2. pH of Acid 1 ph of Acid 2 Concentration ph of Acid 3 pH of Acid 4 (M) 0.010 3.44 2.00 2.92 2.20 0.050 3.09 1.30 2.58 1.73 0.10 2.94 1.00 2.42 1.55 0.50 2.69 0.30 2.08 1.16 1.00 2.44 0.00 1.92 0.98 The pH of solutions of four acids prepared at various concentrations were measured and recorded in the table above. The four acids are, in no particular order: chlorous, hydrochloric, lactic, and propanoic. Which of the four acids listed in the table is hydrochloric acid? Justify your answer.
2. pH of Acid 1 ph of Acid 2 Concentration ph of Acid 3 pH of Acid 4 (M) 0.010 3.44 2.00 2.92 2.20 0.050 3.09 1.30 2.58 1.73 0.10 2.94 1.00 2.42 1.55 0.50 2.69 0.30 2.08 1.16 1.00 2.44 0.00 1.92 0.98 The pH of solutions of four acids prepared at various concentrations were measured and recorded in the table above. The four acids are, in no particular order: chlorous, hydrochloric, lactic, and propanoic. Which of the four acids listed in the table is hydrochloric acid? Justify your answer.
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter16: Reactions Between Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16.79QE
Related questions
Question
Can this be solved with work, please? thank you!
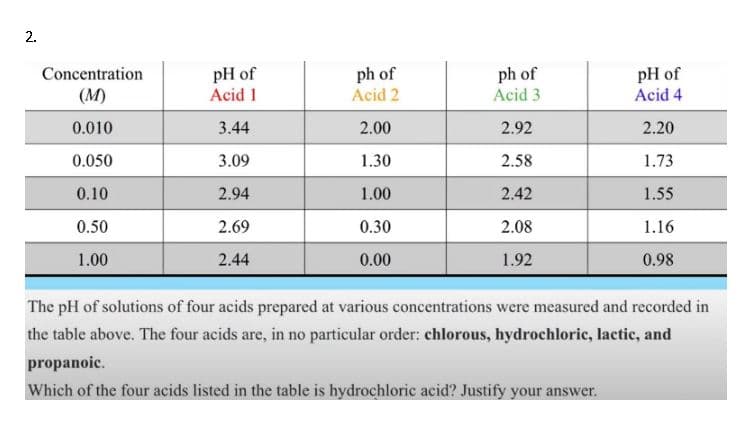
Transcribed Image Text:pH of
Acid 1
ph of
Acid 2
ph of
Acid 3
Concentration
pH of
Acid 4
(M)
0.010
3.44
2.00
2.92
2.20
0.050
3.09
1.30
2.58
1.73
0.10
2.94
1.00
2.42
1.55
0.50
2.69
0.30
2.08
1.16
1.00
2.44
0.00
1.92
0.98
The pH of solutions of four acids prepared at various concentrations were measured and recorded in
the table above. The four acids are, in no particular order: chlorous, hydrochloric, lactic, and
propanoic.
Which of the four acids listed in the table is hydrochloric acid? Justify your answer.
2.
Expert Solution
Introduction
There are two types of bases/acids. One is strong base/acid which is completely dissociable in into its ions and other is weak base/acid which cannot completely dissociate into its ions rather there is an equilibrium sign between the dissociation of these acids/bases.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning