11. Refer to the figure below. нн Н `NH2 NH2 N' N- 2e-+H* R NAD+ NADH NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure. It is likely that, in these reactions, NAD+ functions as an electron acceptor (reducing agent) in redox reactions. functions as an electron donor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions. functions as a base in acid-base catalytic mechanisms. functions as an electron donor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions. functions as an electron acceptor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions. +Z-
11. Refer to the figure below. нн Н `NH2 NH2 N' N- 2e-+H* R NAD+ NADH NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure. It is likely that, in these reactions, NAD+ functions as an electron acceptor (reducing agent) in redox reactions. functions as an electron donor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions. functions as a base in acid-base catalytic mechanisms. functions as an electron donor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions. functions as an electron acceptor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions. +Z-
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter6: Energy, Enzymes, And Biological Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6TYK: Which of the following methods is not used by enzymes to increase the rate of reactions? a. covalent...
Related questions
Question
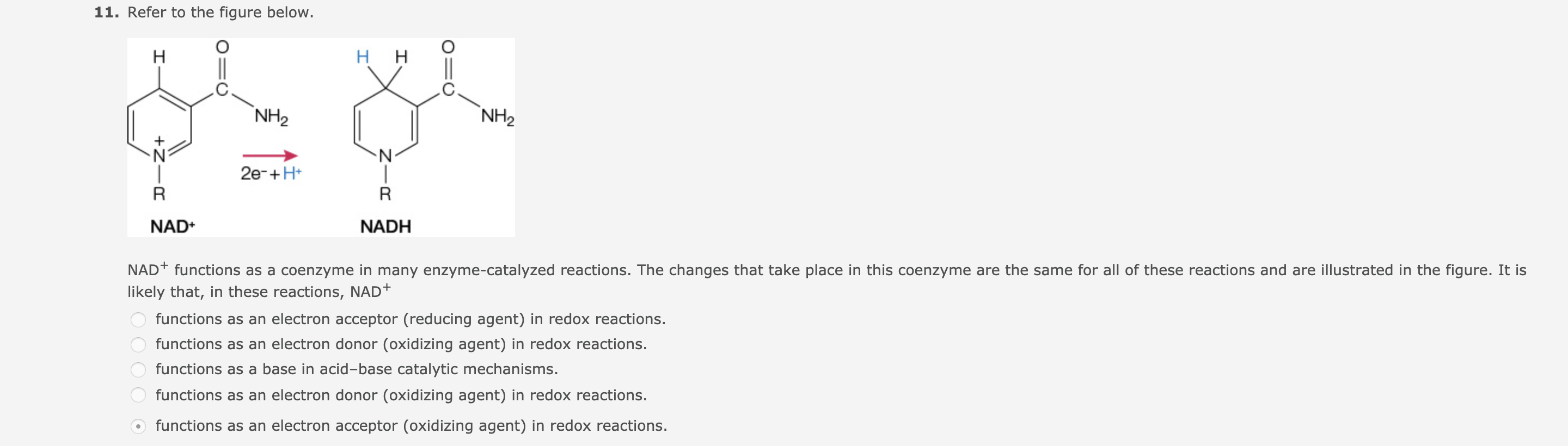
Transcribed Image Text:11. Refer to the figure below.
нн
Н
`NH2
NH2
N'
N-
2e-+H*
R
NAD+
NADH
NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure. It is
likely that, in these reactions, NAD+
functions as an electron acceptor (reducing agent) in redox reactions.
functions as an electron donor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions.
functions as a base in acid-base catalytic mechanisms.
functions as an electron donor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions.
functions as an electron acceptor (oxidizing agent) in redox reactions.
+Z-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning