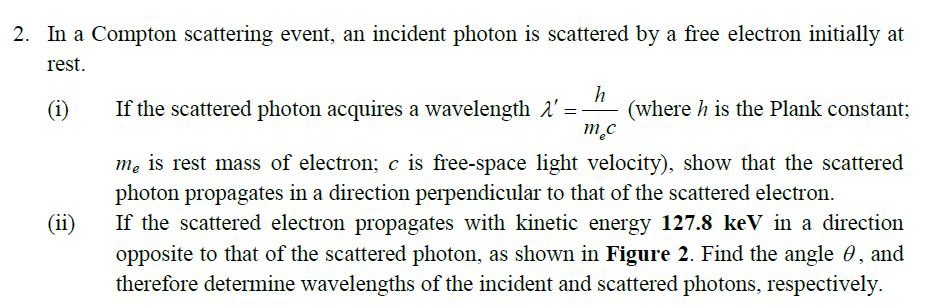
2. In a Compton scattering event, an incident photon is scattered by a free electron initially at rest. h (where h is the Plank constant; m.c (i) If the scattered photon acquires a wavelength 1' = me is rest mass of electron; c is free-space light velocity), show that the scattered photon propagates in a direction perpendicular to that of the scattered electron. If the scattered electron propagates with kinetic energy 127.8 keV in a direction opposite to that of the scattered photon, as shown in Figure 2. Find the angle 0 , and therefore determine wavelengths of the incident and scattered photons, respectively. (ii)
Compton effect
The incoming photons' energy must be in the range of an X-ray frequency to generate the Compton effect. The electron does not lose enough energy that reduces the wavelength of scattered photons towards the visible spectrum. As a result, with visible lights, the Compton effect is missing.
Recoil Velocity
The amount of backward thrust or force experienced by a person when he/she shoots a gun in the forward direction is called recoil velocity. This phenomenon always follows the law of conservation of linear momentum.
In a Compton scattering event, an incident photon is scattered by a free electron initially at
rest.
(i) If the scattered photon acquires a wavelength
e
h
m c
(where h is the Plank constant;
me is rest mass of electron; c is free-space light velocity), show that the scattered
photon propagates in a direction perpendicular to that of the scattered electron.
(ii) If the scattered electron propagates with kinetic energy 127.8 keV in a direction
opposite to that of the scattered photon, as shown in Figure 2. Find the angle
, and
therefore determine wavelengths of the incident and scattered photons, respectively.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 13 images








