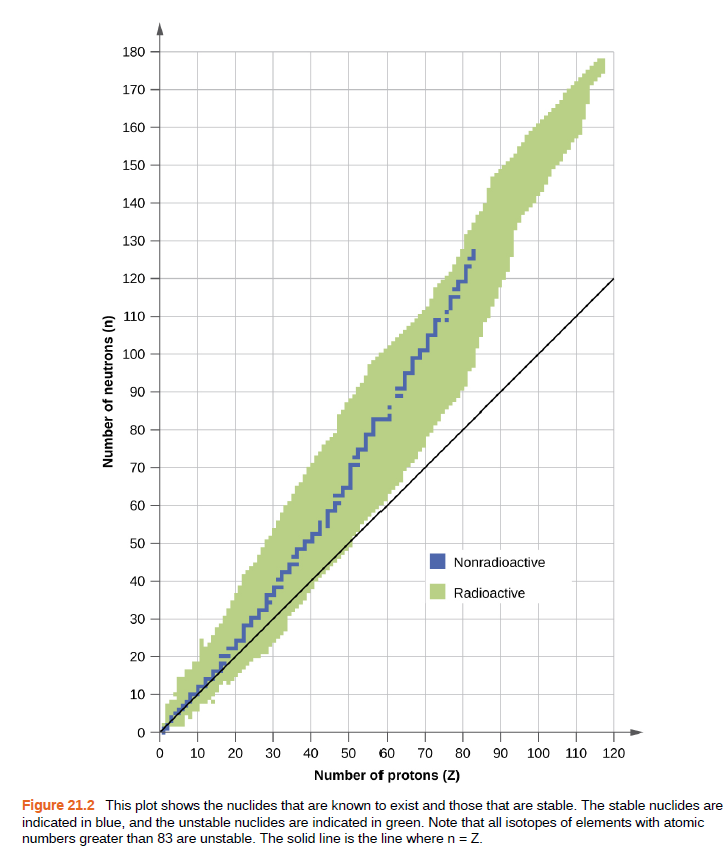
180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 Nonradioactive 40 Radioactive 30 20 10 O 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Number of protons (Z) Figure 21.2 This plot shows the nuclides that are known to exist and those that are stable. The stable nuclides are indicated in blue, and the unstable nuclides are indicated in green. Note that all isotopes of elements with atomic numbers greater than 83 are unstable. The solid line is the line where n = Z. Number of neutrons (n)
180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 Nonradioactive 40 Radioactive 30 20 10 O 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Number of protons (Z) Figure 21.2 This plot shows the nuclides that are known to exist and those that are stable. The stable nuclides are indicated in blue, and the unstable nuclides are indicated in green. Note that all isotopes of elements with atomic numbers greater than 83 are unstable. The solid line is the line where n = Z. Number of neutrons (n)
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter21: Nuclear Chemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24E: Explain, in terms of Figure 21.2, how unstable heavy nuclides (atomic number > 83) may decompose to...
Related questions
Question
100%
Explain, in terms as shown, how unstable heavy nuclides (
Transcribed Image Text:180
170
160
150
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
Nonradioactive
40
Radioactive
30
20
10
O 10
20
30
40
50
60 70
80
90
100
110
120
Number of protons (Z)
Figure 21.2 This plot shows the nuclides that are known to exist and those that are stable. The stable nuclides are
indicated in blue, and the unstable nuclides are indicated in green. Note that all isotopes of elements with atomic
numbers greater than 83 are unstable. The solid line is the line where n = Z.
Number of neutrons (n)
Expert Solution
Step 1
(a)


Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
