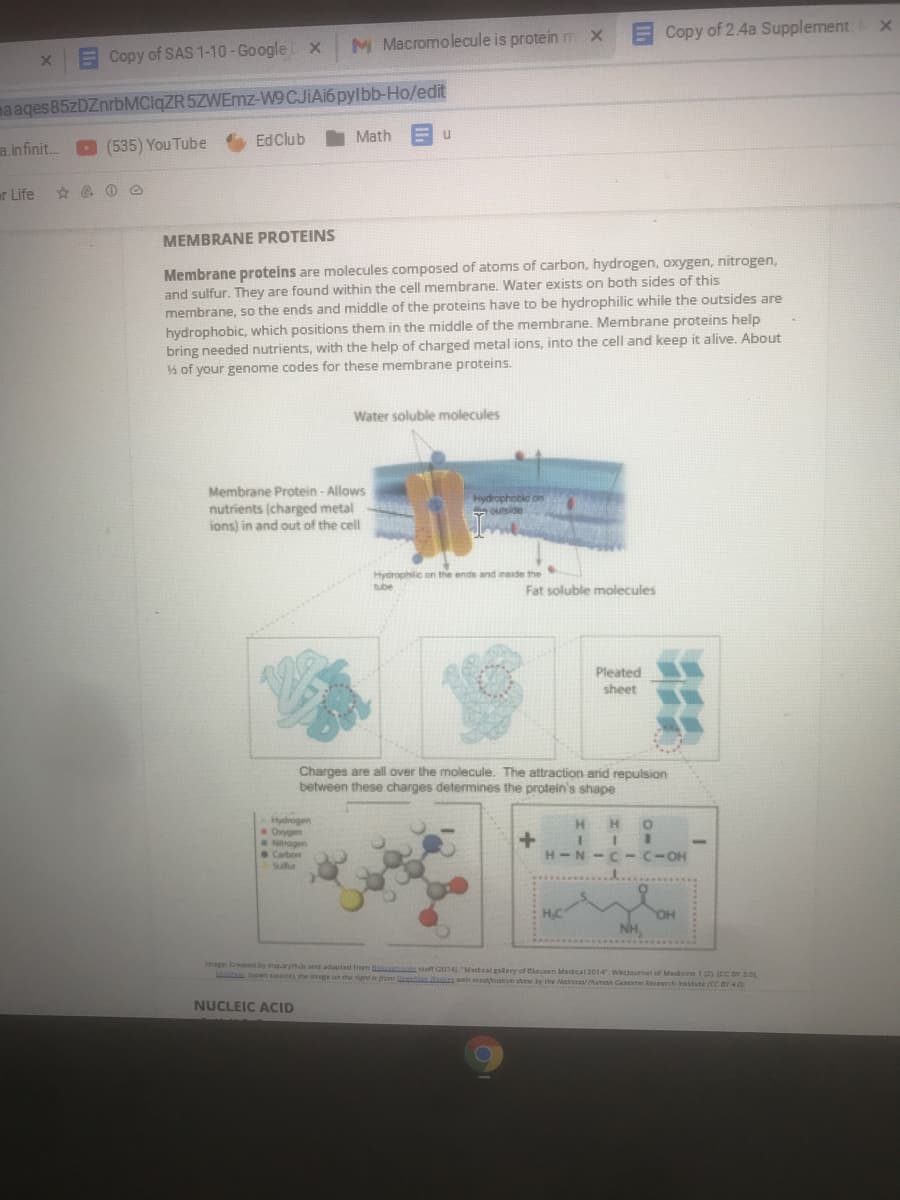
1. We examined how different elements combine to form compounds using two models, the Periodic Table and Lewis diagrams. Looking back to the macromnolecules in Lesson 2, what type(s) of compounds do you think are formed by these macromolecules?
Formal Charges
Formal charges have an important role in organic chemistry since this concept helps us to know whether an atom in a molecule is neutral/bears a positive or negative charge. Even if some molecules are neutral, the atoms within that molecule need not be neutral atoms.
Polarity Of Water
In simple chemical terms, polarity refers to the separation of charges in a chemical species leading into formation of two polar ends which are positively charged end and negatively charged end. Polarity in any molecule occurs due to the differences in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Water, as we all know has two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom. As oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen thus, there exists polarity in the bonds which is why water is known as a polar solvent.
Valence Bond Theory Vbt
Valence bond theory (VBT) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. It gives a quantum mechanical approach to the formation of covalent bonds with the help of wavefunctions using attractive and repulsive energies when two atoms are brought from infinity to their internuclear distance.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps







